NHSNCoLab
Ushering in a new era of NHSN data modernization, innovation, and collaboration for public health surveillance.
The NHSN Collaborative, or NHSNCoLab, is a collaboration between public and private stakeholders to pilot, implement, and validate new National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) healthcare surveillance measures and approaches in alignment with CDC’s Data Modernization Initiative.
The program established a committed network of CDC’s healthcare partners, with institutional commitments, data-use agreements, and technical infrastructure already in place to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of collaboration.
This collaboration will inform new NHSN measures and approaches to healthcare event data collection, including the feasibility and validity of new NHSN surveillance concepts that support patient safety, quality reporting, national benchmarking, and public health preparedness and response.
Maximize Data, Minimize Burden: Innovative strategies to strengthen and advance NHSN’s healthcare surveillance capacity by automating data collection, enabling direct data linking between CDC and healthcare partners, and conducting real-world testing
- Enroll in NHSNCoLab
- Facility enrolls in NHSNCoLab by signing the NHSNCoLab Charter Agreement and NHSNCoLab Stipend Acknowledgement.
- Complete Assessment
- Facility completes technical assessment.
- Establish Connectivity in Sandbox
- NHSN establishes connectivity to facility Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources®* (FHIR) R4 API in electronic health record (EHR) Sandbox environment (with non-PHI/PII data).**
- Complete NHSN Agreement
- Facility completes NHSN Agreement to Participate and Consent form.
- Establish Connectivity in Production
- NHSN establishes connectivity to facility FHIR R4 API* in EHR Production environment (with PHI/PII data).
- *HL7, CDA, FHIR and the FHIR [FLAME DESIGN] are the registered trademarks of Health Level Seven International and their use does not constitute endorsement by HL7.
**Some facilities collaborate on exploratory work prior to FHIR implementation.
EHR: Electronic Health Record, PHI: Protected Health Information, PII: Personally Identifiable Information.
Access to optimum healthcare data for national surveillance to improve NHSN-data accuracy, quality, and validity.
Improve speed and efficiency to reduce wait times for data transmission between NHSN and its healthcare partners
Advance new healthcare data exchange approaches (e.g., FHIR®)
- Move towards fully electronic definitions of healthcare-acquired events
- Minimize reporting burden for facilities and providers
