What CDC is Doing About Global Tetanus
Updated March 28, 2022
CDC works with partners to support the achievement and maintenance of maternal and neonatal tetanus elimination (MNTE) and prevent tetanus throughout the lifespan. In 1989, the World Health Assembly endorsed the elimination of neonatal tetanus, and in 1999, the initiative was relaunched and renamed the Maternal and Neonatal Tetanus Elimination initiative.external icon CDC has been supporting the MNTE initiative for over 20 years.
Support Maternal and Neonatal Tetanus Elimination Goals

- Participate in review of data and field missions to validate the achievement of MNTE
- Work with partners and expert workgroups to determine the best approach to validating MNTE in the remaining 12 countries, especially in hard-to-reach areas
- Improve coverage with tetanus vaccine among pregnant women by educating healthcare workers and pregnant women on the importance of tetanus vaccination and linking pregnant women to antenatal (prenatal) care services
Maintain Maternal and Neonatal Tetanus Elimination in Countries and Prevent Tetanus With Vaccination Throughout the Lifespan
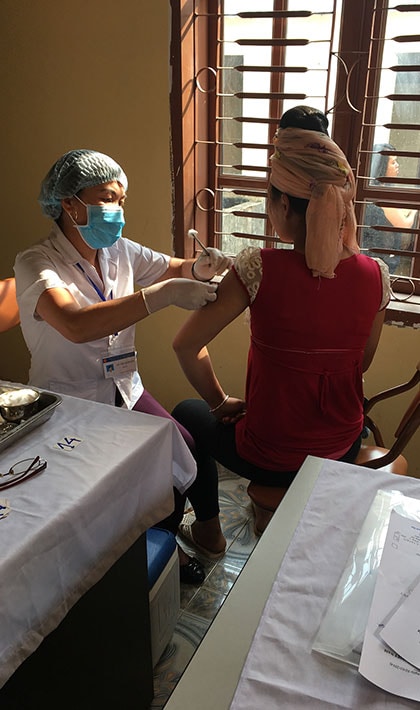
- CDC works with partners to develop global and regional guidanceexternal icon on sustaining MNTE in countries and preventing tetanus with vaccination throughout the lifespan
- Support assessments and serological surveys among women of childbearing age, to evaluate maintenance of MNTE
- Document immunity gaps in older children and adults to inform decision makers about the need to introduce tetanus booster doses for lifelong protection against tetanus
- Participate in the assessment of cost, impact, and cost-effectiveness of sustaining MNTE
- Evaluate immune responses in children and adult men after tetanus booster doses to inform vaccination schedule with tetanus booster doses
- Support the introduction of tetanus vaccine booster doses, strengthening national immunization systems, and offering tetanus protection across the lifespan
- Support the development and pilot of a mathematical model to estimate the health and economic benefits of adding booster doses of tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine (TTCV)
Improving Tetanus Surveillance

- Support the development of global surveillance standardsexternal icon for neonatal and non-neonatal tetanus
- Strengthen neonatal tetanus surveillance to detect and respond to potential cases and have accurate data to validate elimination of maternal and neonatal tetanus
- Conduct assessments of tetanus surveillance and provide evidence of the need to introduce tetanus vaccine booster doses to inform decision makers and national immunization systems
- Validate new testing methods that are more efficient at measuring tetanus immunityexternal icon in field surveys
Read our Stories on tetanus.
Page last reviewed: March 22, 2022
Content source: Global Immunization