At a glance
- In the United States, nearly 300 lives are lost to drugs each day.
- Overdose Data to Action (OD2A) supports jurisdictions in implementing prevention activities and in collecting accurate, comprehensive, and timely data on nonfatal and fatal overdoses and in using those data to enhance programmatic and surveillance efforts.
- OD2A focuses on understanding and tracking the complex and changing nature of the drug overdose crisis by seamlessly integrating data and prevention strategies.

Linking trends with tactics
CDC launched the first multiyear OD2A cooperative agreement in 2019 with 66 recipients (referred to as jurisdictions) from state, territorial, county, and city health departments. In August 2023, CDC awarded new five-year cooperative agreements to 90 jurisdictions under two distinct OD2A programs, one designed for states, and one designed specifically for localities and territories.
CDC created OD2A in States and OD2A: LOCAL to:
- Address the evolving epidemiology of the drug overdose crisis.
- Close identified gaps in prevention activities.
- Apply lessons learned from the previous OD2A funding opportunity.
- Leverage the differing roles and spheres of influence state and local health departments and their partners have.
Applying the Overdose Data to Action framework
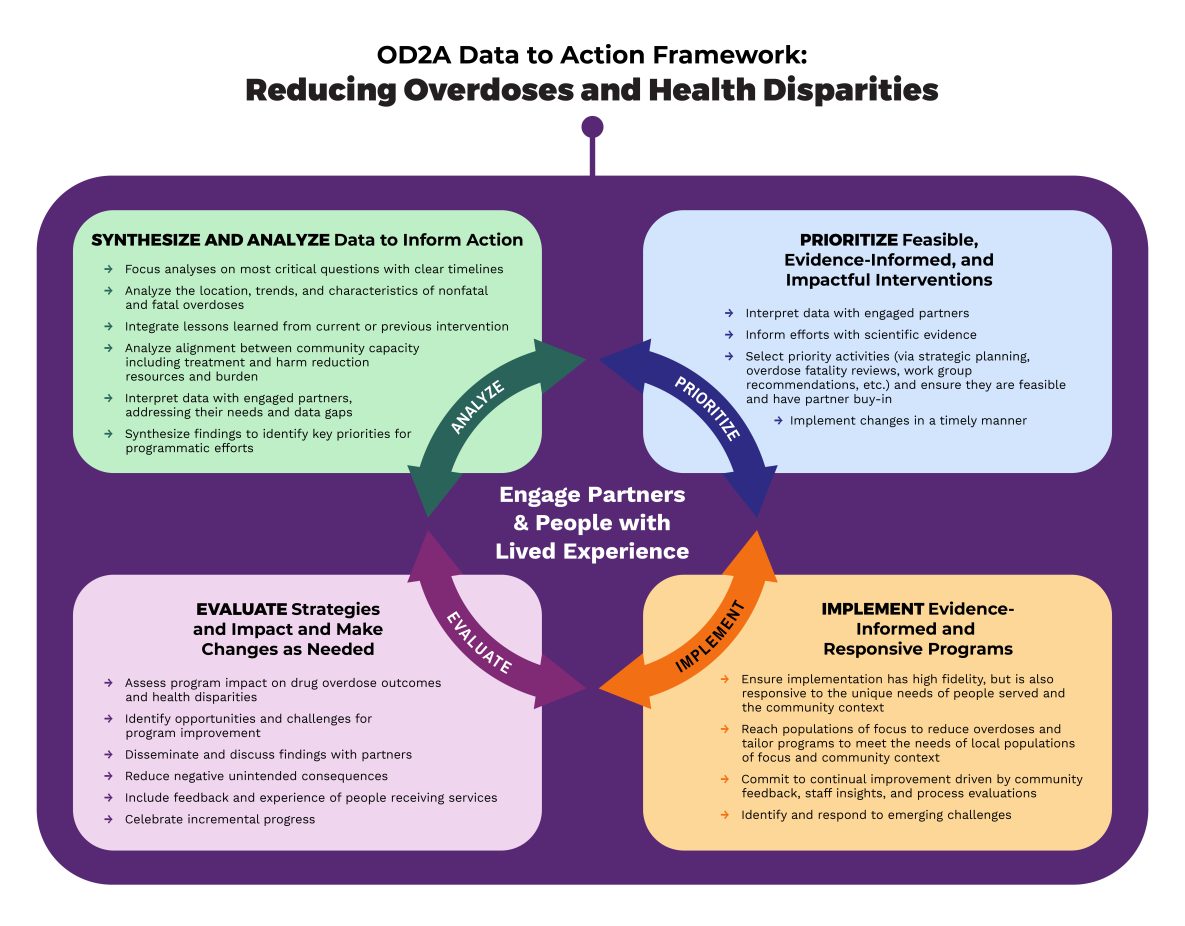
OD2A is guided by a data to action framework. Data to action means using different types of data to select, improve, and scale up drug overdose prevention programs and policies. These data include surveillance data, process and outcome evaluation data, and data from partners including those who use drugs or have lived experience with drug use. In addition, jurisdictions explore how they can use data from focus groups, community meetings, or partner interactions to inform or adapt surveillance data collection or analysis.
At the core of this model is a focus on health equity and reducing health disparities by engaging partners and integrating people with lived experience into all components of the work. Funded jurisdictions will be able to respond more quickly, more effectively, and more equitably to their constituents' needs, using data to drive action steps that reduce overdose deaths and substance use-related harms.
In partnership with CDC, jurisdictions focus on some or all of the following strategies:
Surveillance Strategies
Enhanced surveillance strategies enable jurisdictions to track nonfatal and fatal overdoses involving opioids and/or stimulants and polysubstance use, and identify emerging drug threats:
- Required: Overdose surveillance infrastructure
- Required: Morbidity surveillance
- Required: Mortality surveillance
- Optional and competitive: Biosurveillance
- Optional and competitive: Data linkage
- Required: Overdose surveillance infrastructure
- Optional and competitive: Toxicologic testing of drug products and/or paraphernalia
- Optional and competitive: Surveillance of linkage to and retention in care
Prevention Strategies
Evidence-based prevention strategies are aligned with shifts in the overdose crisis, including changes in the illegal drug supply and a rise in stimulant and polysubstance use:
- Required: Clinician/health system engagement and health IT/PDMP enhancement
- Required: Public safety partnerships/interventions
- Required: Harm reduction
- Required: Community-based linkage to care
- Required in community, public safety, and healthcare settings: Linkage to and retention in care
- Required in community, public safety, and healthcare settings: Harm reduction
- Required in healthcare settings: Clinician and health systems best practices
- Optional: Stigma reduction
- Optional: Health IT enhancements
