StatCalc: Statistical Calculators
‹View Table of Contents
Binomial
The binomial distribution states the probability that a number of positive outcomes occurs given the expected percentage of positive outcomes and the total number of observations taken.
Example
Suppose 23.5% of individuals in a given patient population are HIV positive. If 16 individuals are selected from this patient population, what are the chances that at least eight of these individuals are HIV positive?
- From the Epi Info™ main page, select StatCalc.
- Select Population Binomial (Proportion vs Std). The Unmatched Case-Control window opens.
- Enter the Numerator as 8. This is the number of patients with the disease.
- Enter the Total Observations as 16. This is the patient population of the study.
- Enter the Expected Percentage as 23.5. This is the expected percentage of cases infected with a particular disease.
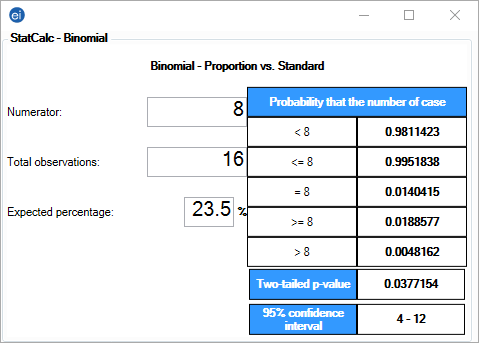
Figure 10.15: Binomial Distribution
Based on the inputs for this binomial distribution, there is a 1.9% chance that eight or more of the 16 patients are HIV positive. Additional percentages are stated for the ranges outlined in the left column of the table.