Key points
- Use the hierarchy of controls to prioritize control solutions to occupational hazards.
- Developing a site-specific safety and health plan is an important step in minimizing workplace exposures.
- Below are examples of different strategies to prevent histoplasmosis exposure by level.

Prevention steps and strategies
Occupational health and safety specialists use the hierarchy of controls, below, to determine how to implement feasible and effective control solutions to occupational hazards.
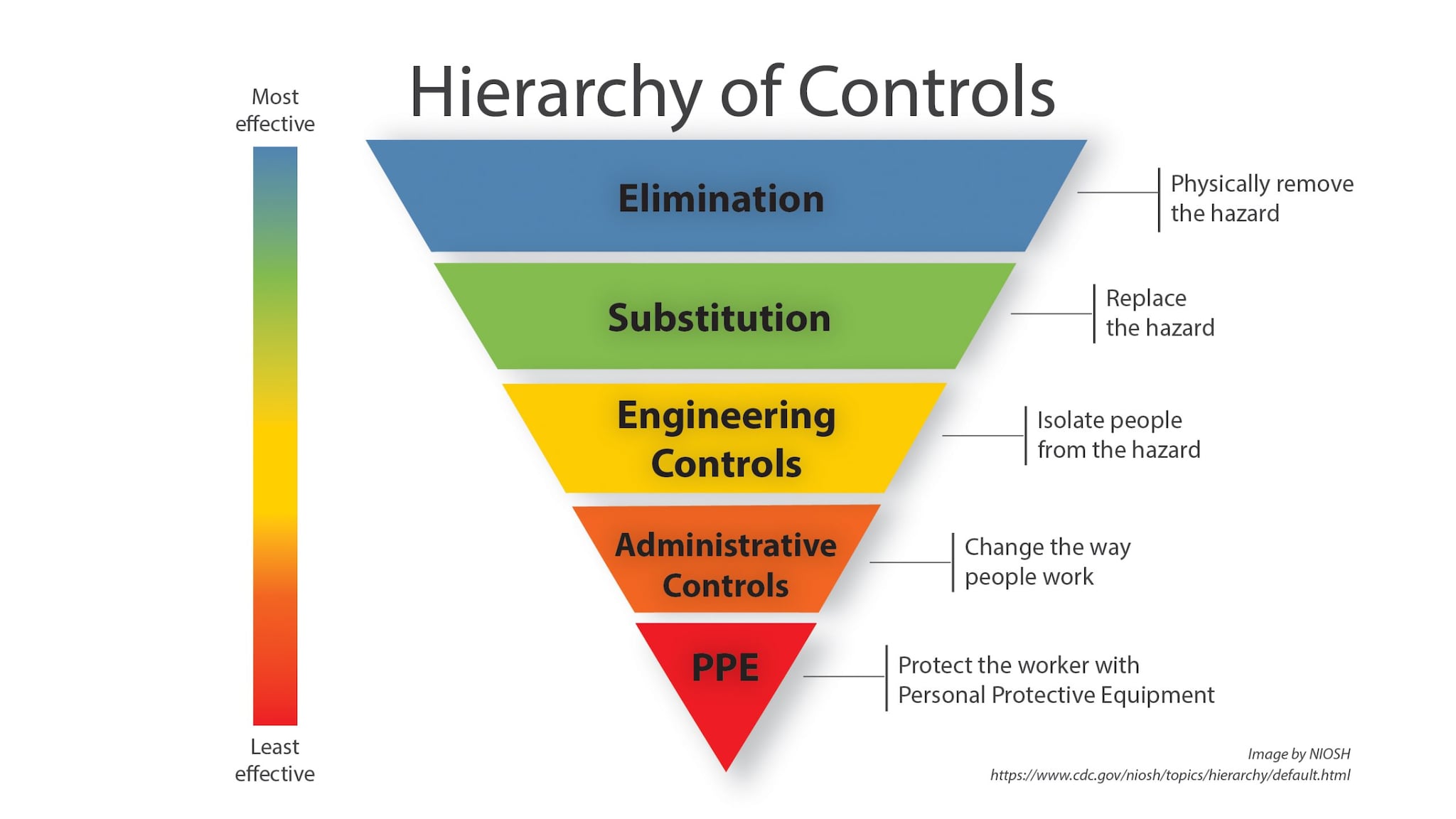
This framework can be used to prevent exposure to histoplasmosis in the workplace.1,2 Elimination (removing the hazard) and substitution (replacing the hazard) are the most effective ways to reduce occupational hazards but can be difficult to implement for infectious agents such as Histoplasma. In some cases, large amounts of bird or bat droppings should be cleaned up by a professional company that specializes in handling hazardous waste.
Making a plan
Developing a site-specific safety and health plan is an important step in minimizing workplace exposures.3 The plan should have input from:
- Management
- Employee representatives
- Health and safety professionals
A comprehensive plan not only identifies potential hazards. It also contains a description of the necessary measures to prevent, control, and reduce those hazards. Measures should include engineering and administrative controls and use of PPE.
Elimination and engineering controls
There are many elimination and engineering controls you can employ to reduce Histoplasma exposures.
- Remove bats and birds from a building
- Control dust
- Dispose of waste
Administrative controls
- Post health risk warnings
- Communicate about and train for hazards
Personal protective equipment
In addition to elimination, engineering and administrative controls, personal protective equipment (PPE) protect workers from Histoplasma. The following PPE can protect workers on the job.
- Respiratory and eye protection
- Gloves
- Disposable protective clothing
- Su CP, de Perio MA, Cummings KJ, McCague AB, Luckhaupt SE, Sweeney MH [2019]. Case investigations of infectious diseases occurring in workplaces, United States, 2006-2015. Emerg Infect Dis 2019;25(3):397–405.
- Armstrong PA, Beard JD, Bonilla L, Arboleda N, Lindsley MD, Chae SR, Castillo D, Nuñez R, Chiller T, de Perio MA, Pimentel R, Vallabhaneni S [2018]. Outbreak of severe histoplasmosis among tunnel workers-Dominican Republic, 2015. Clin Infect Dis 2;66(10):1550–1557.
- Raterman SM. Methods of control. In: Plog B ed. Fundamentals of Industrial Hygiene. Itasca: National Safety Council; 2000:585–605.
