Comparative Effectiveness of Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) Vaccines in Preventing COVID-19 Hospitalizations Among Adults Without Immunocompromising Conditions — United States, March–August 2021
Weekly / September 24, 2021 / 70(38);1337–1343
On September 17, 2021, this report was posted online as an MMWR Early Release.
Wesley H. Self, MD1,*; Mark W. Tenforde, MD, PhD2,*; Jillian P. Rhoads, PhD1,*; Manjusha Gaglani, MBBS3,4; Adit A. Ginde, MD5; David J. Douin, MD5; Samantha M. Olson, MPH2; H. Keipp Talbot, MD1; Jonathan D. Casey, MD1; Nicholas M. Mohr, MD6; Anne Zepeski, PharmD6; Tresa McNeal, MD3,4; Shekhar Ghamande, MD3,4; Kevin W. Gibbs, MD7; D. Clark Files, MD7; David N. Hager, MD, PhD8; Arber Shehu, MD8; Matthew E. Prekker, MD9; Heidi L. Erickson, MD9; Michelle N. Gong, MD10; Amira Mohamed, MD10; Daniel J. Henning, MD11; Jay S. Steingrub, MD12; Ithan D. Peltan, MD13; Samuel M. Brown, MD13; Emily T. Martin, PhD14; Arnold S. Monto, MD14; Akram Khan, MD15; Catherine L. Hough, MD15; Laurence W. Busse, MD16; Caitlin C. ten Lohuis16; Abhijit Duggal, MD17; Jennifer G. Wilson, MD18; Alexandra June Gordon, MD18; Nida Qadir, MD19; Steven Y. Chang, MD, PhD19; Christopher Mallow, MD20; Carolina Rivas20; Hilary M. Babcock, MD21; Jennie H. Kwon, DO21; Matthew C. Exline, MD22; Natasha Halasa, MD1; James D. Chappell, MD, PhD1; Adam S. Lauring, MD, PhD23; Carlos G. Grijalva, MD1; Todd W. Rice, MD1; Ian D. Jones, MD1; William B. Stubblefield, MD1; Adrienne Baughman1; Kelsey N. Womack, PhD1; Christopher J. Lindsell, PhD1; Kimberly W. Hart, MA1; Yuwei Zhu, MD1; Lisa Mills, PhD2; Sandra N. Lester, PhD2; Megan M. Stumpf2; Eric A. Naioti, MPH2; Miwako Kobayashi, MD2; Jennifer R. Verani, MD2; Natalie J. Thornburg, PhD2,*; Manish M. Patel, MD2,*; IVY Network (View author affiliations)
View suggested citationSummary
What is already known about this topic?
Two 2-dose mRNA COVID-19 vaccines (from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) and a 1-dose viral vector vaccine (from Janssen [Johnson & Johnson]) are currently used in the United States.
What is added by this report?
Among U.S. adults without immunocompromising conditions, vaccine effectiveness against COVID-19 hospitalization during March 11–August 15, 2021, was higher for the Moderna vaccine (93%) than the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (88%) and the Janssen vaccine (71%).
What are the implications for public health practice?
Although these real-world data suggest some variation in levels of protection by vaccine, all FDA-approved or authorized COVID-19 vaccines provide substantial protection against COVID-19 hospitalization.
