Museum Holiday Hours
Christmas Eve: 9:00am to 1:00PM - Closed Christmas Day
CDC Museum COVID-19 Timeline
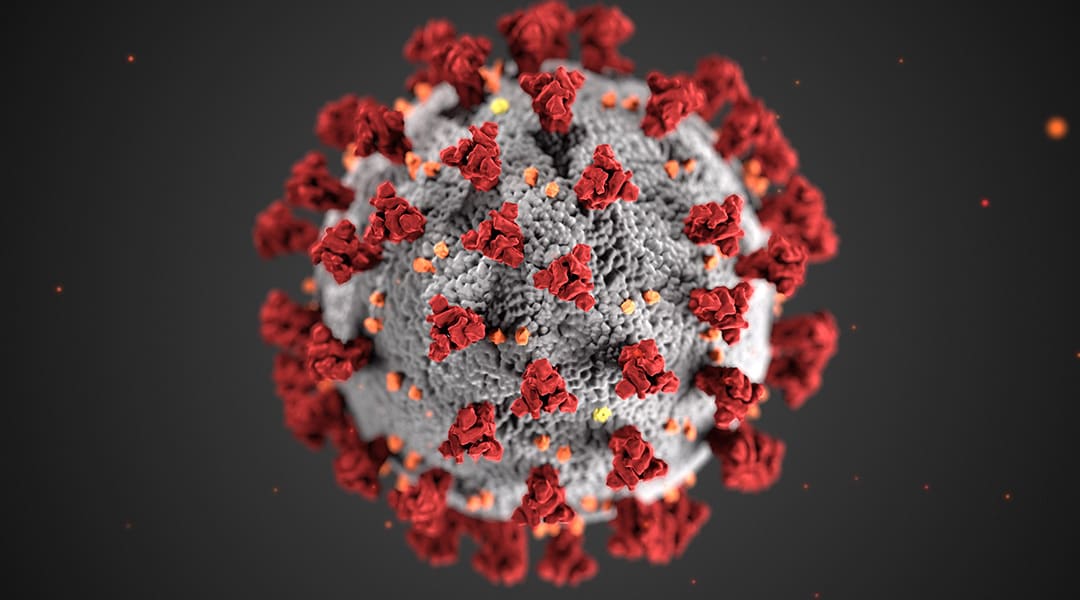
This timeline provides information about select moments in the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States and around the world beginning from its known origins to today.
Late 2019 | Early 2020 | Mid 2020 | Late 2020 | Early 2021 | Mid-2021 | Late-2021 | Early 2022 | Mid 2022
December 12, 2019
A cluster of patients in China’s Hubei Province, in the city of Wuhan, begin to experience the symptoms of an atypical pneumonia-like illness that does not respond well to standard treatments.
December 31, 2019
The World Health Organization (WHO) Country Office in China is informed of several cases of a pneumonia of unknown etiology (cause) with symptoms including shortness of breath and fever occurring in Wuhan, China. All initial cases seem connected to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market.
January1, 2020
The Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan is closed amid worries in China of a reprise of the 2002–2004 SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus or SARS-CoV-1) outbreak.
January 2, 2020
WHO activates its Incident Management Support Team (IMST) across all three organizational levels: Country Office, Regional Office, and Headquarters.
January 3, 2020
China informs WHO that they have identified over 40 cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology.
January 5, 2020
CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD) activates a center-level response to investigate this novel pneumonia of unknown etiology.
The genetic sequence for the atypical pneumonia virus, Wuhan-Hu-1, is submitted to the Department of Zoonoses, National Institute of Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, in Beijing, China by Yong-Zhen Zhang of Fudan University, Shanghai. The complete genetic sequence of the virus remains unavailable to the rest of the world as the virus spreads.
January 7, 2020
Public health officials in China identify a novel coronavirus as the causative agent of the outbreak.
CDC establishes an incident management structure to guide their response to the novel coronavirus by following the preparedness plan for developing tests and managing cases made for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
January 10, 2020
WHO begins using the phrase “2019 Novel Coronavirus” or “2019-nCoV” to refer to disease causing the outbreak in Wuhan, China.
CDC publishes information about the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak caused by the SARS CoV-2 virus on its website.
Edward C. Holmes of the University of Sydney, Australia posts online that the viral genome sequence of the unknown pneumonia causing the outbreak in Wuhan has been uploaded to GenBank as “Wuhan-Hu-1” (MN908947) and will be released shortly. He does so on behalf of Yong-Zhen Zhang of Fudan University, Shanghai in collaboration with the Shanghai School of Public Health, the Central Hospital of Wuhan, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, the Wuhan Center for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control, and the University of Sydney. Hours later, Holmes and Zhang publish the sequence.
January 11, 2020
WHO tweets that it has received the genetic sequences of the novel coronavirus from China and expects that the information will shortly become publicly available.
CDC updates its Travel Health Notice (THN) system for persons traveling to Wuhan, China to Level 1 or “practice usual precautions.”
China reports the first death from the novel coronavirus and publishes a draft genome of the newly discovered coronavirus suspected of causing the outbreak. By January 12, 2020, four other genomes have been uploaded to the viral sequence database curated by the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID).
January 13, 2020
The Thailand Ministry of Public Health confirms the first laboratory-confirmed case of the SARS-CoV-2 virus outside of China.
January 14, 2020
WHO finds evidence of possible human-to-human transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, but WHO scientists say that human-to-human transmission is not surprising given our knowledge of respiratory pathogens.
January 15, 2020
The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare reports an additional laboratory-confirmed case of the SARS-CoV-2 virus outside of China.
January 17, 2020
CDC begins screening passengers for symptoms of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus on direct and connecting flights from Wuhan, China to San Francisco, California, New York City, New York, and Los Angeles, California and plans to expand screenings to other major airports in the U.S.
January 19, 2020
Worldwide, 282 laboratory-confirmed cases of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus have been reported in four countries: China (278 cases), Thailand (2 cases), Japan (1 case) and the Republic of Korea (1 case).
January 20, 2020
CDC reports the first laboratory-confirmed case of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the U.S. from samples taken on January 18 in Washington state and on the same day activates its Emergency Operations Center (EOC) to respond to the emerging outbreak.
January 21, 2020
CDC artists Alissa Eckert and Dan Higgins create “an identity” for the SARS-CoV-2 virus by designing the red and white virus image.
Chinese government officials confirm that human-to-human transmission is driving the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in China.
January 22, 2020
WHO’s International Health Regulation Emergency Committee meets and decides to not declare the 2019 Novel Coronavirus a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). Instead, the committee decides to monitor the situation and reconvene in 10 days to re-evaluate.
January 23, 2020
Wuhan, China— a city of 11 million people— is placed under lockdown due to the 2019 Novel Coronavirus outbreak.
January 24, 2020
CDC confirms a travel-related infection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in Illinois, bringing the total number of cases in the U.S. to two.
January 26, 2020
CDC confirms additional travel-related infections of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in Arizona and California, bringing the total number of cases in the U.S. to five.
January 27, 2020
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announces that it will take “critical actions to advance development of novel coronavirus medical countermeasures” with interagency partners, including CDC.
January 28, 2020
CDC issues a Level 3 Travel Health Notice— advising travelers to avoid all non-essential travel to China due to the 2019 Novel Coronavirus outbreak.
The U.S. government relocates U.S. citizens from Wuhan, China back to the U.S. due to the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV).
January 29, 2020
A team of CDC medical officers meets the flight carrying the repatriated U.S. citizens from Wuhan, China at the March Air Reserve Base in California to screen the passengers for symptoms of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
January 30, 2020
CDC confirms that the SARS-CoV-2 virus has now spread between two people in Illinois with no history of recent travel. This is the first recorded instance of person-to-person spread of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the U.S and brings the total number of cases up to seven.
January 31, 2020
CDC issues 14-day federal quarantine orders to all 195 U.S. citizens who were repatriated back to the U.S. on January 29, 2020, from Wuhan, China.
WHO’s International Health Regulation Emergency Committee reconvenes early to declare the 2019 Novel Coronavirus outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC).
The Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), Alex Azar, declares the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak a public health emergency.
February 3, 2020
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) directs all flights from China and all passengers who have traveled to China within the last 14 days to be routed through one of eleven airports in the U.S. for enhanced screening procedures and possible quarantine. U.S. citizens who have been in Hubei province within 14 days of their return are subject to up to 14 days of mandatory quarantine;, U.S. citizens who have been in other areas of mainland China within 14 days of their return are subject to 14 days of self-quarantine with health monitoring;, and foreign nationals (other than immediate family of U.S. citizens, permanent residents, and flight crew) who have traveled in China (excluding Hong Kong and Macau) within 14 days of their arrival, will be denied entry into the U.S.
CDC submits an emergency use authorization (EUA) to FDA to expedite approval for a CDC developed SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic test.
February 4, 2020
FDA approves the EUA for the CDC developed SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic test kit.
February 5, 2020
CDC begins shipping its laboratory test kit to detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus, “CDC 2019-nCoV Real Time RT-PCR,” to select domestic and international laboratories.
CDC medical officer teams meet additional planes carrying passengers from Wuhan, China at Travis Air Force Base in Sacramento, CA, Marine Corps Air Station Miramar in San Diego, CA, Lackland Air Force Base in San Antonio, TX, and Eppley Airfield in Omaha, NE to screen the passengers for the symptoms of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). All passengers are placed under mandatory 14-day quarantine orders.
February 8, 2020
Some of the first CDC test kits for detecting the SARS-CoV-2 virus arrive at a public health laboratory in east Manhattan, New York City, N.Y. The laboratory reports that the tests produce “untrustworthy results.”
February 10, 2020
Worldwide deaths from the 2019 Novel Coronavirus reach 1,013. The SARS-CoV-2 virus has now killed more people than the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-1) outbreak, which claimed 774 lives globally from November 2002 to July 2003.
