Key points
Map
Data sources
Major Findings
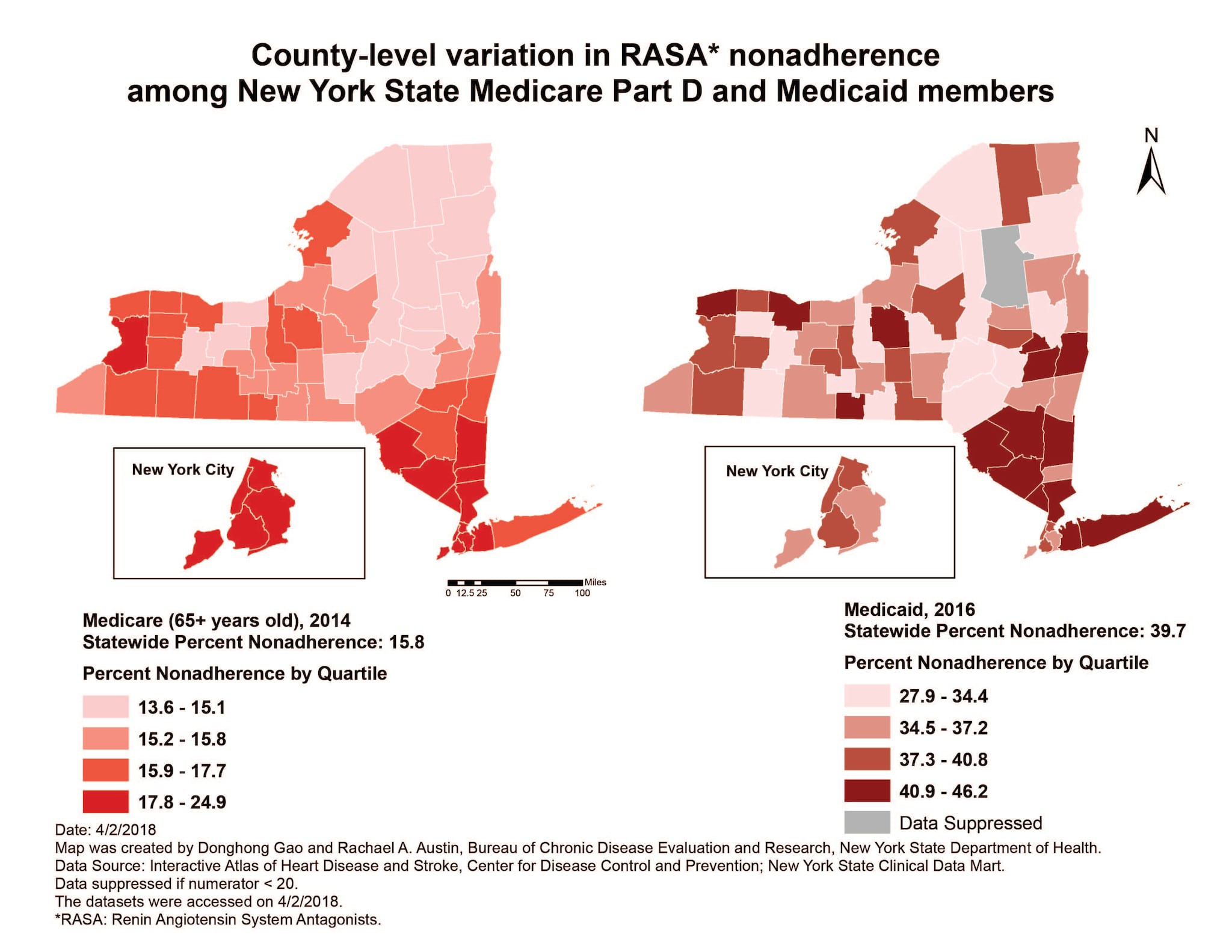
Larger population centers across the state experience a higher burden of non-adherence, except for NYC. The burden of nonadherence is significantly greater among Medicaid members compared to Medicare members. The prevalence of RASA medication nonadherence is higher among Medicaid members compared to the Medicare Part D beneficiaries. Among NYS Medicaid members, the prevalence of RASA medication nonadherence by county ranged from a low of 27.9% in Lewis county to a high of 46.2% in Schenectady county. Among Medicare Part D beneficiaries, the prevalence of RASA medication nonadherence by county ranged from a low of 13.6% in Ontario county to a high of 24.9% in Kings county. The pattern of RASA nonadherence was similar among Medicare and Medicaid members, except for New York City (NYC).
The views and opinions expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the New York State Department of Health. Examples of Analysis performed within this publication are only examples. They should not be utilized in real-world analytic products.
How the map will be used, or has been used
Findings have been shared with NYS Department of Health program staff working on hypertension initiatives, including the Office of Quality and Patient Safety and the Division of Chronic Disease Prevention. This map has been used to help allocate resources to areas with a high burden of medication non-adherence.
ArcGIS 10.4 ESRI
Medicare Part D claims data for 2014 obtained through the Interactive Atlas of Heart Disease and Stroke, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Medicaid data for 2016 obtained through New York State (NYS) Medicaid Clinical Data Mart.
RASA medication nonadherence was defined as the proportion of days a Medicaid or Medicare member was covered with an RASA blood pressure medication of <80%. The prevalence and count of RASA nonadherence was mapped using the quantile classification.
Donghong Gao, Research Scientist, New York State Department of Health
518-473-0459
donghong.gao@health.ny.gov
Donghong Gao, New York State Department of Health; Rachael A. Austin, New York State Department of Health. Accessed from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Chronic Disease Map Gallery.