Three COVID-19 vaccines are authorized or approved for use among adults in the United States (1,2). Two 2-dose mRNA vaccines, mRNA-1273 from Moderna and BNT162b2 from Pfizer-BioNTech, received Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 2020 for persons aged ≥18 years and aged ≥16 years, respectively. A 1-dose viral vector vaccine (Ad26.COV2 from Janssen [Johnson & Johnson]) received EUA in February 2021 for persons aged ≥18 years (3). The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine received FDA approval for persons aged ≥16 years on August 23, 2021 (4). Current guidelines from FDA and CDC recommend vaccination of eligible persons with one of these three products, without preference for any specific vaccine (4,5). To assess vaccine effectiveness (VE) of these three products in preventing COVID-19 hospitalization, CDC and collaborators conducted a case-control analysis among 3,689 adults aged ≥18 years who were hospitalized at 21 U.S. hospitals across 18 states during March 11–August 15, 2021. An additional analysis compared serum antibody levels (anti-spike immunoglobulin G [IgG] and anti–receptor binding domain [RBD] IgG) to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, among 100 healthy volunteers enrolled at three hospitals 2–6 weeks after full vaccination with the Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, or Janssen COVID-19 vaccine. Patients with immunocompromising conditions were excluded. VE against COVID-19 hospitalizations was higher for the Moderna vaccine (93%; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 91%–95%) than for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (88%; 95% CI = 85%–91%) (p = 0.011); VE for both mRNA vaccines was higher than that for the Janssen vaccine (71%; 95% CI = 56%–81%) (all p<0.001). Protection for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine declined 4 months after vaccination. Postvaccination anti-spike IgG and anti-RBD IgG levels were significantly lower in persons vaccinated with the Janssen vaccine than the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines. Although these real-world data suggest some variation in levels of protection by vaccine, all FDA-approved or authorized COVID-19 vaccines provide substantial protection against COVID-19 hospitalization.
For the VE analysis, adults aged ≥18 years without an immunocompromising condition admitted to 21 hospitals within the Influenza and Other Viruses in the Acutely Ill (IVY) Network were prospectively recruited for a case-control analysis (6,7). Case-patients were admitted to a hospital with COVID-19–like illness† and a positive SARS-CoV-2 reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or antigen test result. Control-patients were adults admitted to a hospital§ who received a negative SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR test result.
Patients or their proxies were interviewed to obtain information about demographic characteristics, clinical history, and COVID-19 vaccination.¶ Information regarding vaccine product received by patients was collected by interview and source verification (e.g., state vaccination registries, hospital electronic medical records, and pharmacy records), including vaccine lot numbers, when these were documented. A patient was considered fully vaccinated if the final vaccine dose (second dose for Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech and the single Janssen dose) was received ≥14 days before illness onset.** Patients were excluded if they received a COVID-19 vaccine other than Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, or Janssen; received ≥1 vaccine dose but did not meet criteria for full vaccination; or received doses of two different COVID-19 vaccine products.
For the postvaccination antibody analysis, healthy adults aged ≥18 years with no known prior SARS-CoV-2 infection were recruited during April 6–June 4, 2021, at three IVY sites. Blood was collected 2–6 weeks after receipt of the second Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine dose or the single Janssen vaccine dose. Sera were shipped to CDC, where they underwent testing for IgG against three SARS-CoV-2 antigens: the spike protein (anti-spike); the spike RBD (anti-RBD); and nucleocapsid (anti-nucleocapsid). IgG levels were measured using the V-PLEX SARS-CoV-2 panel 2 kit (Meso Scale Diagnostics) and reported in international binding antibody units (BAU) per milliliter. Two participants with anti-nucleocapsid antibodies (>11.8 BAU), which is suggestive of a prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, were excluded.
VE against COVID-19 hospitalization was estimated using logistic regression, comparing the odds of being fully vaccinated versus unvaccinated between case-patients and controls using the equation VE = 100 × (1 – adjusted odds ratio) (6,7). The regression model included an indicator variable for vaccine type (Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, or Janssen) and was adjusted for admission date, geographic region, age, sex, and race and Hispanic ethnicity. A separate model added an interaction term between product type and time since vaccination. Using these models, VE for mRNA vaccine products was estimated for the full surveillance period (March 11–August 15), as well as 14–120 days and >120 days after the receipt of the second dose. Because a limited number of patients received Janssen vaccine >120 days before illness onset (19 total), VE for the Janssen vaccine was not stratified by time. In addition to a VE estimate defining full vaccination as 14 days after a Janssen vaccine dose, a sensitivity analysis was conducted defining full vaccination as 28 days after a Janssen vaccine dose. Statistical differences by vaccine product and time were assessed based on p-values generated using the Tukey method for pair-wise multiple comparisons.