February 11, 2020
WHO announces the official name for the disease that is causing the 2019 Novel Coronavirus outbreak: “COVID-19.” The new name of this disease is an abbreviated version of “Coronavirus Disease 2019.”
February 13, 2020
CDC confirms the 15th case of COVID-19 in the U.S.
February 18, 2020
Due to the high case load and numbers of asymptomatic individuals testing positive for COVID-19, all passengers and crew of the Diamond Princess cruise ship are quarantined off the coast of Japan, placed under travel restrictions, and are prevented from returning to the U.S. for at least 14 days after they have left the Diamond Princess.
February 23, 2020
As Italy becomes a global COVID-19 hotspot, the Italian government issues Decree-Law No. 6, containing urgent measures to contain and manage the epidemiological emergency caused by COVID-19, effectively locking down the country.
February 25, 2020
CDC’s Dr. Nancy Messonnier, the incident manager for the COVID-19 response, holds a telebriefing and braces the nation to expect mitigation efforts to contain the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the U.S. that may include school closings, workplace shutdowns, and the canceling of large gatherings and public events, stating that the “disruption to everyday life may be severe.”
February 28, 2020
CDC reports four additional presumptive positive cases of COVID-19 in California, Oregon, and Washington: one case is likely travel-related, but three are likely due to community spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the U.S.
February 29, 2020
CDC updates its Criteria to Guide Evaluation and Testing of Patients Under Investigation (PUI) for COVID-19 to any patients with a severe respiratory illness even in the absence of travel history to affected areas or known exposure to another case to prepare for possible widespread person-to-person transmission.
FDA announces a “new policy…for certain laboratories that develop and begin to use validated COVID-19 diagnostics before FDA has completed review of their emergency use authorization (EUA) requests,” allowing laboratories to create tests to address testing shortages in the U.S.
CDC and the Washington Department of Public Health report the first death in an individual with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 in the U.S. The patient was a male in his 50s who was hospitalized with a pneumonia of unknown cause and later died of his illness.
March 1, 2020
CDC creates a hospitalization surveillance network for the SARS-CoV-2 virus called “COVID-NET” to track the numbers and rates of COVID-19 hospitalizations by modifying existing respiratory virus surveillance networks that monitor for hospitalizations associated with influenza and Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV).
March 3, 2020
CDC reports 60 cases of COVID-19 across Arizona, California, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New York, Oregon, Rhode Island, Washington, and Wisconsin. Of the 60 COVID-19 infections detected, 21 are travel-related, 11 are from person-to-person spread, and 27 are unknown.
March 6, 2020
The Grand Princess cruise ship is stranded off the California coast after officials learn that a California man who had traveled on the ship last month contracted COIVID-19 and died. The California Air National Guard drops off a limited supply of testing kits by helicopter; more than 3,500 people are aboard the ship, but only 46 are able to be tested and 21 (mostly crew members) test positive.
March 11, 2020
After more than 118,000 cases in 114 countries and 4,291 deaths, the WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic.
March 12, 2020
FDA no longer requires CDC to perform confirmatory testing for a positive COVID-19 diagnosis.
March 13, 2020
The Trump Administration declares a nationwide emergency and issues an additional travel ban on non-U.S. citizens traveling from 26 European countries due to COVID-19.
March 14, 2020
CDC issues a “no sail order” for all cruise ships— calling for them to cease activity in all waters that the U.S. holds jurisdiction over.
March 15, 2020
States begin to implement shutdowns in order to prevent the spread of COVID-19. The New York City public school system— the largest school system in the U.S., with 1.1 million students— shuts down, while Ohio calls for restaurants and bars to close.
March 16, 2020
CDC launches “Clara-Bot,” a COVID-19 symptom checker, on its website.
New and old guidelines begin circulating among state health departments for who gets critical care in the event of ventilator shortages: Massachusetts and Pennsylvania use a point system prioritizing patients by likelihood of benefitting from ICU care, while New York’s 2015 plan relies on “exclusion criteria”— a list of medical conditions that would make a patient ineligible, like traumatic brain injury, severe burns, or cardiac arrest. Alabama’s exclusion criteria list, released in 2010 and since removed from publication, included both “severe or profound mental retardation” and “moderate to severe dementia.”
March 17, 2020
Moderna Therapeutics begin the first human trials of a vaccine to protect against COVID-19 at a research facility in Seattle, Washington.
The University of Minnesota launches a clinical trial testing hydroxychloroquine, an FDA-approved drug for the prevention and treatment of malaria, for the treatment of COVID-19.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid (CMS) temporarily expands telehealth benefits, enabling beneficiaries to receive a wider range of healthcare services from their doctors without having to travel to a healthcare facility.
March 19, 2020
CDC asks healthy people to donate blood if they are able amid a national shortage of blood during the COVID-19 pandemic.
California governor Gavin Newsom issues a statewide stay-at-home order to slow the spread of COVID-19 instructing residents to only leave their homes when necessary and shutting down all but essential businesses.
March 27, 2020
The Trump Administration signs the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act into law. The act includes funding for $1,200 per adult (with expanded payments for families with children), expanded unemployment benefits, forgivable small business loans, loans to major industries and corporations, and expanded funding to state and local governments in response to the economic crisis caused by COVID-19.
Apple, in partnership with HHS, CDC, and the White House Coronavirus Task Force, releases an app with a COVID-19 symptom and exposure questionnaire telling people how to isolate and monitor symptoms and giving recommendations on testing and when to contact a medical provider if they believe they have contracted or have been exposed to the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
March 28, 2020
To prevent the spread of COVID-19, the White House extends all social distancing measures until through the end of April 2020.
FDA issues an EUA to allow hydroxychloroquine sulfate and chloroquine phosphate products to be added the Strategic National Stockpile for the treatment of COVID-19.
CDC distributes a Health Alert Network (HAN) warning against using chloroquine phosphate without the recommendation of a doctor or pharmacy after one person is made seriously ill and a second dies from ingesting non-pharmaceutical chloroquine phosphate (a chemical aquariums use that is commercially available for purchase at stores or online) to prevent or treat COVID-19.
CDC issues a domestic travel advisory for New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut due to high community transmission of COVID-19 in those states, urging residents to refrain from all non-essential domestic travel for at least 14 days, effective immediately.
March 31, 2020
At a White House Press Briefing, Dr. Anthony Fauci and Dr. Deborah Brix announce that between 100,000 and 240,000 deaths in the U.S. are expected— even if social distancing and public health measures are perfectly enacted.
The Journal of the American Medical Association Ophthalmology reports that COVID-19 can be transmitted through the eye. One of the first warnings of the emergence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus came late in 2019 from a Chinese ophthalmologist treating patients in Wuhan, Li Wenliang, MD, who died at age 34 from COVID-19.
April 3, 2020
At a White House press briefing, CDC announces new mask wearing guidelines and recommends that all people wear a mask when outside of the home.
CDC warns the public about phone scams and phishing attacks that appear to originate from CDC and ask for donations from individuals. This is government impersonation fraud— federal agencies do not request donations from the public.
April 23, 2020
Using funds from the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act, CDC announces $631 million to fund and expand the existing Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Prevention and Control of Emerging Infectious Diseases (ELC), allowing state health departments to expand their capacity for the testing, contact tracing, and containment of COVID-19.
April 4, 2020
CDC launches a new weekly SARS-CoV-2 virus surveillance report called “COVIDView” summarizing weekly data on COVID-19 hospitalizations, deaths, and testing.
More than 1 million cases of COVID-19 had been confirmed worldwide, a more than ten-fold increase in less than a month.
April 6, 2020
Hundreds of doctors and civil rights groups urge CDC and the U.S. government to release race and ethnicity data on COVID-19 case-numbers in order to reveal the true impact of the virus on communities of color.
April 7, 2020
Data from the Chicago Department of Public Health reported by the Chicago Tribune shows that despite being about 30% of the total population, Black people account for 68% of the COVID-19 related deaths in Chicago and are dying of COVID-19 at a rate nearly six-times greater than that of White Chicagoans, who account about 33% of the population and approximately 14% of deaths. These numbers illuminate for many the racial disparities of the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S.
HHS announces $186 million in additional funding to state and local jurisdictions for the COVID-19 response.
April 8, 2020
HHS announces first contract for ventilator production under the Defense Production Act with General Motors.
April 9, 2020
CDC modifies and extends the no sail order for all cruise ships.
April 10, 2020
With over 18,600 confirmed deaths and more than 500,000 confirmed cases in under four months, the U.S. is the country with the most reported COVID-19 cases and deaths, surpassing Italy and Spain as a global hot-spot for the virus.
With 159,937 confirmed cases, New York State now has more reported cases of COVID-19 than Spain (153,000), Italy (143,000), or China (82,000). Amid critical hospital bed and ventilator shortages, aerial images emerge of workers in hazmat suits burying coffins in mass graves at Hart Island off the Bronx, an area used for over 150 years by New York City officials as a mass burial site for those with no next-of-kin or who cannot afford funerals.
April 13, 2020
Most states in the U.S. report widespread cases of COVID-19.
At a White House press briefing, President Trump announces that the U.S. will cease contributing funding to the WHO, shaking the global public health community.
April 16, 2020
The Trump Administration releases a plan outlining how states should reopen, calling for states or metropolitan areas to meet benchmarks like reducing COVID-19 cases or deaths before reopening or stopping mitigation strategies (like required masking), also known as “gating
April 20, 2020
As the COVID-19 pandemic grows, shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE) like gowns, eye shields, masks, and even body bags, become dire– particularly in New York
April 22, 2020
After two pet cats in separate areas of New York state test positive for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, CDC recommends that people restrict their pets’ interactions with other people or animals outside their household to prevent the spread of COVID-19.
April 24, 2020
Georgia, Alaska, and Oklahoma begin to partially reopen their states despite concerns from health experts saying it was too early to reopen.
