Key points
Data sources
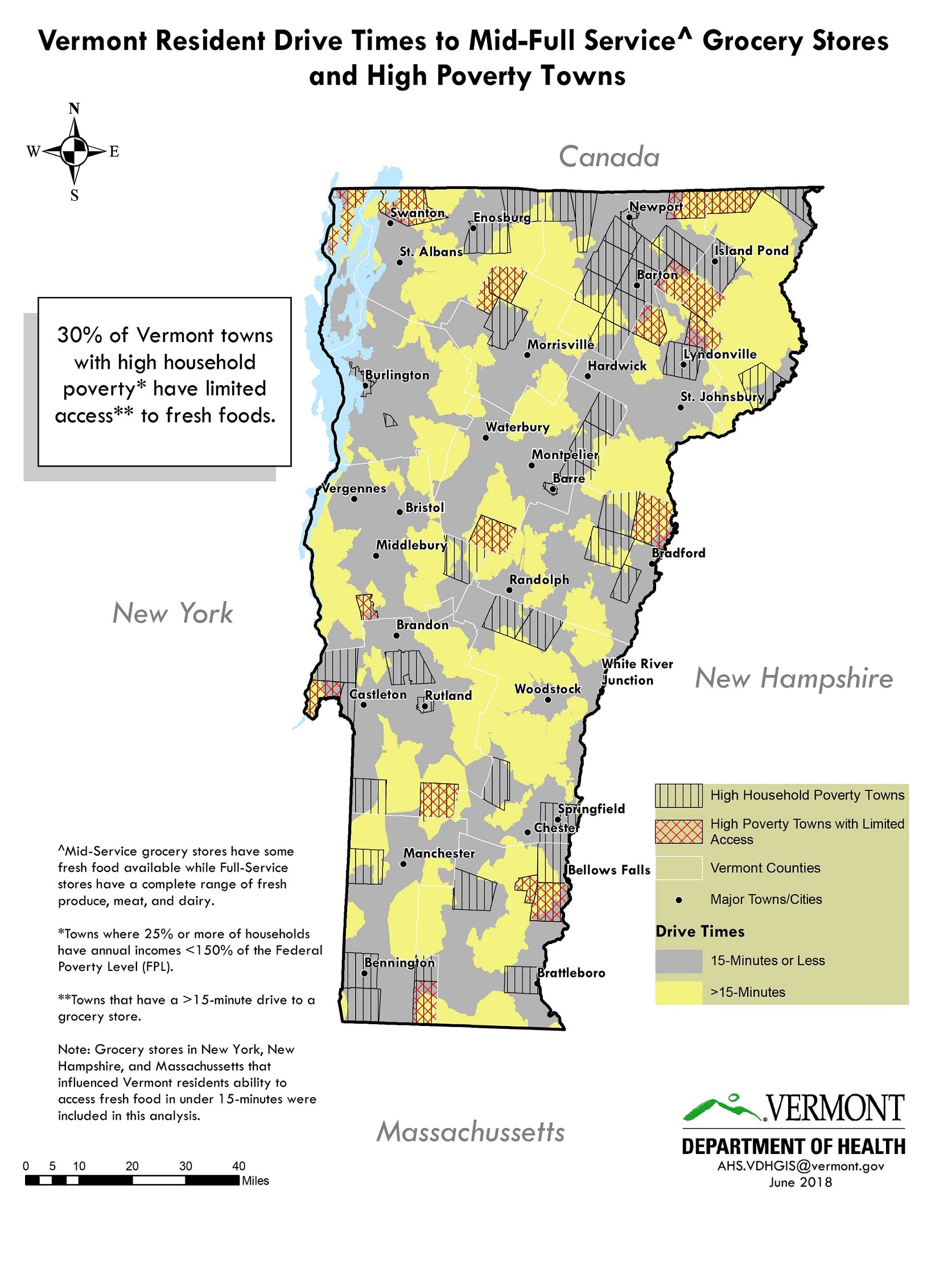
A number of pockets of greater than 15-minute drive times to grocery stores were identified around the state. About 30% of Vermont towns with high town household poverty had limited access to grocery stores with the largest concentration in the northeast. The views and opinions expressed here are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Vermont Department of Health.
ArcMap 10.5
List of grocery stores, addresses, and foods sold assembled by VDH staff. Poverty data from the American Community Survey (ACS), 2015 5-year estimates.
Grocery stores were classified as mid-service stores if they sold at least some fresh, canned, or frozen healthy food (produce, meats, or dairy). Full-service stores sold the full range fresh, canned, or frozen produce, meat, and dairy, that would be expected to be found in a typical grocery store. Stores, addresses and products sold were determined by staff that had previously surveyed the stores. Grocery stores were geolocated using VDH’s self-designed address locater tool. Drive times were determined by using the ArcMap Network Analyst tool by selecting an impedance of ‘time (minutes)’ with a break at 15-minutes and directionality ‘towards’ the facility, and using ‘hierarchy.’ All Vermont grocery stores plus stores in New York, New Hampshire, and Massachusetts that were within 20-miles of Vermont’s borders were included. Poverty level was established by creating a proportion using the total town population and town population estimated to be living in households below 150% of the Federal Poverty Level (FPL). Towns with 25% or more households below 150% of the FPL were defined as ‘high household poverty towns.’ Limited access was defined as a greater than 15-minute drive time to a grocery store. High poverty and limited grocery store access towns were identified by conducting a spatial selection based on features from the poverty layer and drive time layers where 25% of the town was living in households with annual household incomes < 150% of the FPL AND more than a 15-minutes drive to a grocery store, this selection was used to create the unique layer of High Poverty Towns with Limited Access.
This map is being used as a programmatic communications tool to discuss food insecurity and has been presented at a statewide hunger conference. It is also being used to highlight the important role of nutrition in chronic disease prevention and management.
Paul Meddaugh, Public Health Analyst, Vermont Department of Health
802-951-0133
paul.meddaugh@vermont.gov
Paul Meddaugh, Vermont Department of Health. Accessed from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Chronic Disease Map Gallery.