Area Chart
Best Practices
Overview
An Area Chart is a descendant of the line chart where the space below each line is filled in to create a shape or volume. The lines along the top of each shape contain the actual data points. The colored areas are used to emphasize the relationship between the data’s volumes. The data must have a relationship to ZERO.
Variation – Stacked Area Chart: A Stacked Area Chart is the extension of a basic area chart. It displays the evolution of a numerical value for several groups on the same chart, stacked on top of each other. This allows the user to see how the whole behaves across time. However, Stacked area charts may be misleading for the progression of individual groups within the whole. An individual may be progressing upwards, but seem to be diminishing in comparison to the progress of the other groups in the chart.
Usage
An area chart is best used to show trends over time. Select an area chart when:
- There are six or more time periods to compare
- You are communicating an overall trend, not specific values
- Showing the rise and fall of data series over time
- All data has a relationship with zero
Consider using a different visualization type if:
- The differences between the data are small
- There is only a single data series
- Several series of data show volatile changes
To see a “live” Area Chart, go to the example chart at the bottom of the page.
- Building Area Charts in the WCMSSee key tips and guidelines for working with Area Charts in the WCMS.
- TP4 UX Best Practices [PPT - 14 MB]For general guidance on colors, layouts, and overall presentation, see this overview of TP4 best practices.
Interacting with the labels in the legend will highlight or isolate the selected data series. Each data series can be toggled on and off individually, allowing users to view a wide variety of combinations.
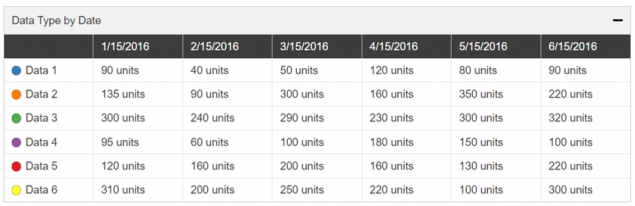
Sorting: Selecting the top row of a column will sort the entire table by the content within the selected column. Selecting the same column multiple times rotates the sorting feature between 3 different states: Descending, Ascending and Off. Only a single column can be sorted at one time.
Source: When referencing information from outside of the current page it is highly recommended that a source link is provided. Source link text should be short and descriptive; it should not be the full URL. Source information can be added to the “Description” box under the “General” section of the “Configure” tab.
Other Guidance
- Logarithmic Scale: This is a way of displaying numerical data over a very wide range of values in a compact way. If your data series vary greatly, such as hundreds to ten-thousands, consider using the logarithmic scale option for your chart..
- Chart Title: Good titles are invaluable. Your chart title should be long enough so your audience can make sense of the chart. A glance at the title should clearly convey what the chart contains. A good title requires a balance between a short title and one with enough descriptive information to clearly describe the chart.
- Number of Series: Too many series result in visual clutter and make the chart difficult to interpret. One to four areas with a maximum of six areas is recommended. The Chart Builder will support up to nine different colored areas in a chart. However, if you have more than six sets of quantitative values consider breaking them into multiple charts.
- Grid Lines: In most cases, both horizontal and vertical grid lines should be hidden to reduce chart clutter. Approximate values can be perceived without grid lines. When the difference in data values is close, horizontal grid lines can be shown to better support data value comparison.
- Data Source: The data source makes your graphic more reputable. It also allows those who are interested to dig deeper. Consider adding a link to your data source in one of the additional text display areas.
Chart Color Palettes
Example Area Chart with Annotations
Annotations can provide context or call out specific points of your visualization. In smaller viewports, only the numbers will appear, with the text displaying in the Annotation Dropdown below the Data Table, so it is best practice to always include this for mobile users.
This was built using the “Area Chart Sample Data” in the COVE editor.
Example Area Chart with Categorical Axis
A categorical axis allows chart creators to show their data by category. Applying a categorical axis will remove numerical values and the axis label from the value axis. It is recommended to use the Message area to describe the categories.
This example was built using the “Area Chart Sample Data” in the COVE editor.