April 26, 2020
Clinicians in the U.S. and U.K. report clusters of children and adolescents requiring admission to intensive care units (ICUs) with a multisystem inflammatory condition that can lead to multiorgan failure— similar to Kawasaki disease and toxic shock syndrome. This condition will become known as Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C), a serious inflammatory condition that affects children with current or recent COVID-19 infections.
April 28, 2020
Polls show that many people in the U.S., particularly those ages under 30 years or making less than $40,000 per year, plan to defer medical care because of the cost of treatment due to the lack of insurance or being under-insured, potentially leading to the further spread of COVID-19, the under-reporting of case numbers, and excess deaths from COVID-19 and other preventable diseases.
April 30, 2020
The Trump Administration launches Operation Warp Speed, an initiative to produce a vaccine against the SARS-CoV-2 virus as quickly as possible. The operation funds the development of six promising vaccine candidates while they are still in the clinical trial phase, including the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna mRNA vaccines.
Since mid-March 2020, more than 26.5 million people in the U.S. have filed for unemployment, increasing the number of people without health insurance amid a pandemic.
May 1, 2020
FDA issues an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the use of the antiviral drug Remdesivir for the treatment of suspected or confirmed COVID-19 in people who are hospitalized with severe disease.
CDC develops the “PPE Burn Rate Calculator,” a spreadsheet-based model made to help healthcare facilities plan and optimize the use of personal protective equipment or PPE for the COVID-19 response and publishes it on the Apple and Android App stores.
CDC launches the SARS-CoV-2 Sequencing for Public Health Emergency Response, Epidemiology and Surveillance (SPHERES), a national network to provide real-time genomic sequencing data to public health response teams investigating COVID-19 cases, allowing them to track the SARS-CoV-2 virus as it evolves.
As some countries discuss re-opening, WHO convenes the International Health Regulation Emergency Committee for a third time and declares that the global COVID-19 pandemic remains a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC).
May 8, 2020
The Associated Press reports that top White House officials blocked a CDC document “Guidance for Implementing the Opening Up America Again Framework” that included detailed advice on how to safely reopen the country.
FDA authorizes the first COVID-19 test with the option of using home-collected saliva samples.
May 9, 2020
The unemployment rate in the U.S. is 14.7%— the highest since the Great Depression. With 20.5 million people out of work, the hospitality, leisure, and healthcare industries take the greatest hits overall, affecting essential workers, people with lower incomes, and racial and ethnic minority workers disproportionally.
May 11, 2020
President Trump holds a briefing in the White House Rose Garden to claim that anyone who wants to get a coronavirus test can get one and encourages businesses around the country to reopen. He does not wear a mask.
May 12, 2020
Dr. Anthony Fauci, the Director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), testifies before the U.S. Senate that experts believe more people have died from COVID-19 than have been officially reported and warns against “re-opening” too quickly.
May 15, 2020
New estimates from a University of Michigan study revise the survival rate for people with COVID-19 who are put on a ventilator from as low as 10% – 12% to between 25% – 50%.
CDC’s Chief Health Equity Officer officially joins CDC’s COVID-19 response. This is the first time in the agency’s history that a senior leader within the incident management structure has the sole purpose of advocating for greater health equity across an entire emergency response.
CDC distributes a warning for clinicians through the Health Alert Network describing Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C), a serious inflammatory condition that affects children with current or recent COVID-19 infections.
May 18, 2020
HHS awards states, territories, and local jurisdictions $11 billion in new funding to support testing for COVID-19: CDC will provide $10.25 billion to states, territories, and local jurisdictions through CDC’s Epidemiology and Laboratory Capacity for Prevention and Control of Emerging Infectious Diseases (ELC) and the Indian Health Service (IHS) will provide $750 million to IHS, tribal, and urban Indian Health programs to expand testing capacity.
Navajo Nation now has the highest COVID-19 infection rate per capita in the U.S.
May 21, 2020
AstraZeneca receives more than $1 billion from the U.S. government in funding for the development of the AstraZeneca/Oxford University COVID-19 vaccine, with the first doses due to arrive in September 2020.
May 22, 2020
The Lancet publishes a large study showing that COVID-19 patients who received the anti-malaria drug hydroxychloroquine die at higher rates and experience more cardiac complications than COVID-19 patients who do not receive the drug. This study will shortly be retracted due to data misuse, but multiple other studies have since shown that hydroxychloroquine is neither harmful nor beneficial in the treatment of COVID-19.
May 26, 2020
Navajo officials implement a series of mitigation efforts including extended weekend lockdowns, curfews, stay-at-home orders, masking, and checkpoints, as younger generations of Navajo begin to launch grassroots social media campaigns like “Protect the Sacred” to provide health information and help defend their people and cultural heritage from COVID-19— the Navajo become a model for implementing a unified pandemic response.
May 28, 2020
The recorded death toll from COVID-19 in the U.S. surpasses 100,000.
June 4, 2020
HHS announces new laboratory date reporting guidance for COVID-19 testing to include demographic data on race, ethnicity, age, and sex.
The Lancet and the New England Journal of Medicine retract the two publications that halted global trials of the antimalarial drug hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19 after investigations found inconsistencies in the data.
June 8, 2020
The World Bank states that the COVID-19 pandemic will plunge the global economy into the worst recession since World War II.
June 10, 2020
The number of confirmed COVID-19 cases in the U.S. surpasses 2 million.
June 13, 2020
CDC releases consolidated guidelines for COVID-19 testing— including for nursing homes, long-term care facilities, and high-density critical infrastructure workplaces, like food production facilities.
June 15, 2020
FDA rescinds the EUA that allowed hydroxychloroquine sulfate and chloroquine phosphate products to be donated to the Strategic National Stockpile for the treatment of COVID-19.
June 16, 2020
HHS announces that COVID-19 vaccines will be provided free of charge to older adults and other groups experiencing disproportionate impacts from the COVID-19 pandemic.
June 18, 2020
WHO halts its trial of hydroxychloroquine after a large, randomized study conducted in the U.K. found that the drug had no apparent effect on mortality when treating COVID-19.
June 22, 2020
The journal Science Translational Medicine releases a study suggesting that as many as 80% of the Americans who sought care for flu-like illnesses in March 2020 were likely infected with undetected COVID-19.
June 24, 2020
Three weeks after Black Lives Matter protests broke out across the country in the wake of the deaths of George Floyd and Breonna Taylor, data from 300 of the largest U.S. cities found no evidence of a COVID-19 spike in the weeks following the beginning of the protests— researchers determined that social distancing behaviors went up as people tried to avoid the protests.
June 25, 2020
CDC expands the list of people at increased risk for severe COVID-19 illness by removing the specific age threshold, instead noting that risk increases with age. CDC also includes people experiencing chronic kidney disease, COPD, obesity, serious heart conditions, sickle cell disease, and type 2 diabetes, and those who are immunocompromised from solid organ transplants.
June 29, 2020
Despite its development and clinical trials being supported by as much as $6.5 billion in public funds, Gilead Sciences sets the price of Remdesivir, an anti-viral used to treat COVID-19 that can shorten hospital stays and reduce the need for mechanical ventilation, at $3,120 for one typical treatment course ($520 per vial) for insured patients in the U.S.
June 30, 2020
Dr. Anthony Fauci warns a Senate committee that the number of new COVID-19 cases in the U.S. could soon rise from 40,000 to 100,000 new infections every day, likely overwhelming an already burdened healthcare system.
July 6, 2020
More than 200 scientists sign an open letter asking WHO to update its COVID-19 guidelines to include warnings about airborne transmission.
July 7, 2020
The number of confirmed COVID-19 cases in the U.S. surpasses 3 million.
The U.S. begins the process of withdrawing from WHO.
July 9, 2020
WHO announces that the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 can be transmitted through the air and is likely being spread by asymptomatic individuals.
July 14, 2020
CDC again calls on all people to wear cloth face masks when leaving their homes to prevent the spread of COVID-19, calling masks “a critical tool in the fight against COVID-19.”
Florida, Texas, Oklahoma, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia have both the greatest percentage of adults who are currently uninsured and the highest numbers of new COVID-19 cases.
July 15, 2020
A mandate from the Trump Administration directs hospitals nationwide to stop sending critical information about COVID-19 hospitalization rates and equipment availability to CDC and instead report this data to a new system set up by HHS using a private contractor, raising concerns over the politicization of public health, data, and privacy.
July 16, 2020
Many states, including California, Michigan, and Indiana postpone re-opening plans as COVID-19 case numbers rise.
The U.S. reports a record number of COVID-19 infections in a single day, with 75,600 new cases reported.
CDC extends the no sail order for all cruise ships through September 30, 2020.
July 22, 2020
The Department of Defense (DOD) and HHS reach a deal with Pfizer BioNTech for the delivery and distribution of 100 million doses of the Pfizer BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine candidate in December 2020, upon confirmation that the vaccine is safe and effective.
Antibody data examined by CDC shows that there were about 10 times more SARS-CoV-2 infections than first reported in March 2020 – May 2020 (depending on the region, there were 6 to 24 times more cases than were initially reported).
July 23, 2020
CDC releases resources for school administrators, teachers, parents, guardians, and caregivers to help build appropriate public health strategies to slow the spread of COVID-19 in a school environment.
August 4, 2020
A study finds that more than 50% of all people living in rural areas in the U.S. have no intensive care unit (ICU) beds available (only 3% of the communities with higher incomes had no ICU beds). High rates of COVID-19 infections, chronic health conditions, limited testing, and inadequate access to healthcare could all lead to significant COVID-19 mortality among people living in rural communities.
August 11, 2020
The Trump Administration agrees to pay $1.5 billion, or $15 per-dose, to Moderna for 100 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine.
