Key points
- The five main types of gynecologic cancer are: cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, and vulvar.
- There are several ways to treat gynecologic cancer. The treatment depends on the type of cancer and how far it has spread.

What it is
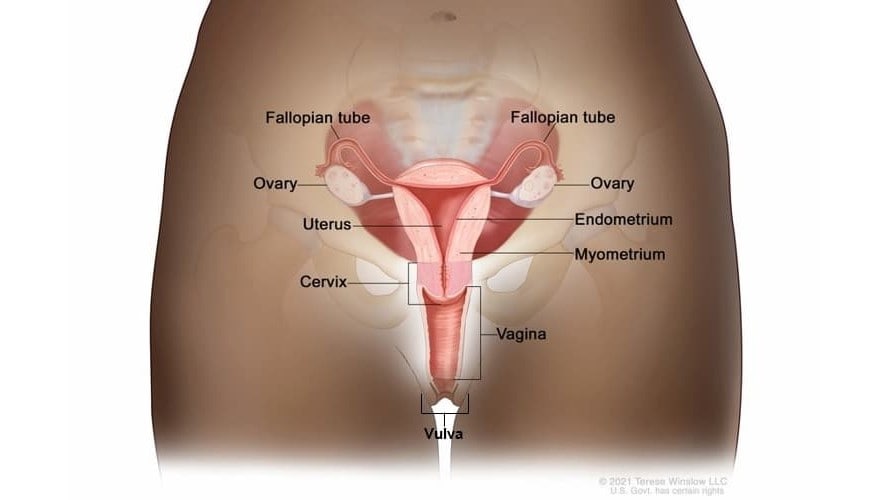
Gynecologic cancer is a disease in which cells in a woman's reproductive organs grow out of control. The five main types of gynecologic cancer are: cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, and vulvar. (A sixth type of gynecologic cancer is the very rare fallopian tube cancer.)
© 2021 Terese Winslow LLC. US government has certain rights. Used with permission. Contact artist at www.teresewinslow.com for licensing.
Types
- Cervical cancer begins in the cervix, which is the lower, narrow end of the uterus. (The uterus is also called the womb.)
- Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries, which are located on each side of the uterus. Some ovarian cancers can also begin in the fallopian tubes or peritoneum.
- Uterine cancer begins in the uterus, the pear-shaped organ in a woman's pelvis where the baby grows when she is pregnant.
- Vaginal cancer begins in the vagina, which is the hollow, tube-like channel between the bottom of the uterus and the outside of the body.
- Vulvar cancer begins in the vulva, the outer part of the female genital organs.
Each gynecologic cancer is unique, with different signs and symptoms, different risk factors (things that may increase your chance of getting a disease), and different prevention strategies.
Knowledge Is Power: Gynecologic Cancer Symptoms
This short animated video encourages women to learn the symptoms of gynecologic cancers.
