At a glance
- Germicidal ultraviolet (GUV), otherwise known as ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI), is the use of ultraviolet (UV) energy to kill viral, bacterial, and fungal organisms in the workplace.
- GUV is best used as part of a layered approach to reducing exposures to airborne pathogens, along with other strategies such as ventilation systems.
- GUV is best used in group settings such an open concept office buildings or schools.
Overview
GUV is the use of UV energy to kill viral, bacterial, and fungal organisms and is typically used in residential, commercial, educational, and healthcare settings.
When designed and installed correctly, the technology uses UV energy to inactivate (kill) microorganisms, including viruses. GUV is a supplemental form of ventilation intervention and does not replace code requirements for outdoor air delivery or filtration.
Ventilation interventions can help reduce the number of infectious viral particles (e.g., SARS-CoV-2) in the air. Ventilation interventions include
- opening windows
- using fans
- adding high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) fan/filter systems
- adding upper-room GUV
This page has information on upper-room GUV.
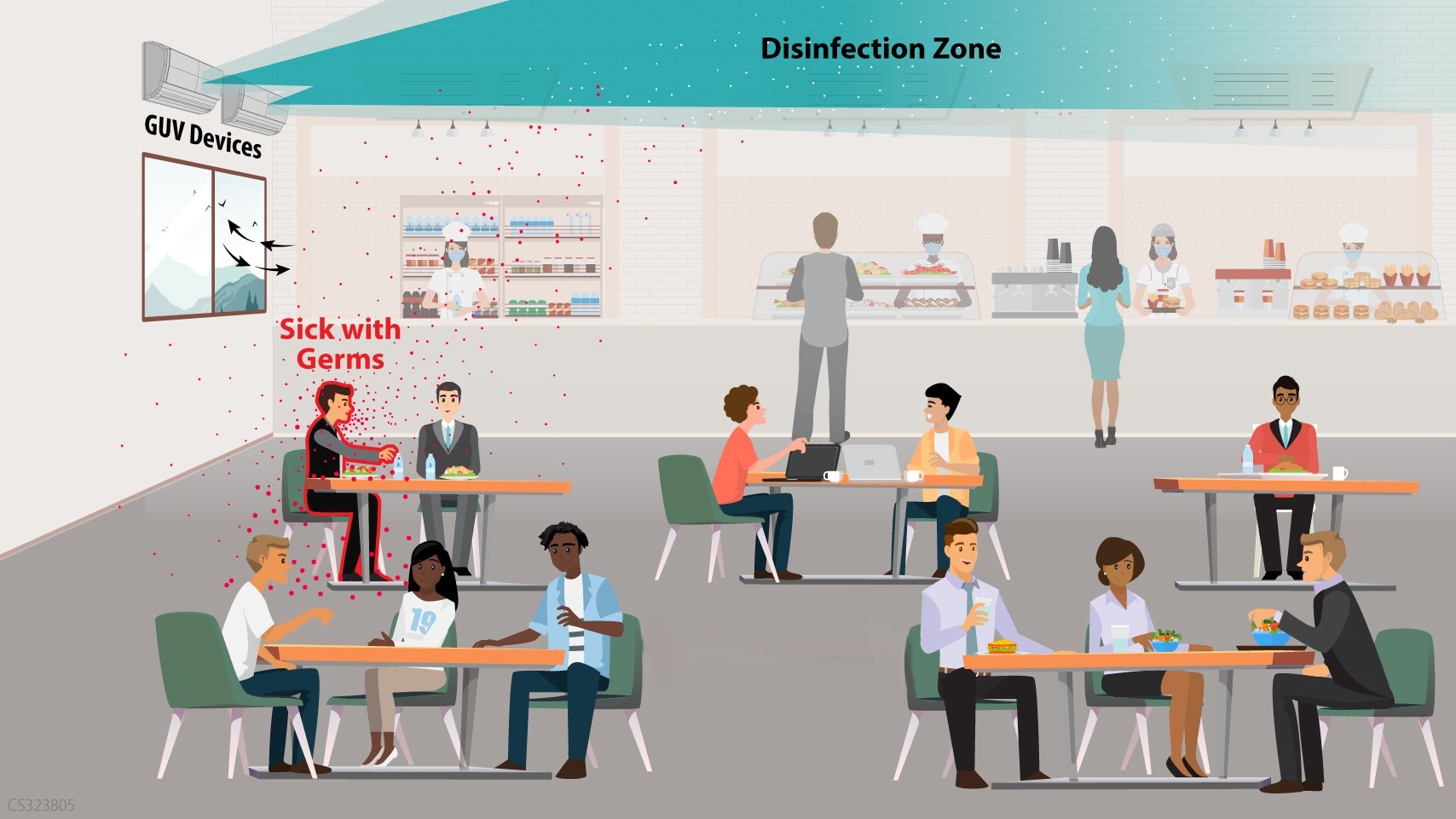
Upper-room GUV
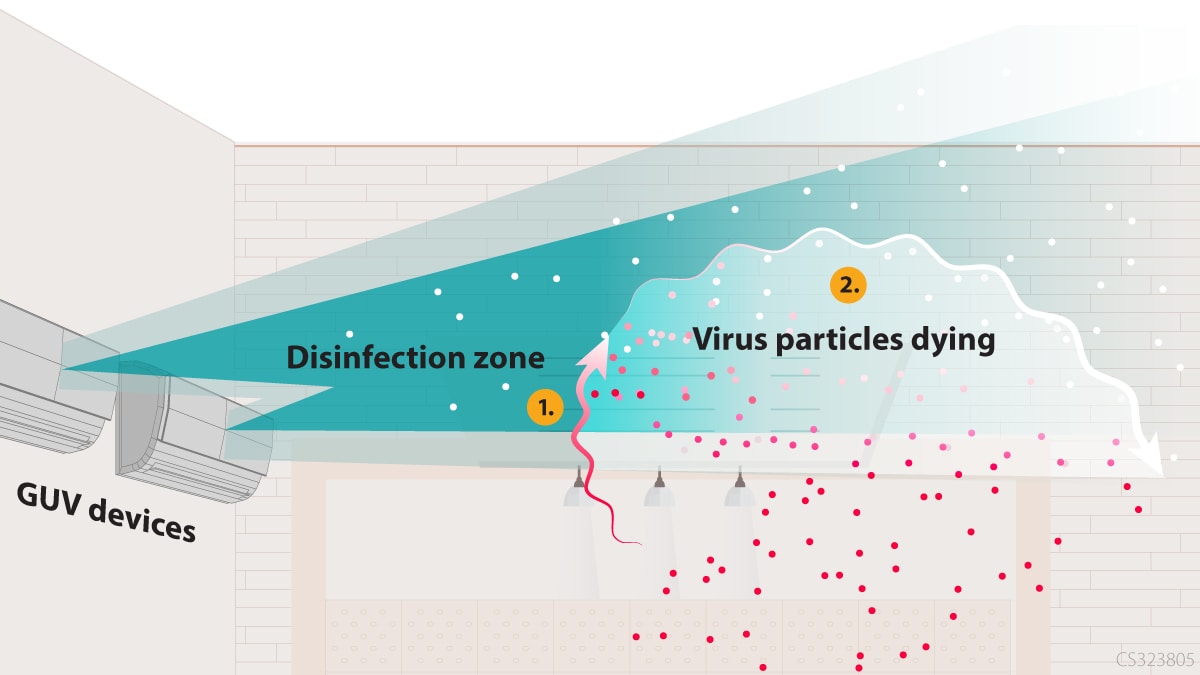
How it works:
- Air passes through the disinfection zone from air flow through HVAC system, fans, and/or open windows.
- The airborne viral particles are killed once they receive an appropriate amount of UV energy. The particles remain in the air, but they are no longer infectious.
Note: For airborne viral particles, upper-room GUV systems provide air changes per hour that are similar to the introduction of clean air into the space.
Considerations for use
- The most important locations for GUV are high-risk indoor settings. These include:
- Areas with an increased likelihood of sick people (for example, school nurse's office, hospital waiting room).
- Crowded spaces, particularly when the health status of occupants is unknown (for example, courtrooms, lobbies, homeless shelter sleeping areas).
- Areas with an increased likelihood of sick people (for example, school nurse's office, hospital waiting room).
- GUV is especially recommended in spaces with insufficient or no mechanical HVAC systems or where adequate natural ventilation cannot be maintained year-round. Spaces must be at least 8 feet tall, but a minimum ceiling height of 8.5 feet is preferred, with some airflow to move air (for example, fans at low speed). Upper-room GUV is not necessary in open-air environments, such as outdoor open-air seating areas.