August 12, 2020
Obesity is found to increase the risk of mortality from COVID-19 disease, especially among men and younger people– even when isolated from racial, ethnic, or socioeconomic disparities.
August 14, 2020
CDC reports results from a representative panel survey on mental health conducted among adults across the U.S. in June of 2020: 41% of responders reported struggling with mental health and 11% had seriously considered suicide recently. Essential workers, unpaid caregivers, young adults, and racial and ethnic minority groups were found to be at higher risk for experiencing mental health struggles, with 31% of unpaid caregivers reporting considering suicide.
CDC releases data indicating that most COVID-19 positive people are infectious to others for up to 10 days after symptoms first appear, but that individuals with severe illness or who are immunocompromised may be infectious for up to 20 days.
August 15, 2020
FDA issues an EUA to the Yale School of Public Health for its rapid diagnostic test for COVID-19 SalivaDirect. The test uses a new and more flexible method of containing and processing saliva samples when testing for COVID-19, allowing laboratories to increase capacity and efficiency in testing.
August 17, 2020
COVID-19 becomes the 3rd leading cause of death in the U.S. Deaths from COVID-19 now exceed 1,000 per day and nationwide cases exceed 5.4 million.
August 19, 2020
After CDC studies show that American Indians and Alaska Natives are among the racial and ethnic minority group at higher risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes, CDC provides more that $200 million in COVID-19 funding to Indian Country.
August 22, 2020
A study published by the Journal of the American Medical Association calls into question the clinical benefits of the anti-viral drug Remdesivir being used to treat patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
August 23, 2020
FDA issues an EUA for use of convalescent plasma (the liquid component of blood that, when taken from someone who has recently recovered from an infection, can contain antibodies to that illness) to treat people hospitalized with severe COVID-19.
August 24, 2020
The first documented case of COVID-19 reinfection is confirmed by the University of Hong Kong.
August 26, 2020
FDA issues an EUA for Abbott’s BinaxNOW Covid-19 Test Kit— a rapid antigen test that can detect a COVID-19 infection in 15 minutes using the same technology as a flu test.
August 28, 2020
The first documented case of COVID-19 reinfection in the U.S. is confirmed by the Nevada State Public Health Laboratory.
September 1, 2020
The U.S. and China decline to join the COVID-19 Vaccine Global Access Facility, or COVAX, a global program spearheaded by WHO that aims to develop and distribute COVID-19 vaccines worldwide— more than 170 other nations sign on.
September 3, 2020
The Journal of the American Medical Association and WHO now recommend the use of steroids for the treatment of severe COVID-19 disease after multiple studies find that steroids like dexamethasone, hydrocortisone, and methylprednisolone— a group of cheap and widely available drugs that reduce inflammation and immune response— can reduce mortality in severe cases of COVID-19 by up to 36%.
September 11, 2020
CDC releases data in a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) showing that because of concerns about COVID-19, an estimated 41% of U.S. adults had delayed or avoided seeking medical care, including urgent or emergency care. Unpaid caregivers for adults, people with underlying medical conditions, Black adults, non-White Hispanic adults, young adults, and people with disabilities are the most affected.
September 14, 2020
CDC ends the symptom-based COVID-19 screenings of air travelers from China (including Hong Kong and Macau), Iran, the Schengen area of Europe (26 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders), and the U.K., citing limited effectiveness due to asymptomatic spread.
Pfizer BioNTech expands phase 3 clinical trials of its COVID-19 vaccine to 44,000 participants— increasing the trial population diversity to include adolescents as young as 16 years and people with chronic, stable HIV, hepatitis C, or hepatitis B infections. The Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine is a 2-shot series given 3 weeks apart and must be stored at a temperature of –70 degrees Celsius (or –94 degrees Fahrenheit).
September 15, 2020
CDC releases data in MMWR from a study showing that people who recently tested positive for the SAR-CoV-2 virus were more than twice as likely to have recently dined out and more than four times as likely to have recently visited a bar or café.
CDC releases an infographic guide to help schools mitigate COVID-19 transmission in schools.
September 16, 2020
HHS announces a plan to make COVID-19 vaccines free in the U.S.
September 21, 2020
Johnson & Johnson begins phase 3 clinical trials of its COVID-19 vaccine with 60,000 participants. The J&J vaccine does not need to be frozen and may require just one shot.
September 22, 2020
The reported death toll in the U.S from COVID-19 surpasses 200,000.
September 23, 2020
HHS and CDC awards states, territories, and local jurisdictions $200 million from the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act in new funding to support vaccine distribution for COVID-19.
September 28, 2020
The reported death toll from COVID-19 reaches more than 1 million worldwide— in just 10 months.
September 30, 2020
CDC extends the no sail order for all cruise ships through October 31, 2020.
October 2, 2020
President Trump tests positive for the SARS CoV-2 virus and is treated at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center with antiviral drugs, including Remdesivir.
October 5, 2020
More staff at the White House, including the press secretary, test positive for COVID-19.
CDC updates its “How COVID-19 is Spread” guidelines to acknowledge the potential for the airborne spread of the COVID-19 virus— even when 6 feet of social distance is maintained if the area is poorly ventilated or enclosed and activities occur that require heavy breathing, like singing or exercise.
October 6, 2020
Food insecurity in the U.S. reaches 52 million people due to the COVID-19 pandemic— 17 million more people than pre-pandemic numbers.
October 7, 2020
New Zealand lifts restrictions and declares COVID-19 “beaten” after a cluster of 179 cases in Auckland (the country’s largest outbreak yet) is fully contained.
October 30, 2020
CDC announces the end of the no sail order for cruise ship companies, replacing it with a conditional sail order that requires companies to meet testing and safety requirements and to test those rules on simulated voyages before cruises resume.
November 4, 2020
One day after the presidential election, the U.S. reports 100,000 new cases of COVID-19 in 24 hours.
November 9, 2020
FDA issues an EUA for Eli Lilly’s drug Bamlanivimab, a monoclonal antibody treatment that mimics the immune system’s response to infection with SARS-CoV-2 and appears to protect patients at increased risk from a COVID-19 infection progressing to more severe forms of disease.
November 11, 2020
The journal Nature releases a study showing that most COVID-19 cases originate at indoor gathering spaces— places of worship, restaurants, gyms, and grocery stores. Areas of lower socioeconomic status were found to be at much greater risk: many residents are essential workers or cannot work from home and public spaces in these areas tend to be scarcer and more densely populated. The study’s model suggested that a trip to a grocery store would be about twice as risky in a neighborhood of lower incomes as in one of higher incomes.
November 13, 2020
Two weeks after large groups gathered for Halloween celebrations, COVID-19 case numbers spike across the U.S.
November 16, 2020
Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine is found to be 95.4% effective in its clinical trial.
November 17, 2020
Dr. Anthony Fauci discusses the need to understand the “long COVID” symptoms like persistent fatigue, shortness of breath, muscle aches, sporadic fevers, and concentration issues, that as many as one-third of patients experience for weeks or months after contracting COVID-19.
November 18, 2020
Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine is found to be 95% effective in their 44,000-person trial.
November 20, 2020
As COVID-19 case numbers in the U.S. surge past 11 million, CDC recommends that Americans stay home for Thanksgiving and avoid contact with all people not living in their household for the last 14 days.
November 21, 2020
CDC revises the Travel Health Notice system for COVID-19; adding a fourth alert level (low, moderate, high, and very high) and recommending that all travelers test 1-3 days before and 3-5 days after all international air travel in addition to staying home for 7-14 days after travel to avoid transmitting the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
November 23, 2020
FDA grants an EUA for a COVID-19 antibody treatment manufactured by Regeneron. In a clinical trial of 800 people, the drug significantly reduced virus levels within days.
December 3, 2020
ACIP recommends that healthcare professionals and older people living in long-term care facilities be offered a vaccine first in the initial phases of the COVID-19 vaccination program. CDC also notes that people ages 70 years and older who live in multi-generational households should be given priority as soon as more vaccine doses are available
December 11, 2020
FDA issues an EUA for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
ACIP recommends the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for all people ages 16 years or older for the prevention of COVID-19
December 14, 2020
The recorded death toll from COVID-19 in the U.S surpasses 300,000.
Sandra Lindsay, a nurse in New York, becomes the first American outside of clinical trials to receive a COVID-19 vaccine.
The U.K. announces the detection of a new and more contagious COVID-19 variant, B.1.1.7.
December 17, 2020
CDC records the highest number of drug overdose deaths ever in a 12-month period ending in May 2020 in the U.S.—more than 81,000. Overdose deaths involving synthetic opioids (primarily illicitly manufactured fentanyl) increased by 38%, methamphetamines by 35%, and cocaine (likely linked to co-use or contamination of cocaine with illicitly manufactured fentanyl or heroin) by 27%.
December 18, 2020
FDA issues an EUA for the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine.
December 19, 2020
ACIP recommends the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine in persons ages 18 years or older for the prevention of COVID-19.
December 22, 2020
CDC releases a report in MMWR outlining the ACIP’s recommendations for the “phases” of COVID-19 vaccination allocation while supply is still limited in the U.S. The suggested model for efficient and equitable vaccination distribution: phase 1a – healthcare personnel and residents of long-term care facilities; phase 1b – essential workers and all persons ages 75 years and older; phase 1c – all persons ages 65–74 and all persons ages 16–64 with a medical condition that increases their risk of severe disease from COVID-19; phase 2 – all persons ages 16 years and older not already recommended in phase 1.
December 23, 2020
The Trump Administration announces the purchase of 100 million additional doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
December 24, 2020
More than 1 million COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered in the U.S. in just 10 days: healthcare workers and older adults living in long-term care facilities are the first to be vaccinated with the goal of vaccinating every person as soon as enough vaccine doses are available
December 27, 2020
The Trump Administration signs the second COVID Relief Act into law. The bill includes $900 billion in funding for enhanced unemployment benefits, business loans, the purchase and distribution of COVID-19 vaccines and testing kits, and direct cash payments of $600.