In the postvaccination antibody analysis, pairwise comparisons of the quantity of anti-spike IgG and anti-RBD IgG were made among participants, by vaccine product received, using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Analyses were conducted using R statistical software (version 4.0.3; R Foundation) and STATA (version 16; StataCorp). Procedures were approved as public health surveillance by each participating site and CDC†† and were conducted consistent with applicable federal law and CDC policy.§§
After excluding 1,786 patients from the VE analysis (936 for having an immunocompromising condition,¶¶ 566 who received ≥1 vaccine dose but were not fully vaccinated, and 284 who did not meet other eligibility criteria), 3,689 patients were included (1,682 case-patients and 2,007 control-patients). Overall, 2,362 (64.0%) patients were unvaccinated; 476 (12.9%) were fully vaccinated with the Moderna vaccine; 738 (20.0%) were fully vaccinated with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine; and 113 (3.1%) were fully vaccinated with the Janssen vaccine. Among all participants, median age was 58 years, 48% were female, 23% were non-Hispanic Black, and 18% were Hispanic (Table 1). VE against COVID-19 hospitalization during March 11–August 15, 2021, was higher for the Moderna vaccine (VE = 93%) than for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (VE = 88%) (p = 0.011); VE for both mRNA vaccines was higher than that for the Janssen vaccine (VE = 71%) (all p<0.001) (Table 2). VE for the Moderna vaccine was 93% at 14–120 days (median = 66 days) after receipt of the second vaccine dose and 92% at >120 days (median = 141 days) (p = 1.000). VE for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine was 91% at 14–120 days (median = 69 days) after receipt of the second vaccine dose but declined significantly to 77% at >120 days (median = 143 days) (p<0.001).
The postvaccination antibody analysis included 100 healthy volunteers, 32 fully vaccinated with Moderna (median age = 31 years; median interval from second vaccine dose to blood draw = 28 days), 51 fully vaccinated with Pfizer-BioNTech (median age = 27 years; median interval from second dose to blood draw = 27 days), and 17 fully vaccinated with Janssen (median age = 31 years; median interval from vaccine dose to blood draw = 35 days). Anti-RBD levels were higher in participants vaccinated with the Moderna vaccine (median = 4,333; interquartile range [IQR] = 3,134–7,197; geometric mean = 4,274; 95% CI = 3,393–5,384 BAU/mL) than in those who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (median = 3,217; IQR = 2,048–4,668; geometric mean = 2,950; 95% CI = 2,325–3,742 BAU/mL) (p = 0.033) or the Janssen vaccine (median = 57; IQR = 26–94; geometric mean = 51; 95% CI = 30–90 BAU/mL) (p<0.001) (Figure). Anti-spike IgG levels in participants vaccinated with the Moderna vaccine (median = 3,236; IQR = 2,125–4,975, geometric mean = 3,059; 95% CI = 2,479–3,774 BAU/mL) did not significantly differ from those in recipients of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine (median = 2,983; IQR = 1,954–4,059; geometric mean = 2,444; 95% CI = 1,936–3,085 BAU/mL) (p = 0.217), but were significantly higher than levels in participants who received the Janssen vaccine (median = 59; IQR = 30–104; geometric mean = 56; 95% CI = 32–97 BAU/mL) (p<0.001).
Discussion
Two-dose regimens of the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccines provided a high level of protection against COVID-19 hospitalizations in a real-world evaluation at 21 U.S. hospitals during March–August 2021. VE against COVID-19 hospitalization for Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines was 93% and 88%, respectively, whereas the single-dose Janssen vaccine had somewhat lower VE at 71%. Persons vaccinated with Janssen vaccine also had lower postvaccination anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels than did recipients of mRNA vaccines. Although an immunologic correlate of protection has not been established for COVID-19 vaccines, antibody titers after infection and vaccination have been associated with protection (8). These real-world data suggest that the 2-dose Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine regimens provide more protection than does the 1-dose Janssen viral vector vaccine regimen. Although the Janssen vaccine had lower observed VE, 1 dose of Janssen vaccine still reduced risk for COVID-19–associated hospitalization by 71%.