Integrate user perspectives into NHSN surveillance to increase input and adoption from healthcare partners
Planned Measures for Piloting
- Adult sepsis events (ASE) and sepsis outcome
- Antimicrobial use (acute care and long-term care)
- Glycemic control (inpatient medication-related hypoglycemia and inpatient hyperglycemia)
- Healthcare-associated venous thromboembolism (HA-VTE) and VTE prophylaxis
- Healthcare facility-onset, antibiotic-treated C. difficile infection (CDI)
- Hospital-onset acute kidney injury (AKI)
- Hospital-onset bacteremia and fungemia (HOB)
- Neonatal late onset sepsis / meningitis (LOS/MEN)
- Opioid-associated adverse events (ORAE)
- Respiratory pathogen surveillance (RPS)
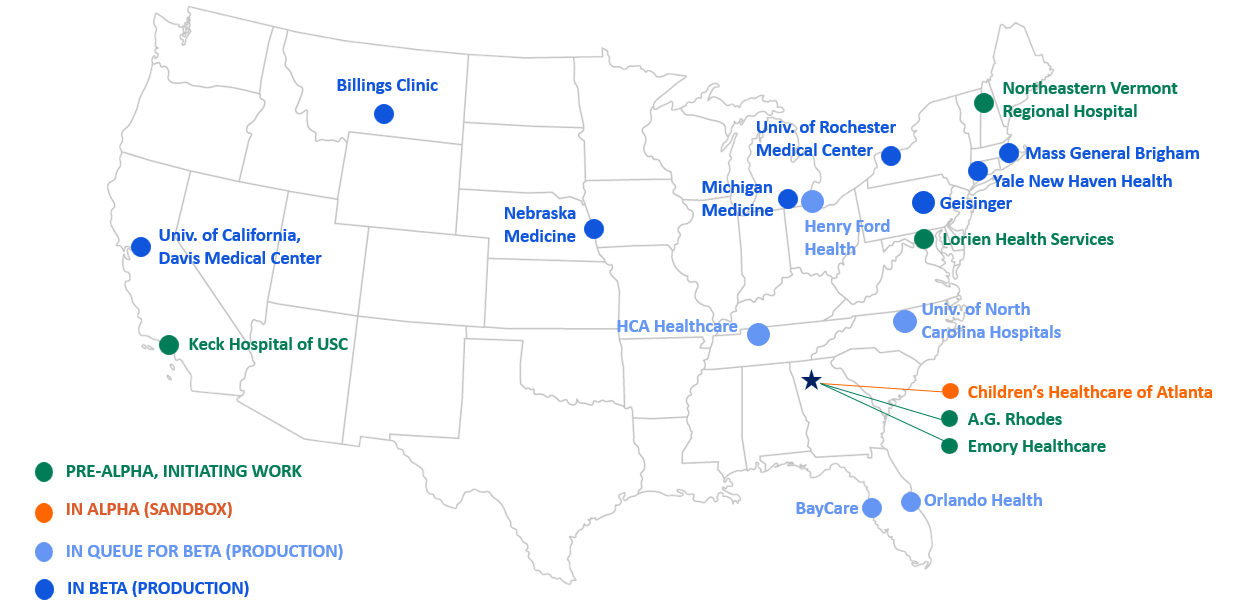
| Site | Site Name | EHR Vendor* | Measure(s) | Site Leads |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A.G. Rhodes | PointClickCare | Long-term care AU | Mabela Libosada, MBA, BSN, RN; Ariane Moreau |
| 2 | BayCare | Oracle/Cerner | AKI, Glycemic Control, HA-VTE, HT-CDI/HOB | Paul Lewis, MD, FAAFP; Randy McGlothin |
| 3 | Billings Clinic | Oracle/Cerner | Glycemic Control | Randy Thompson, MD; Lisa Ranes, RD, LN, CDCES |
| 4 | Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta | Epic | RPS | Jonathan Beus, MD |
| 5 | Geisinger | Epic | HT-CDI/HOB, RPS | Mark Shelly, MD |
| 6 | HCA Healthcare | Veradigm, Meditech, Oracle/Cerner, Epic via dbMotion | Glycemic Control, HT-CDI/HOB | Kenneth Sands, MD, MPH; William Gregg, MD, MS, MPH |
| 7 | Henry Ford Health | Epic | AKI, HA-VTE, HT-CDI/HOB | Scott Kaatz, DO |
| 8 | Keck Hospital of USC | Oracle/Cerner | RPS, CDI/HOB | Kymberly Lengyel BSN, CIC, PHN |
| 9 | Lorien Health Services | PointClickCare | Long-term care AU | Wayne Brannock; Lena Sturgeon |
| 10 | Mass General Brigham | Epic | HT-CDI/HOB, Sepsis | Sayon Dutta, MD, MPH; Chanu Rhee, MD, MPH |
| 11 | Michigan Medicine | Epic | Glycemic Control, HT-CDI/HOB, HA-VTE | Michael Lanham, MD |
| 12 | Nebraska Medicine | Epic | Glycemic Control | Andjela Drincic, MD; Ron Carson |
| 13 | Northeastern Vermont Regional Hospital | Meditech | Glycemic Control, HT-CDI/HOB, RPS | ShawnTester;Shawn Burroughs, MBA |
| 14 | Orlando Health | Epic | HT-CDI/HOB, LOS/MEN | Eric Rose, PharmD |
| 15 | Univ. of California, Davis Medical Center | Epic | Glycemic Control, HT-CDI/HOB, HA-VTE | Greg Maynard, MD |
| 16 | Univ. of North Carolina Hospitals | Epic | HT-CDI/HOB, RPS | Lisa Stancill, MPH |
| 17 | Univ. of Rochester Medical Center | Epic | HT-CDI/HOB, RPS | Brenda Tesini, MD |
| 18 | Univ. of Southern California (USC) Health System | Oracle/Cerner | RPS, CDI/HOB | Kymberly Lengyel BSN,CIC, PHN |
| 19 | Yale New Haven Health | Epic | Glycemic Control | Hyung Paek, MD, MSEE |