December 28, 2020
Proof of a negative COVID-19 test taken within 72 hours of departure is mandated for all foreign national travelers entering the U.S. from the U.K. due to the highly transmissible COVID-19 B.1.1.7 / “Alpha” variant circulating in the U.K.
December 29, 2020
The first case of the COVID-19 B.1.1.7 / “Alpha” variant is detected in the U.S. by the Colorado Department of Health.
December 30, 2020
The Oxford University / AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine is authorized for emergency use in the U.K. Within a week, 530,000 doses are available for care-home residents, adults ages 80 years and older, and healthcare workers.
December 31, 2020
One year anniversary of the first reported case of COVID-19 to WHO.
2.8 million people in the U.S. have received a COVID-19 vaccine dose— far short of the nation’s goal of 20 million.
January 6, 2021
HHS and CDC announce plans to provide $22 billion in funding for states, localities, and territories to support expanded COVID-19 testing and vaccine distribution from the Coronavirus Response and Relief Supplemental Appropriations Act.
January 8, 2021
Amid vaccine shortages, scientists at Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), look for ways to double the supply to prevent future shortages.
January 12, 2021
CDC expands the COVID-19 negative test requirement to include all air passengers entering the U.S. CDC continues to recommend that people test again 3-5 days after arrival and stay home for 7 days after traveling to help slow the spread of COVID-19.
January 18, 2021
The reported death toll from COVID-19 in the U.S. surpasses 400,000.
January 20, 2021
Dr. Rochelle Walensky begins her term as the director of the CDC with the goal of rapidly accelerating COVID-19 testing, surveillance, and vaccination, while confronting the public health challenges posed by suicide, substance use disorder and overdose, chronic diseases and the tolls caused by social and racial injustice and inequity.
First anniversary of the first laboratory-confirmed case of COVID-19 in the U.S. from samples taken in Snohomish County, Washington and of CDC activating its Emergency Response Center (EOC) to respond to the novel coronavirus.
January 21, 2021
The Biden Administration announces the National Strategy for the COVID-19 Response, an outline of 7 goals to restore trust, vaccinate, test, and treat COVID-19 while protecting schools, businesses, and workers in addition to advancing health equity and building the nation’s preparedness for future pandemics, calling it “a wartime undertaking.”
The Biden Administration reverses the Trump Administration’s attempt to withdraw from WHO and joins the COVID-19 Vaccine Global Access Facility “COVAX”, a program aimed at vaccinating people in low- and middle-income countries against COVID-19.
January 22, 2021
CDC releases data in MMWR on the emerging and more transmissible COVID-19 B.1.1.7 / “Alpha” variant— now detected in more than 30 countries and in 12 U.S. states. CDC recommends universal and increased compliance with mitigation strategies, like social distancing and masking, and higher vaccination coverage to protect the public.
January 25, 2021
The first case of the COVID-19 P.1 / “Gamma” variant, first identified by scientists in Brazil, is detected in Minnesota.
January 26, 2021
More than 23 million COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered in the U.S.
The number of recorded COVID-19 cases worldwide surpasses 100 million.
January 28, 2021
The first case of the COVID-19 B 1.351 / “Beta” variant, first identified by scientists in South Africa, is detected in South Carolina.
January 29, 2021
CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky signs an extension of the eviction moratorium through March 31, 2021, in an effort to help slow the spread of COVID-19.
January 30, 2021
As part of the Biden Administration’s Executive Order on Promoting COVID-19 Safety in Domestic and International Travel, CDC requires face masks to be worn by all travelers while on public transportation and inside transportation hubs to prevent the spread of COVID-19 effective February 2, 2021.
February 1, 2021
The Biden Administration, with the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD), HHS, and CDC, reach a $231.8 million deal with the Australian company Ellume to supply rapid at-home COVID-19 tests in the U.S., committing to ship 100,000 test kits per month February through July.
February 16, 2021
Vaccine distribution is disrupted in several states, including Texas, Missouri, Alabama, and New Hampshire, due to severe winter storms.
February 18, 2021
An estimated 2.5 million women and 1.8 million men have left the workforce since the start of the pandemic in the U.S.
February 21, 2021
The recorded COVID-19 death toll in the U.S. surpasses 500,000.
February 27, 2021
FDA approves an emergency use authorization (EUA) for Johnson & Johnson’s one-shot COVID-19 vaccine for all people ages 18 years and older.
February 28, 2021
ACIP recommends Johnson & Johnson’s COVID-19 vaccine for all people ages 18 years and older.
March 2, 2021
The Biden Administration directs all states to make pre-K-12 teachers, school staff, and childcare workers eligible for COVID-19 vaccinations and to prioritize this group during the month of March within the Federal Retail Pharmacy Program. After this directive, the number of states where these essential workers are eligible to be vaccinated increases by more than 50%.
March 8, 2021
CDC recommends that people who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19 can safely gather with other fully vaccinated people indoors without masks and without socially distancing.
March 11, 2021
First anniversary of WHO declaring COVID-19 a global pandemic.
The Biden Administration announces plans for all adult Americans to be eligible and able to receive a COVID-19 vaccine by May 1, 2021. They plan to make COVID-19 vaccines accessible by delivering vaccines to 700 community health centers in under-resourced communities, doubling the number of pharmacies providing COVID-19 vaccines and the number of federally run mass vaccination centers, deploying more than 4,000 active-duty troops to support these efforts, and by launching the “Find a Vaccination Website” and a 1-800 Number.
The Biden Administration signs the $1.9 trillion American Rescue Plan into law. The stimulus bill includes funding for expanded unemployment benefits, rental assistance, and COVID-19 vaccinations, as well as extending the child tax credit for one year and providing direct cash payments of up to $1,400 per person.
The Biden Administration announces a $1.75 billion investment in expanding genomic sequencing to identity and track new variants and $50 billion to expand the nation’s testing capabilities.
March 13, 2021
More than 100 million COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered in the U.S.
March 14, 2021
Ireland, Iceland, Denmark, and Norway suspend distribution of AstaZeneca’s COVID-19 vaccine as the European Union (EU) investigates if the shot may be linked to reports of blood clots.
March 17, 2021
CDC announces $2.25 billion in spending over two years to address COVID-19 related health disparities for people living in rural areas and racial and ethnic minority groups.
March 18, 2021
The U.S. announces it will send 4 million unused doses of AstraZeneca’s COVID-19 vaccine from its stockpile to Mexico and Canada.
After 13 European countries halt distribution of the AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine pending review, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) announces that they did not find any evidence that the vaccine causes blood clots, and while they were unable to definitively rule out a link between rare blood clots events and the vaccine, the AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine is still considered safe, is effective, and the benefits of this vaccine still outweigh its risks.
March 19, 2021
CDC updates its guidance on social distancing in K-12 schools: most elementary students can safely socially distance from at least 3 feet instead of 6 feet inside the classroom with universal masking, but middle and high school students should still maintain at least 6 feet apart in communities where the transmission level is high.
March 25, 2021
CDC announces $300 million in funding for states, localities, territories, tribes, and tribal organizations for community health worker (CHW) services to address: 1) disparities in access to COVID-19 related services, such as testing, contact tracing, and immunization; 2) factors that increase risk of severe COVID-19 illness, such as chronic diseases, smoking, and pregnancy; and 3) community public health needs that have been exacerbated by COVID-19, such as health and mental health care access and food insecurity.
CDC announces a plan to provide the patients and staff of dialysis clinics easy access to COVID-19 vaccinations on-site. People with chronic kidney disease on dialysis who contract COVID-19 are at higher risk of severe adverse health outcomes— half require hospitalization and 20% – 30% die. Additionally, advanced stage chronic kidney disease disproportionately affects African Americans, Non-White Hispanics, and American Indians and Alaska Natives. To date, only 35% of healthcare workers in U.S. dialysis centers have been vaccinated.
March 29, 2021
A CDC study finds that mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, are highly effective at preventing infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus in real-world conditions among healthcare personnel, first responders, and other essential workers (groups that are more likely than the general population to be exposed to the virus because of their occupations), reducing their risk of infection by 90%.
CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky extends the eviction moratorium through June 30, 2021, in an effort to help slow the spread of COVID-19.
March 31, 2021
CDC, in collaboration with the National Institutes of Health (NIH), launches the community health testing program called “Say Yes! COVID Test” in Pitt County, North Carolina and Chattanooga/Hamilton County, Tennessee, providing 160,000 residents with access to free, at-home COVID-19 tests to use up to three times a week for one month in an effort determine if frequent self-testing can reduce community spread of COVID-19.
April 2, 2021
CDC recommends that people who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19 can safely travel at lower-risk to themselves.
April 3, 2021
CDC announces $3 billion in additional funding for expanded COVID-19 vaccination programs.
April 6, 2021
CDC estimates that nearly 80% of pre-K-12 teachers, school staff, and childcare workers in the U.S. have received at least their first shot of COVID-19 vaccine.
April 8, 2021
CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky releases a statement on racism and health amid the COVID-19 pandemic, writing: “Yet, the disparities seen over the past year were not a result of COVID-19. Instead, the pandemic illuminated inequities that have existed for generations and revealed for all of America a known, but often unaddressed, epidemic impacting public health: racism.”
April 13, 2021
CDC and FDA issue a joint statement recommending pausing the use of the Johnson & Johnson’s COVID-19 vaccine while six cases of a rare and serious blood clot in people who received the J&J COVID-19 vaccine are investigated.
April 21, 2021
More than 200 million COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered in the U.S.
April 23, 2021
ACIP and FDA recommend the continued use of Johnson & Johnson’s COVID-19 vaccine for all people ages 18 years and older in the U.S., following a thorough safety review after the use of the vaccine was paused when 6 cases of rare and severe type of blood clots were reported.