VE against COVID-19 hospitalization was slightly lower for the 2-dose Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine than the Moderna vaccine, with this difference driven by a decline in VE after 120 days for the Pfizer-BioNTech but not the Moderna vaccine. The Moderna vaccine also produced higher postvaccination anti-RBD antibody levels than did the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Differences in VE between the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine might be due to higher mRNA content in the Moderna vaccine, differences in timing between doses (3 weeks for Pfizer-BioNTech versus 4 weeks for Moderna), or possible differences between groups that received each vaccine that were not accounted for in the analysis (9).
The findings in this report are subject to at least six limitations. First, this analysis did not consider children, immunocompromised adults, or VE against COVID-19 that did not result in hospitalization. Second, the CIs for the Janssen VE estimates were wide because of the relatively small number of patients who received this vaccine. Third, follow-up time was limited to approximately 29 weeks since receipt of full vaccination, and further surveillance of VE over time is warranted. Fourth, although VE estimates were adjusted for relevant potential confounders, residual confounding is possible. Fifth, product-specific VE by variant, including against Delta variants (B.1.617.2 and AY sublineages), was not evaluated. Finally, antibody levels were measured at only a single time point 2–6 weeks after vaccination and changes in antibody response over time as well as cell-mediated immune responses were not assessed.
Two-dose series of the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccines provided high VE for the prevention of COVID-19 hospitalizations during March–August 2021. Protection for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine declined 4 months after vaccination. A single dose of the Janssen viral vector vaccine had comparatively lower anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody response and VE against COVID-19 hospitalizations. Understanding differences in VE by vaccine product can guide individual choices and policy recommendations regarding vaccine boosters. All FDA-approved or authorized COVID-19 vaccines provide substantial protection against COVID-19 hospitalization.
IVY Network
Nicole Calhoun, Baylor Scott & White Health; Kempapura Murthy, Baylor Scott & White Health; Judy Herrick, Baylor Scott & White Health; Amanda McKillop, Baylor Scott & White Health; Eric Hoffman, Baylor Scott & White Health; Martha Zayed, Baylor Scott & White Health; Michael Smith, Baylor Scott & White Health; Natalie Seattle, Baylor Scott & White Health; Jason Ettlinger, Baylor Scott & White Health; Elisa Priest, Baylor Scott & White Health; Jennifer Thomas, Baylor Scott & White Health; Alejandro Arroliga, Baylor Scott & White Health; Madhava Beeram, Baylor Scott & White Health; Ryan Kindle, Baystate Medical Center; Lori-Ann Kozikowski, Baystate Medical Center; Lesley De Souza, Baystate Medical Center; Scott Ouellette, Baystate Medical Center; Sherell Thornton-Thompson, Baystate Medical Center; Omar Mehkri, Cleveland Clinic; Kiran Ashok, Cleveland Clinic; Susan Gole, Cleveland Clinic; Alexander King, Cleveland Clinic; Bryan Poynter, Cleveland Clinic; Nicholas Stanley, Emory University; Audrey Hendrickson, Hennepin County Medical Center; Ellen Maruggi, Hennepin County Medical Center; Tyler Scharber, Hennepin County Medical Center; Jeffrey Jorgensen, Intermountain Medical Center; Robert Bowers, Intermountain Medical Center; Jennifer King, Intermountain Medical Center; Valerie Aston, Intermountain Medical Center; Brent Armbruster, Intermountain Medical Center; Richard E. Rothman, Johns Hopkins University; Rahul Nair, Montefiore Medical Center; Jen-Ting (Tina) Chen, Montefiore Medical Center; Sarah Karow, Ohio State University; Emily Robart, Ohio State University; Paulo Nunes Maldonado, Ohio State University; Maryiam Khan, Ohio State University; Preston So, Ohio State University; Joe