- If the HVAC system allows for efficient filtration or provides outdoor air flow above minimum code requirements, it will remove most airborne virus particles and upper-room GUV would not add as much benefit.
Installation and maintenance
- Upper-room GUV systems are generally custom designed for the space in which they will be used. Systems should be designed, installed, and tested with the help of a qualified HVAC professional or a reputable UV-system manufacturer. These professionals have the tools and experience to provide an effective and safe system, including proper installation and positioning of the fixtures, code-compliant electrical connections, and training on proper use.
- A typical room with 500 square feet (ft2) of floor space will generally require two to three UV fixtures. The cost to install the system in a 500 ft2 space is approximately $1,500 to $2,500.
- Once installed, the systems require little maintenance. The lamps will need to be replaced once per year, although some manufacturers offer lamps with 2-year replacement schedules. If the lamps become covered with dust, they can be cleaned when the unit is turned off by wiping with rubbing alcohol.
- Any time maintenance on the lamps is required or workers need to access areas near the ceiling (for example, maintaining lighting fixtures, testing smoke detectors), the UV fixtures should be powered off. Maintenance workers should receive special training before working on GUV systems.
Implementation
Considerations for implementation include the following:
- Upper-room GUV systems have been used safely and effectively for decades. However, UV energy directed or reflected into the occupied space has the potential to cause temporary eye or skin damage. Assistance from a qualified HVAC professional or a reputable UV system manufacturer will ensure the system is installed properly so UV energy is directed above occupied space and operates safely.
- The systems should be connected to designated electrical switches with limited access to the public and staff or volunteers not trained in managing the system. For example, consider using lockable switches or placing switches in a restricted area that only trained staff can access using a lock and key. This prevents the UV lamps from being turned on or off unintentionally and allows the fixtures to be safely powered off, when necessary, without fear of them being powered on during maintenance.
- Influenza viruses are more susceptible to UV energy than the bacteria that causes TB. Thus, any upper-room GUV systems designed with sufficient radiance to inactivate TB will also be effective against seasonal flu, SARS-COV-2, and many other respiratory viruses if it is properly maintained.1
- UV-C energy can damage plants placed in the disinfection zone (for example, on the top of tall bookcases or high shelves). The energy can also cause fading and cosmetic blemishes to wood surfaces and wallpapers (most wall and ceiling paints are not affected). Thus, care should be taken when installing upper-room GUV systems in spaces with ornate architectural elements and plants.
Recommendations
Selecting an upper-room GUV system
- Care should be taken when using GUV in areas where people could gain access to the GUV unit's disinfection zone near the ceiling (for example, overhead storage, bunkbeds). This includes reviewing safety precautions, placing warning stickers where GUV is located, and having trained staff familiar with the product.
- CDC does not provide recommendations for, or against, any manufacturer or product. Consult with a reputable GUV professional (a GUV fixture manufacturer or an experienced GUV system designer) who is familiar with NIOSH upper-room GUV guidelines, to design and install the system. Consumers are encouraged to ask professionals for information on previous system installations, testing to ensure safety for room occupants, and training provided with the system. Do not hire a contractor who provides unsubstantiated claims or limited support throughout the design, installation, and operation phase. When hiring an expert:
- Ask for proof of Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) registration and for a portfolio of GUV installation projects. The facility that manufactures the UV device that is hung on the wall or suspended from the ceiling should be registered with EPA and the manufacturer should have a significant portfolio of GUV installation projects, preferably some within medium and larger healthcare facilities.
- Consider asking about any professional associations the GUV manufacturer/system designer may be involved with such as the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers and if so, in what capacity are they involved.
- Consider asking about performance guarantees that the manufacturer or professional may provide, and whether they offer ongoing maintenance or training programs for users of their products.
- Ask for proof of Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) registration and for a portfolio of GUV installation projects. The facility that manufactures the UV device that is hung on the wall or suspended from the ceiling should be registered with EPA and the manufacturer should have a significant portfolio of GUV installation projects, preferably some within medium and larger healthcare facilities.
What's being done
Upper-room GUV has been used for over 70 years to eliminate airborne pathogens. Since 1950, the bulk of the research on upper-room GUV systems focused on controlling the spread of tuberculosis. Current guidance [6 MB, 87 pages] from CDC and NIOSH on the design, installation, testing, and safe operation of upper-room GUV systems is based on science and practice-based evidence to control tuberculosis.