April 27, 2021
In March 2021, according to data from the Census Bureau, 18 million adults (16% of Black adults, 16% of Latino adults, and 6% of White adults) and up to 8.8 million children, over one-fifth of Black and Latino children, lived in a household without enough food sometime in the last seven days.
April 28, 2021
CDC finds that the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna mRNA COVID-19 vaccines reduce the risk of hospitalization with SARS-CoV-2 in people ages 65 years and older by 94%.
May 10, 2021
FDA expands the emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine to include all adolescents ages 12–15 years.
May 12, 2021
ACIP recommends the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for all adolescents ages 12–15 years.
May 14, 2021
CDC finds that mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, reduce the risk of infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus by approximately 94%.
May 17, 2021
An estimated 5.1 million women left the workforce when COVID-19 closed schools and child-care centers in 2020. Today, 1.3 million remain out of the workforce and only 56% of women in the U.S. are working for a salary– the lowest percentage since 1986.
June 1, 2021
The COVID-19 B.1.617.2 / “Delta” variant, first identified in India, becomes the dominant variant in the U.S. The variant begins a third wave of infections during the summer of 2021.
June 7, 2021
CDC finds that the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna mRNA COVID-19 vaccines reduce the risk of infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus by 91% and protect against severe illness and hospitalization if a breakthrough infection does occur.
June 11, 2021
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that while most COVID-19–associated hospitalizations occur in older adults, severe disease requiring hospitalization can occur in all age groups – including adolescents ages 12–17 years.
June 24, 2021
CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky extends the eviction moratorium through July 31, 2021, in an effort to help slow the spread of COVID-19.
June 30, 2021
CDC’s National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program reports that the total number of cancer screenings decreased by an average of 87% for breast cancer and 84% for cervical cancer during early 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, putting individuals at risk for delayed diagnoses and poorer health outcomes. Access to medical care among racial and ethnic minority groups and people with lower incomes declined the most during this period: breast cancer screenings declined 98% among American Indian and Alaskan Native women.
July 6, 2021
American Indian and Alaska Natives had some of the highest rates of hospitalization and death in the U.S. early in the pandemic, but American Indian and Alaskan Native vaccination campaigns are succeeding: CDC’s COVID-19 data tracker shows that American Indians and Alaskan Natives have the highest COVID-19 vaccination rate of any racial or ethnic group in the U.S.
July 9, 2021
CDC and FDA release a joint statement assuring the public that Americans who have been fully vaccinated do not need a booster shot at this time.
July 16, 2021
CDC issues an exception for unaccompanied non-citizen children under Title 42, the order suspending the right to introduce non-citizen persons into the U.S. due to the increased risk from COVID-19.
July 20, 2021
The Lancet reports that more than 1.5 million children worldwide have lost their primary or secondary caregiver due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
July 27, 2021
Amid a Delta variant surge, CDC releases updated masking guidance recommending that everyone in areas with substantial or high transmission wear a mask indoors.
July 30, 2021
CDC releases data in MMWR showing an increase in breakthrough infections of COVID-19 in Barnstable County, Massachusetts in July of 2021. The early data showing high viral loads in people infected with the Delta variant of COVID-19 suggest a concern that, unlike with other variants, vaccinated people infected with Delta can transmit the virus to others. This MMWR becomes the most wildly circulated report in the agency’s history.
August 2, 2021
CDC extends Title 42, the order suspending the right to introduce non-citizen persons into the U.S. at the nation’s southern and northern land borders, except for the unaccompanied non-citizen children covered under the July 16, 2021, order, due to the increased risk from COVID-19.
CDC reports that the Indian Health Service (IHIS) has administered 1,497,047 COVID-19 vaccine doses— more than 70,000 shots given daily.
August 3, 2021
Amid a growing surge of the Delta variant, CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky signs an eviction moratorium in areas of substantial and high COVID-19 transmission in recognition that eviction moratoria, like quarantine, isolation, and social distancing, can be effective public health measures taken to prevent the spread of a communicable disease like COVID-19.
August 6, 2021
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that unvaccinated individuals are more than twice as likely to be reinfected with COVID-19 than those who were fully vaccinated after initially contracting the virus – in other words, COVID-19 vaccines offer stronger protection than natural immunity alone
August 11, 2021
CDC releases a statement assuring the public that COVID-19 vaccination is safe for pregnant and breastfeeding people. CDC studies have found that an infection with COVID-19 during pregnancy increases the risk of developing severe illness from COVID-19 and that there is no evidence that any vaccines, including the COVID-19 vaccines, cause fertility problems in women or men.
August 13, 2021
ACIP recommends an additional dose of COVID-19 vaccine after the two-dose vaccine series for all people with moderately to severely compromised immune systems.
August 18, 2021
CDC announces a new center, the Center for Forecasting and Outbreak Analytics (CFA), which aims to improve the nation’s ability to forecast and model emerging health threats, including pandemics like COVID-19, using data analytics.
HHS, CDC, and FDA release a statement concluding that booster shots of the Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccines will be needed to protect against severe disease, hospitalization, and death in the coming months.
August 23, 2021
FDA fully approves the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for all people ages 18 years and older. Full FDA approval further reinforces that the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine has been shown to meet the agency’s high standards for safety, effectiveness, and consistent quality in manufacturing.
August 30, 2021
ACIP recommends Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine for all people ages 16 years and older.
September 1, 2021
CDC releases a digital toolkit for individuals with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities (IDD) and their caregivers to navigate the COVID-19 pandemic, with communication resources like videos, stories, posters, and interactive activities about getting tested, vaccinated, masking, and social distancing. To date, CDC has also released more than 40 videos and 25 web resources in American Sign Language (ASL) on COVID-19.
September 3, 2021
CDC announces an additional $300 million in funding for community health worker services to support COVID-19 prevention and control.
September 17, 2021
The Biden Administration, working through CDC, invests $2.1 billion in funding for state, local, and territorial public health departments to give them the resources needed to prevent infections in healthcare settings, detect and contain infectious organisms, enhance laboratory capacity, and combat infectious disease threats, including COVID-19.
September 24, 2021
ACIP recommends Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine boosters for all people ages 65 years and older, residents of long-term care settings, people ages 50–64 years with underlying medical conditions, and people ages 18–49 years with underlying medical conditions and / or who live or work in high-risk settings to be given at least 6 months after their primary vaccination series.
CDC releases three studies in MMWR looking at the COVID-19 pandemic’s effect on education. Despite school closures in some areas, around 96% of K-12 schools have remained open for in-person learning and schools without universal indoor mask mandates were more than three times more likely to have COVID-19 outbreaks than the K-12 schools that required universal masking from day one.
September 29, 2021
CDC issues an urgent health advisory to increase COVID-19 vaccination rates among people who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or who are trying to become pregnant. More than 22,000 pregnant people have been hospitalized with COVID-19 and 161 have died. COVID-19 in pregnant people carries a two-fold risk of admission to intensive care, a 70% increased risk of death, and adverse pregnancy outcomes that can include preterm birth, stillbirth, and the admission of a newborn into the ICU with COVID-19
October 6, 2021
WHO publishes a clinical case definition of “post COVID-19 condition” or long COVID. The symptoms of long COVID include, but are not limited to, fatigue, shortness of breath, and / or cognitive dysfunction that persists for at least two months and impacts everyday life, three months from the onset of an initial COVID-19 infection.
October 7, 2021
More than 140,000 children in the U.S. have lost their primary or secondary caregiver to the COVID-19 pandemic. One of every 168 American Indian and Alaska Native children, 1 of every 310 Black children, 1 of every 412 non-White Hispanic children, 1 of every 612 Asian children, and 1 of every 753 White children have now experienced orphanhood or the death of caregivers.
CDC adds mental health conditions to the list of risk factors associated with severe illness from COVID-19.
October 21, 2021
ACIP recommends Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine boosters for all people ages 65 years and older and all people ages 18 years and older who are residents of long-term care settings, have underlying medical conditions, and who live or work high-risk settings to be given least 6 months after their primary vaccination series. ACIP also recommends booster shots for everyone who received Johnson & Johnson’s COVID-19 vaccine more than two months ago.
October 26, 2021
CDC announces $26 million in funding for CDC’s new Center for Forecasting and Outbreak Analytics (CFA).
October 29, 2021
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that unvaccinated individuals who had been recently infected with COVID-19 were about 5 times more likely to be re-infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus than fully vaccinated individuals with no prior COVID-19 infections.
November 2, 2021
ACIP recommends the Pfizer-BioNTech pediatric COVID-19 vaccine for all children ages 5–11 years.
November 3, 2021
On the sixth annual One Health Day, a global campaign that highlights the interconnected relationship between people, animals, and their environment, CDC releases a statement on the COVID-19 pandemic, noting that more than 400 different animals have been found to be infected with COVID-19 and, as a zoonotic virus, SARS-CoV-2 can spread between people and animals.
November 8, 2021
All non-citizens who are traveling to the U.S. will now be required to be fully vaccinated and provide proof of their vaccination status to fly to the U.S. All travelers will continue to be required to show a negative pre-departure COVID-19 test taken no more than three days before they board their flights.
November 10, 2021
CDC and WHO report that more than 22 million infants missed their first dose of the measles vaccine in 2020. This is the largest global increase of unvaccinated children in two decades and is due in-part to the disruptions the COVID-19 pandemic has had on health care and immunization
November 19, 2021
Amid worries of an upcoming Omicron surge, CDC strengthens its recommendation urging that everyone ages 18 years and older who received a Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer-BioNTech, or Moderna COVID-19 vaccine should receive a booster after they are fully vaccinated.
November 26, 2021
WHO designates the COVID-19 “Omicron” variant, first identified by scientists in South Africa, as a “variant of concern.” Changes in the spike protein of the Omicron variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, concern scientists around the world due to the potential for increased transmissibility and decreased vaccine protection.