Levitt, Stanford University; Cynthia Perez, Stanford University; Anita Visweswaran, Stanford University; Jonasel Roque, Stanford University; Adreanne Rivera, University of California; Los Angeles; Trevor Frankel, University of California; Los Angeles; Jennifer Goff, UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital; David Huynh, UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital; Michelle Howell, UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital; Jennifer Friedel, UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital; Michael Tozier, UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital; Conner Driver, UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital; Michael Carricato, UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital; Alexandra Foster, UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital; Paul Nassar, University of Iowa; Lori Stout, University of Iowa; Zita Sibenaller, University of Iowa; Alicia Walter, University of Iowa; Jasmine Mares, University of Iowa; Logan Olson, University of Iowa; Bradley Clinansmith, University of Iowa; Carolina Rivas, University of Miami; Hayley Gershengorn, University of Miami; EJ McSpadden, University of Michigan; Rachel Truscon, University of Michigan; Anne Kaniclides, University of Michigan; Lara Thomas, University of Michigan; Ramsay Bielak, University of Michigan; Weronika Damek Valvano, University of Michigan; Rebecca Fong, University of Michigan; William J. Fitzsimmons, University of Michigan; Christopher Blair, University of Michigan; Andrew L. Valesano, University of Michigan; Julie Gilbert, University of Michigan; Christine D. Crider, University of Washington; Kyle A. Steinbock, University of Washington; Thomas C. Paulson, University of Washington; Layla A. Anderson, University of Washington; Christy Kampe, Vanderbilt University Medical Center; Jakea Johnson, Vanderbilt University Medical Center; Rendie McHenry, Vanderbilt University Medical Center; Marcia Blair, Vanderbilt University Medical Center; Douglas Conway, Vanderbilt University Medical Center; Mary LaRose, Wake Forest University; Leigha Landreth, Wake Forest University; Madeline Hicks, Wake Forest University; Lisa Parks, Wake Forest University; Jahnavi Bongu, Washington University; David McDonald, Washington University; Candice Cass, Washington University; Sondra Seiler, Washington University; David Park, Washington University; Tiffany Hink, Washington University; Meghan Wallace, Washington University; Carey-Ann Burnham, Washington University; Olivia G. Arter, Washington University.
Corresponding author: Wesley H. Self, welsey.self@vumc.org.
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee; 2CDC COVID-19 Response Team; 3Baylor Scott & White Health, Temple, Texas; 4Texas A&M University College of Medicine, Temple, Texas; 5University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, Colorado; 6University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa; 7Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center, Winston-Salem, North Carolina; 8Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland; 9Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, Minnesota; 10Montefiore Healthcare Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York; 11University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, Washington; 12Baystate Medical Center, Springfield, Massachusetts; 13Intermountain Medical Center and University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah; 14University of Michigan School of Public Health, Ann Arbor, Michigan; 15Oregon Health & Science University Hospital, Portland, Oregon; 16Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia; 17Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio; 18Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California; 19Ronald Reagan-UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles, California; 20University of Miami, Miami, Florida; 21Washington University, St. Louis, Missouri; 22Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, Ohio; 23University of Michigan School of Medicine, Ann Arbor, Michigan.
