Key points
Data sources
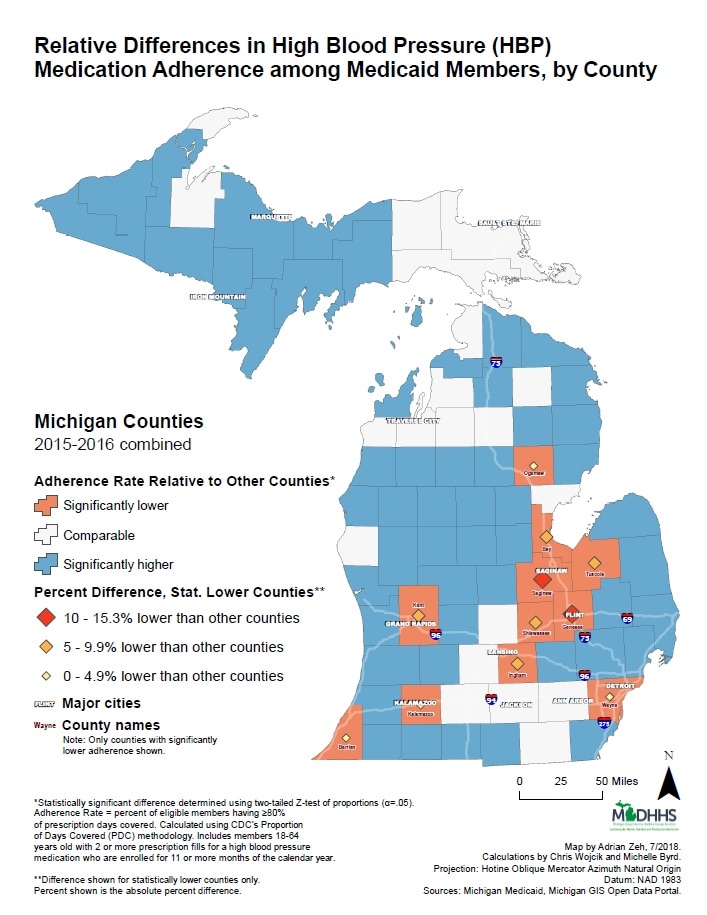
This map identifies counties that have statistically lower adherence to blood pressure medications in the Medicaid population, as well as the magnitude of the difference.
While also taking into consideration the average number of Medicaid members in each county (shown in the prior map), results will be used to prioritize the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services’ efforts to improve high blood pressure medication adherence.
ArcGIS, Excel, and SAS/SPSS
Michigan Medicaid Claims data; Michigan Open GIS data portal
Proportion of Days Covered calculations for each county; tests of statistical difference of county-level rates for each county relative to all other counties.
Adrian Zeh, Evaluation Specialist, Michigan Department of Health and Human Services
517-335-8771
zeha@michigan.gov
Adrian Zeh, Michigan Department of Health and Human Services. Accessed from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Chronic Disease Map Gallery.