November 29, 2021
CDC recommends that everyone ages 18 years and older who received a Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine should receive a booster shot 2 months after their initial J&J vaccine.
December 1, 2021
The first case of the Omicron variant in the U.S. is detected by the California and San Francisco Departments of Public Health.
December 2, 2021
A second case of the Omicron variant in the U.S. is detected by the Minnesota and the New York City Departments of Health.
December 3, 2021
FDA revises the emergency use authorization (EUA) for Eli Lilly’s two monoclonal antibodies, Bamlanivimab and Etesevimab, to allow the drugs to be used together for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in all pediatric patients, including newborns, who have a positive COVID-19 test and are at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19.
December 6, 2021
CDC introduces a new one-day testing policy requiring international travelers to show a negative pre-departure COVID-19 test taken 24 hours before they board their flights to the U.S.
December 8, 2021
FDA issues an EUA for AstraZeneca’s Evusheld, a treatment of two monoclonal antibodies for the pre-exposure prevention of COVID-19 in adults and children ages 12 years and older who weigh at least 88 pounds and have moderate to severely compromised immune function or a history of severe adverse reactions to COVID-19 vaccines.
December 9, 2021
CDC and FDA expand COVID-19 booster recommendations to include everyone ages 16 years and older.
December 15, 2021
The recorded death toll from COVID-19 surpasses 800,000 in the U.S. One in every 100 people ages 65 years and older in the U.S. has died.
December 16, 2021
ACIP updates its recommendations to express a clinical preference for individuals to receive, when possible, an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna, over Johnson & Johnson’s COVID-19 vaccine.
December 17, 2021
CDC releases two reports in MMWR highlighting the use of test-to-stay practices to help keep students in school during the COVID-19 pandemic.
December 20, 2021
CDC releases data estimating that the Omicron variant is around 1.6 times more transmissible than the Delta variant.
December 22, 2021
FDA authorizes Pfizer’s anti-viral pill Paxlovid to treat COVID-19 under an EUA for adults and children ages 12 years and older who weigh at least 88 pounds who test positive and are at high risk for progression to severe disease. It is the first treatment for COVID-19 that is taken orally and can be used at home.
December 23, 2021
FDA authorizes Merck’s anti-viral pill Molnupiravir to treat COVID-19 under an EUA for all adults and children ages 18 years and older who test positive and are at high risk for progression to severe disease. It is the second treatment for COVID-19 that is taken orally and can be used at home but, despite supply concerns, Paxlovid remains the preferred oral anti-viral treatment for COVID-19.
CDC updates its recommendations for the isolation and quarantine periods for healthcare workers, decreasing their isolation time after infection with COVID-19. Asymptomatic healthcare workers can now return to work after 7 days with a negative test and healthcare workers who have received all recommended COVID-19 vaccines doses, including a booster, do not need to quarantine after a high-risk exposure.
December 27, 2021
CDC shortens the recommended isolation period for people with COVID-19 to 5 days, followed by 5 days of wearing a mask around others if they are asymptomatic or if their symptoms are resolving (resolving is defined as without a fever for 24 hours).
CDC updates the recommended quarantine period for people exposed to someone with COVID-19 to wear a mask around others for 10 days and get tested on day 5 if you have been boosted or vaccinated within the last 6 months. If the exposed individual is unvaccinated, CDC now recommends a quarantine period of 5 days, followed by strict mask use for an additional 5 days.
January 1, 2022
As Delta and Omicron spread, New York state records its highest number of new COVID-19 cases in a single day since the pandemic began – with 114,082 new confirmed cases.
January 3, 2022
The U.S. reports nearly 1 million new COVID-19 infections– the highest daily total of any country in the world. The number of hospitalized COVID-19 patients has risen nearly 50% in just one week.
FDA amends the emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine to allow a single booster dose for all individuals ages 12–15 years; shortens the time-period between the completion of primary vaccination series of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and a booster dose to at least five months; and allows for a third primary series dose for certain immunocompromised children ages 5–11 years.
January 4, 2022
ACIP shortens the recommended time between the primary vaccination series and a booster shot for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine from 6 months to 5 months.
ACIP recommends that moderately or severely immunocompromised children ages 5–11 years receive an additional primary dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine 28 days after their second shot.
January 5, 2022
ACIP recommends that all adolescents ages 12–17 years receive a booster shot 5 months after their initial Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination series.
January 7, 2022
FDA amends the EUA for the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine to shorten the time between the primary series of the vaccine and a booster dose from at least 5 months to 6 months for individuals ages 18 years and older. The same day, CDC endorses the FDA’s recommendation.
January 11, 2022
The Biden Administration purchases 600,000 doses of GSK and Vir Biotechnology’s antibody treatment Sotrovimab, after the drug was found to be effective against both the Delta and Omicron variants.
January 14, 2022
CDC updates guidelines on masks to emphasize fit, comfort, and consistent wear.
In one month, the daily average of new COVID-19 infections reported in the U.S. spikes from 119,215 to 805,062.
January 17, 2022
The American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) sues an Arkansas jail on behalf of detainees who reported COVID-19 like symptoms and say they were unknowingly given ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine, two drugs that CDC does not recommend for the treatment of COVID-19.
January 19, 2022
To help meet the demand for testing during the Omicron surge, the Biden Administration purchases 1 billion COVID-19 tests and creates an online portal where people can order free at-home rapid antigen COVID-19 tests through the U.S. Postal Service (USPS).
January 20, 2022
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that during the Delta surge, both COVID-19 vaccination and surviving a prior infection provided protection against infection and hospitalization from COVID-19.
A study published in the American Journal of Epidemiology finds that COVID-19 vaccination has no impact on male or female fertility, but that a COVID-19 infection may be associated with a short-term decline in male fertility.
January 24, 2022
FDA further revises the EUA for Eli Lilly’s two monoclonal antibodies, Bamlanivimab and Etesevimab, to limit their use after the treatment is shown to be ineffective against the Omicron variant.
FDA revises the EUA for Regeneron’s monoclonal antibody, Regen-cov, to limit its use after the treatment is shown to be ineffective against the Omicron variant.
The Omicron variant now accounts for approximately 99% of all current COVID-19 cases in the U.S.
January 31, 2022
FDA fully approves the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine for all people ages 18 years and older. Full FDA approval further reinforces that the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine has been shown to meet the agency’s high standards for safety, effectiveness, and consistent quality in manufacturing. To date, COVID-19 vaccines are estimated to have saved at least a quarter of a million lives and prevented more than 1 million hospitalizations.
February 4, 2022
ACIP recommends the use of Moderna’s vaccine for all people ages 18 years and older.
The death rate from COVID-19 climbs 30% in two weeks amid an Omicron surge, with more than 2,600 people dying from COVID-19 each day.
The number of recorded deaths in the U.S. due to COVID-19 surpasses 900,000.
February 7, 2022
A study is published in Nature showing that even a mild case of COVID-19 appears to increase the risk of heart problems for one year after infection. The study’s authors suggest that COVID-19 might be as much of a risk factor for heart disease as high blood pressure, diabetes, or smoking.
February 11, 2022
CDC releases data showing that COVID-19 vaccine boosters remain safe and were highly effective against severe disease during the Omicron and Delta variant surges for everyone ages 5 years and older.
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that the Omicron variant rose from 1% of all infections in the U.S. to 99% of all infections in just 6 weeks (compared to 18 weeks for Delta).
February 15, 2022
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that maternal COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy with an mRNA vaccine, Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna, reduces the risk of COVID-19 hospitalization in infants (babies under 6 months) by around 60%.
February 18, 2022
CDC releases two reports in MMWR on pediatric emergency department visits during the COVID-19 pandemic and recommends increased awareness of the health concerns among children and adolescents that could arise due to delayed medical care and heightened emotional distress, especially for adolescent girls (ages 12–17 years).
The Wisconsin Department of Health Services confirms that a child in Wisconsin has died from multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), a rare but serious condition associated with COVID-19 infection in children.
March 2, 2022
WHO releases data showing that the COVID-19 pandemic triggered a 25% increase in anxiety and depression worldwide, with young people and women at the highest risk.
March 3, 2022
CDC updates the “COVID-19 Community Level,” showing that more than 90% of the U.S. population is in a location with either low or medium COVID-19 community transmission level.
The U.S. has now donated more than 480 million COVID-19 vaccine doses to 110 countries.
March 4, 2022
While access to COVID-19 vaccines has expanded, the gap in COVID-19 vaccination rates between urban and rural areas in the U.S. has more than doubled since April 2021.
March 5, 2022
More than 10 billion people have received a COVID-19 vaccine, with WHO reporting that 10,704,043,684 COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered worldwide. About 56% of the world is now fully vaccinated, but many regions still lack access, especially on the African continent where less than 20% of the total population is currently vaccinated.
March 8, 2022
Hawaii becomes the last state to announce an end to its universal indoor mask mandate, scheduled for March 26, 2022.
March 10, 2022
On CDC’s recommendation, the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) extends the mask requirement for all public transportation and transportation hubs through April 18, 2022.
The number of recorded deaths due to COVID-19 surpasses 6 million worldwide, with WHO reporting 6,019,085 confirmed deaths. The true number is likely much higher.
The number of recorded COVID-19 cases surpasses 450 million worldwide, with WHO reporting 450,229,635 confirmed infections. The true number is likely much higher.
March 11, 2022
Two-year anniversary of WHO declaring COVID-19 a global pandemic.
CDC updates the “COVID-19 Community Level,” showing that more than 98% of the U.S. population is in a location with either a low or medium COVID-19 community transmission levels.
In the U.S., 92% of all children ages 5–11 years now live within 5 miles of a vaccine provider.
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that school districts in Arkansas with universal mask requirements had a 23% lower incidence of COVID-19 among staff and students compared to districts without mask requirements during August – October 2021.