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. Wesley H. Self reports grants and consultant fees from Merck and consultant fees from Aerpio Pharmaceuticals. Adit A. Ginde reports grant support from AbbVie and Faron Pharmaceuticals. Jonathan D. Casey reports a grant (N23HL153584) from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). D. Clark Files reports consultant fees from Cytovale and membership on a Medpace Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB). David N. Hager reports salary support from Incyte Corporation, EMPACT Precision Medicine, and the Marcus Foundation. Michelle N. Gong reports grant support from NIH and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and fees for participating on a DSMB for Regeneron and for participating on a scientific advisory panel for Philips Healthcare. Daniel J. Henning reports consulting fees from Cytovale and Opticyte. Ithan D. Peltan reports grants from NIH and Janssen Pharmaceuticals, institutional fees from Asahi Kasei Pharma and from Regeneron. Samuel M. Brown reports fees from Hamilton for chairing a DSMB, and institutional fees from Faron, Sedana, and Janssen; grants from Sedana, Janssen, NIH, and the Department of Defense (DoD); book royalties from Oxford University and Brigham Young University; and personal fees from New York University for service on a DSMB. Emily T. Martin reports personal fees from Pfizer for unrelated work and a grant from Merck for unrelated work. Akram Khan reports grants from United Therapeutics, Johnson & Johnson, 4D Medical, Lung LLC, and Reata Pharmaceuticals. Arnold S. Monto reports consulting fees from Sanofi-Pasteur and Seqirus. Steven Y. Chang was a speaker for La Jolla Pharmaceuticals and a Consultant for PureTech Health. Jennie H. Kwon reports grant support from NIH. Matthew C. Exline reports talks on nutrition in COVID pneumonia at APEN conference sponsored by Abbott Labs. Natasha Halasa reports grants from Sanofi and Quidel. James D. Chappell reports a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, NIH. Adam S. Lauring reports consultant fees from Sanofi and fees from Roche for membership on a trial steering committee. Carlos G. Grijalva reports consultant fees from Pfizer, Merck, and Sanofi-Pasteur and grants from Campbell Alliance/Syneos Health, NIH, the Food and Drug Administration, AHRQ, and Sanofi. Todd W. Rice reports personal fees from Cumberland Pharmaceuticals, Inc., as the Director of Medical Affairs, consultant fees from Avisa Pharma, LLC; and DSMB membership fees from Sanofi. Christopher J. Lindsell reports grants from NIH, DoD, and the Marcus Foundation; organizational contract fees from bioMerieux, Endpoint LLC, and Entegrion, Inc.; and a patent issued to Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center for risk stratification in sepsis and septic shock. No other potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
* These authors contributed equally to this report.
† COVID-19–like illness was defined as having one or more of the following: fever, cough, shortness of breath, loss of taste, loss of sense of smell, use of respiratory support for the acute illness, or new pulmonary findings on chest imaging consistent with pneumonia.
§ Control-patients included test-negative controls (persons with COVID-19–like illness who received negative SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR test results) and syndrome-negative controls (a second control group of persons without COVID-19–like illness who also received negative SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR test results). VE estimates stratified by control groups were highly similar and control groups were combined for this analysis.
¶ Vaccine was considered to have been administered if vaccination dates and product names were verified through medical records, state immunization registries, vaccination record cards, or provider or pharmacy records, or if plausibly reported by patient or proxy with date and location of vaccination.
** The date of illness onset was used for cases and controls with COVID-19–like illness with median value imputed if missing. For controls without COVID-19–like illness, the date of admission minus the median number of days between illness onset and admission for patients with COVID-19 was used for a date of illness onset, also referred to as illness onset for this report.
†† All activities were approved by participating institutions as public health surveillance activities, except postvaccination blood collection that received institutional review board approval at a single site (Wake Forest University).
§§ 45 C.F.R. part 46.102(l)(2), 21 C.F.R. part 56; 42 U.S.C. Sect. 241(d); 5 U.S.C. Sect. 552a; 44 U.S.C. Sect. 3501 et seq.
