Who We Are: Global Immunization Division (GID)
Updated November 21, 2023
Vision
CDC’s Global Immunization Division (GID) is a leading partner in U.S. government global immunization efforts to secure a healthier and safer world. GID is guided by a vision of a world with healthy people protected from vaccine-preventable diseases (VPD), disabilities, and death.
We provide scientific and programmatic leadership to end VPD threats around the world.
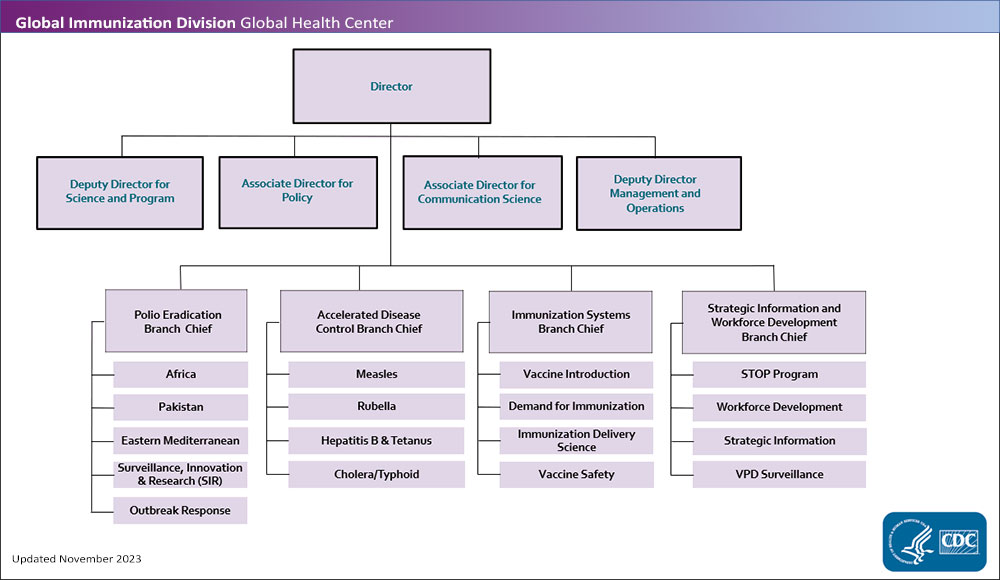
Branch Descriptions
- The Polio Eradication Branch (PEB): Works with global partners to achieve polio eradication by providing technical leadership within the Global Polio Eradication Initiative on programmatic activities around the world. This work includes improving surveillance, data analysis, research, vaccination campaigns, and outbreak preparedness and response. PEB’s work prioritizes disrupting wild poliovirus transmission in the two remaining, polio-endemic countries (Afghanistan and Pakistan); stopping outbreaks of non-wild polioviruses by improving and maintaining high vaccination coverage rates; and strengthening immunization systems to help countries remain polio-free, as well as better prepared to prevent, detect, and respond to vaccine-preventable and emerging disease threats.
- The Accelerated Disease Control Branch (ADCB): Works with countries and global partners to prevent, detect, and respond to vaccine-preventable diseases with control and elimination goals, including cholera, hepatitis b, measles, rubella, tetanus, and typhoid fever. The branch provides expertise and support to improve programmatic activities and strategies, collaborate on analyses to inform decision-making, and assist in surveillance efforts for diseases prevented by existing, new, or underutilized vaccines. In partnership with the Measles and Rubella Initiative, the branch leads activities to eliminate measles and rubella by providing expertise to introduce measles and rubella-containing vaccines into national immunization programs, improve vaccination coverage rates, strengthen laboratory capacity and laboratory networks, and build outbreak preparedness and response capacity to help achieve and sustain regional elimination targets.
- The Immunization Systems Branch (ISB): Works to identify evidence-based solutions to strengthen immunization systems and inform the development, introduction, delivery of, and demand for safe and effective vaccines that meet population needs across the life-course. The branch provides expertise and support to countries and global partners to strengthen global guidance and national vaccine policies, identify strategies to increase demand for vaccines, and promote the introduction and implementation of vaccines to protect at-risk populations. The branch also leads efforts on Infodemic management, which aims to mitigate mis and dis-information in digital and physical environments.
- The Strategic Information and Workforce Development Branch (SIWDB): Helps strengthen delivery of immunization services in high-burden countries by supporting vaccine-preventable disease surveillance, immunization data and information systems, and improving the performance of the immunization workforce. SIWDB identifies evidence-based interventions that support immunization programs in these technical areas. SIWDB works with global partners to recruit, train, and deploy public health professionals to support national ministries of health, strengthen routine immunization services, and improve capacity for preventing, detecting, and responding to outbreaks.
Strategic Framework 2021–2030
The CDC Global Immunization Strategic Framework 2021–2030 (CDC GISF 2021–2030) guides CDC’s investments in building global immunization program capacity and scientific expertise to advance the control, elimination, and eradication of vaccine-preventable diseases over the next ten years.