March 12, 2022
CDC estimates that 23% of all current COVID-19 infections in the U.S. are caused by the Omicron BA.2 subvariant, with initial data suggesting that BA.2 appears to be more transmissible than the Omicron BA.1 variant.
March 14, 2022
Several regions in China face new lockdowns under the “COVID Zero” policy when cases of the Omicron variant are found. Tens of millions of people are required to stay inside their homes, key technology manufacturers like Foxconn and Unimicron close factories, and the production and distribution of goods is disrupted throughout the world.
March 15, 2022
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that the COVID-19 hospitalization rate among infants and children ages 4 years and younger was 5 times higher during the peak of the Omicron variant surge when compared to the Delta variant– 63% of those children hospitalized had no underlying medical conditions.
After officially recording more than 43 million COVID-19 cases, India begins vaccinating adolescents ages 12–14 years with the COVID-19 vaccine Corbevax and schools reopen after two years of closures.
CDC outlines its goals for the third year of a global COVID-19 response: to increase vaccination levels around the world, reduce spread of COVID-19 and its impact, expand scientific knowledge of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, and strengthen public health leadership while improving long-term health security worldwide.
March 16, 2022
At the World Trade Organization (WTO) meeting the U.S., the European Union, India, and South Africa forge a preliminary agreement on a COVID-19 vaccine intellectual property (IP) waiver, hoping to expand access to vaccines around the world.
March 18, 2022
CDC releases data in two MMWRs showing that adults who received 3 doses of a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine were 94% less likely to be put on a ventilator or die from COVID-19 during the Omicron surge compared to non-vaccinated adults in the U.S. and that Black adults are currently 4 times more likely to be hospitalized than White adults.
March 24, 2022
Data from the Census Bureau shows that deaths in the U.S. between 2019 – 2020 increased by approximately 19% after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in March 2020. That is the largest spike in mortality in the U.S. in 100 years.
March 26, 2022
CDC estimates that about 55% of all current COVID-19 cases in the U.S. are caused by the Omicron BA.2 subvariant.
March 29, 2022
CDC and FDA both recommend a second mRNA COVID-19 vaccine booster for immunocompromised individuals and all adults ages 50 and older 4 months after their last booster dose.
CDC recommends that all adults who received a primary vaccine series and booster dose of Johnson & Johnson’s COVID-19 vaccine receive a second booster dose with an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
CDC recommends that all adults who received a primary vaccine series and booster dose of Johnson & Johnson’s COVID-19 vaccine receive a second booster dose with an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
March 30, 2022
The number of recorded deaths due to COVID-19 reaches 976,229, with more than 79,853,683 total reported cases of the virus in the U.S.
March 31, 2022
CDC releases data from the Adolescent Behaviors and Experiences Survey (ABES) showing that from January 2021 – June 2021 among high-school aged adolescents: 44% report feeling persistently sad or hopeless; 55% report emotional abuse in the home; 11% report physical abuse in the home; and 29% report job loss by an adult in the home. Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and female youth reported the poorest overall mental health, the most emotional abuse by a parent or caregiver, and attempted suicide more their peers during the COVID-19 pandemic.
April 1, 2022
CDC announces the termination of Title 42, an Order that suspended the right to introduce migrants into the U.S. due to the public health risk of COVID-19, effective May 23, 2022.
April 8, 2022
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that the risk for cardiac complications in all age groups was significantly higher after COVID-19 infection when compared to after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination.
April 13, 2022
The Omicron subvariant BA.2 now makes up more than 85% of all new COVID-19 infections in the U.S.
April 18, 2022
CDC’s mask mandate for indoor public transportation is struck down by a judge in Florida.
April 19, 2022
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that of the children ages 5–11 years who were hospitalized with COVID-19 during the first few months of the Omicron surge, 3 in 10 had no underlying medical conditions, 9 in 10 were unvaccinated, and 2 in 10 required ICU care.
April 21, 2022
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) extends the COVID-19 vaccine requirement for all non-citizens entering the U.S.– in addition to the requirement that all travelers show a negative antigen test taken within one day of departure.
April 22, 2022
For the second year in a row, COVID-19 was the third leading cause of death in the U.S.– after heart disease and cancer.
April 26, 2022
The Biden Administration purchases 20 million doses of Pfizer’s oral anti-viral drug Paxlovid as part of the Test-to-Treat initiative– 2,200 locations where Americans can receive free COVID-19 testing and, if needed, treatment. These doses will also be used to double the number of pharmacies with Paxlovid stocked from 20,000 to 40,000.
April 27, 2022
It is estimated that during 2000–2018, measles vaccines prevented 23.2 million deaths, but delays in routine vaccinations caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and crises in Ukraine, Ethiopia, Somalia, and Afghanistan have led to a nearly 80% worldwide rise in measles cases in 2022.
April 29, 2022
Data from CDC’s National Commercial Laboratory Seroprevalence Study estimates that, as of February 2022, approximately 75% of children and adolescents showed infection-induced antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 (evidence of a previous infection with SARS-CoV-2 – also called seroprevalence) and that, since December 2021, approximately one third have become newly seropositive.
April 30, 2022
The current proportion of the U.S. population fully vaccinated against COVID-19 broken down by age group is: 5–11, 28%; 12–17, 59%; 18–49, 69%; 50–64, 80%; and ≥65 years, 90%.
May 3, 2022
CDC recommends that everyone continue to wear a mask while in indoor transportation hubs to prevent the spread of COVID-19 – but this is no longer legally enforceable.
May 5, 2022
WHO estimates that there have been approximately 15 million direct or indirect deaths (also called “excess mortality”) globally from January 2020 – December 2021 that were caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. South-East Asia, Europe, and the Americas accounted for 84% of the excess deaths.
May 10, 2022
During the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a 35% increase in the firearm homicide rate, resulting in the highest firearm homicide rate in more than 25 years. Firearm homicide rates are the highest among males, adolescents, young adults, and non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic American Indian and Alaska Native people. Rates of firearm suicide remained high, increasing most notably among American Indian and Alaska Native males ages 10–44, and are highest in rural areas.
May 12, 2022
The number of recorded deaths due to COVID-19 in the U.S. reaches 1 million (1,000,000).
Initial research suggests that between 4% and 36% of all people infected with COVID-19 will experience symptoms lasting at least six-months, potentially leading to between 5 and 25 million people in the U.S. experiencing a long-term disability (approximately 200 million people worldwide). Experts and disability advocates worry that the long-term consequences of this virus are underappreciated.
May 16, 2022
Researchers from Brown University School of Public Health, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, estimate that approximately 50% of COVID-19 deaths in the U.S. were vaccine-preventable deaths.
May 19, 2022
ACIP recommends Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine boosters for everyone ages 5–11 years to be given at least 5 months after their primary vaccination series. ACIP also recommends everyone ages 12 years and older who is immunocompromised and those ages 50 years and older should receive a second booster dose at least 4 months after their first to prevent severe disease, hospitalization, and death.
May 25, 2022
CDC releases data in MMWR showing that COVID-19 survivors are twice as likely to develop a pulmonary embolism or respiratory condition and that approximately 1 in 5 adults now have at least one health condition that may be attributable to a previous COVID-19 infection.
May 26, 2022
CDC updates the “COVID-19 Community Level,” showing that 71.52% of the U.S. population is in a location with low COVID-19 community transmission levels; 20.73% have medium levels and 7.76% have high COVID-19 community levels.
May 27, 2022
North Korea reports a total of 3.27 million “fever patients.”
May 28, 2022
The weekly average of new COVID-19 infections in the U.S. is now six times higher than it was in 2021. Currently, there are 119,725 new cases reported each week– a number that is “grossly underreported” according to experts– compared to May 28, 2021, when there were 17,887.
May 31, 2022
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) asks a federal appeals court to overturn the order that declared CDC’s mandate requiring individuals to wear masks on public transportation unlawful.
Authorities in Shanghai announce that they are partially reopening China’s largest city after two months of a COVID-19 lockdown that has kept millions of people strictly in their homes and employed both mass testing and isolation of anyone infected with COVID-19 in centralized facilities.
June 1, 2022
The U.S. has recorded a total of 84,145,569 COVID-19 infections and 1,003,571 (more than 1 million) deaths from COVID-19.
June 2, 2022
A Kaiser Foundation study tested three widespread false statements about COVID-19 vaccines: “pregnant women should not get the COVID-19 vaccine; it is unsafe for women who are breastfeeding to get a COVID-19 vaccine; and the COVID-19 vaccines have been shown to cause infertility.” Vaccine misinformation is so pervasive that about six in ten U.S. adults and seven in ten women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant either believed or were unsure about at least one of these false statements.
June 10, 2022
The global market for N95 masks is predicted to reach $11.8 billion by 2026.
June 18, 2022
ACIP recommends Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccines for everyone ages 6 months – 5 years, expanding vaccine eligibility to over 20 million additional children in the U.S. All people ages 6 months and older are now eligible for COVID-19 vaccination in the U.S.
June 24, 2022
ACIP recommends Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine for everyone ages 6–17 years.
June 30, 2022
As COVID-19 case numbers rise across the U.S. due to the highly transmissible omicron subvariants BA.4 and BA.5., FDA calls for Omicron-specific updates to COVID-19 vaccine boosters from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna in fall 2022.
July 6, 2022
CDC data shows that Omicron subvariants BA.4 and BA.5 are now dominant in the U.S., making up over 70% of new COVID-19 infections.
July 8, 2022
New York Department of Health recommends that all people should wear N95, KN95, or KF94 masks in all public indoor settings and when in crowded outdoor areas due to high community transmission of COVID-19.
FDA fully approves Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine for everyone ages 12–15 years. Full FDA approval further reinforces that Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine has been shown to meet the agency’s high standards for safety, effectiveness, and consistent quality in manufacturing.