¶¶ Immunocompromising conditions included having one or more of the following: active solid organ cancer (active cancer defined as treatment for the cancer or newly diagnosed cancer in the past 6 months), active hematologic cancer (such as leukemia, lymphoma, or myeloma), HIV infection without AIDS, AIDS, congenital immunodeficiency syndrome, prior splenectomy, prior solid organ transplant, immunosuppressive medication, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, scleroderma, or inflammatory bowel disease including Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
References
- CDC. COVID-19: your COVID-19 vaccination. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2021. Accessed August 25, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/your-vaccination.html
- CDC. COVID-19: ensuring the safety of COVID-19 vaccines in the US. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2021. Accessed August 25, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/safety.html
- CDC. COVID data tracker. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2021. Accessed August 23, 2021. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker
- Food and Drug Administration. Learn more about COVID-19 vaccines from the FDA. Silver Spring, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration; 2021. Accessed August 23, 2021. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/learn-more-about-covid-19-vaccines-fda
- CDC. COVID-19: different COVID-19 vaccines. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2021. Accessed August 25, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/different-vaccines.html
- Tenforde MW, Self WH, Naioti EA, et al.; IVY Network Investigators. Sustained effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines against COVID-19 associated hospitalizations among adults—United States, March–July 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:1156–62. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7034e2 PMID:34437524
- Tenforde MW, Patel MM, Ginde AA, et al.; Influenza and Other Viruses in the Acutely Ill (IVY) Network. Effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines for preventing Covid-19 hospitalizations in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 2021. Epub August 6, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciab687 PMID:34358310
- Khoury DS, Cromer D, Reynaldi A, et al. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med 2021;27:1205–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01377-8 PMID:34002089
- Nanduri S, Pilishvili T, Derado G, et al. Effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines in preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among nursing home residents before and during widespread circulation of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) variant—National Healthcare Safety Network, March 1–August 1, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:1163–6. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7034e3 PMID:34437519
Abbreviations: IQR = interquartile range; N/A = not applicable.
* Hospitals by region included Northeast: Baystate Medical Center (Springfield, Massachusetts), Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (Boston, Massachusetts), Montefiore Medical Center (Bronx, New York); South: Vanderbilt University Medical Center (Nashville, Tennessee), University of Miami Medical Center (Miami, Florida), Emory University Medical Center (Atlanta, Georgia), Johns Hopkins Hospital (Baltimore, Maryland), Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center (Winston-Salem, North Carolina), Baylor Scott & White Health (Temple, Texas); Midwest: University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics (Iowa City, Iowa), University of Michigan Hospital (Ann Arbor, Michigan), Hennepin County Medical Center (Minneapolis, Minnesota), Barnes-Jewish Hospital (St. Louis, Missouri), Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, Ohio), Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center (Columbus, Ohio); West: Stanford University Medical Center (Stanford, California), UCLA Medical Center (Los Angeles, California), UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital (Aurora, Colorado), Oregon Health & Science University Hospital (Portland, Oregon), Intermountain Medical Center (Murray, Utah), University of Washington (Seattle, Washington).
† Data are not complete for all characteristics in the table; denominators are included in the table indicating the number of patients with available data for each characteristic.
§ Fully vaccinated with mRNA COVID-19 vaccines defined as ≥14 days from dose 2; fully vaccinated with Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) vaccine defined as ≥14 days from dose 1.
¶ Racial and ethnic groups were reported by the patient or proxy.
** Northeast: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Vermont; Midwest: Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota, and Wisconsin; South: Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, North Carolina, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and West Virginia; West: Alaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Hawaii, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming.
†† Long-term care facility included reporting living in a nursing home, assisted living home, or rehabilitation hospital or other subacute or chronic facility before the hospital admission.
§§ Underlying medical condition categories were obtained through medical chart review by trained personnel.
¶¶ Among fully vaccinated patients.
Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval; VE = vaccine effectiveness.
* VE was estimated using logistic regression comparing the odds of being fully vaccinated with the Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech or Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) COVID-19 vaccine versus being unvaccinated in case-patients and control-patients using the equation VE = 100 × (1 – odds ratio). Models were adjusted for date of hospital admission (biweekly intervals), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services region of hospital, age group (18–49, 50–64, ≥65 years), sex, and race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, Hispanic of any race, non-Hispanic Other, or unknown). Binary time since full vaccination was added to the model with results for 14–120 days and >120 days shown.
† Hospitals by region included Northeast: Baystate Medical Center (Springfield, Massachusetts), Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (Boston, Massachusetts), Montefiore Medical Center (Bronx, New York); South: Vanderbilt University Medical Center (Nashville, Tennessee), University of Miami Medical Center (Miami, Florida), Emory University Medical Center (Atlanta, Georgia), Johns Hopkins Hospital (Baltimore, Maryland), Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center (Winston-Salem, North Carolina), Baylor Scott & White Health (Temple, Texas); Midwest: University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics (Iowa City, Iowa), University of Michigan Hospital (Ann Arbor, Michigan), Hennepin County Medical Center (Minneapolis, Minnesota), Barnes-Jewish Hospital (St. Louis, Missouri), Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, Ohio), Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center (Columbus, Ohio); West: Stanford University Medical Center (Stanford, California), UCLA Medical Center (Los Angeles, California), UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital (Aurora, Colorado), Oregon Health & Science University Hospital (Portland, Oregon), Intermountain Medical Center (Murray, Utah), University of Washington (Seattle, Washington).
§ The full surveillance period included hospital admissions during March 11–August 15, 2021.
 FIGURE. Serum anti–receptor binding domain and anti-spike immunoglobulin G levels 2–6 weeks after full vaccination among healthy adult volunteers — three hospitals in three U.S. states,*,† April–June 2021
FIGURE. Serum anti–receptor binding domain and anti-spike immunoglobulin G levels 2–6 weeks after full vaccination among healthy adult volunteers — three hospitals in three U.S. states,*,† April–June 2021
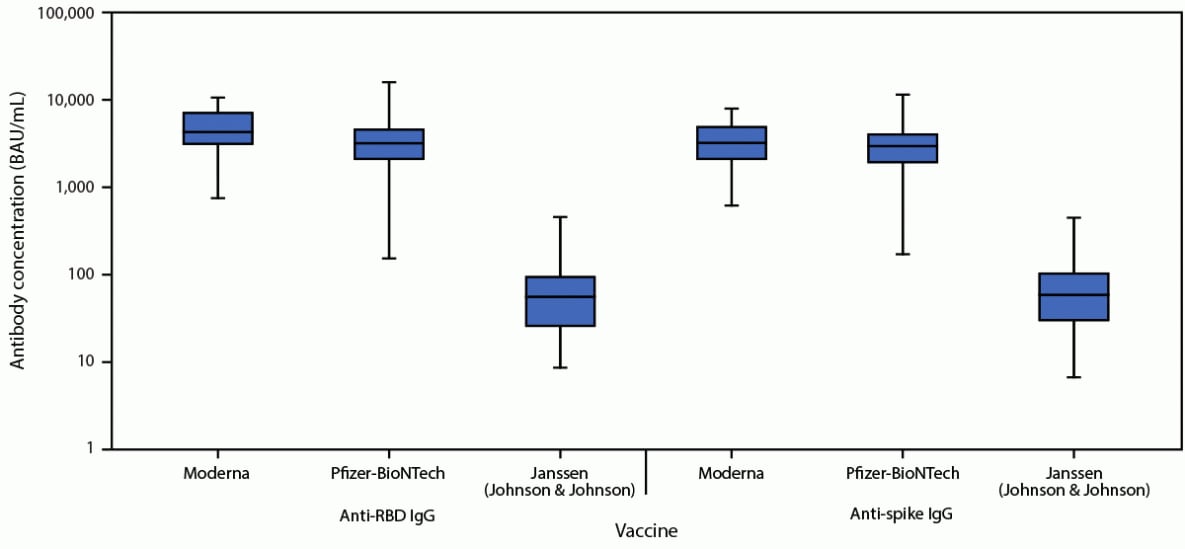
Abbreviations: BAU = binding antibody units; IgG = immunoglobulin G; IQR = interquartile range; RBD = receptor binding domain.
* Anti-RBD and anti-spike IgG levels were measured in sera of healthy volunteers 2-6 weeks after a second dose of the Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine and the first dose of the Janssen COVID-19 vaccine. In these box and whisker plots, the central horizontal line of each box plot represents the median, with the box denoting the IQR, and the whiskers representing the minimum and maximum values. Two volunteers with anti-nucleocapsid IgG antibodies, indicative of a prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, were excluded from this analysis.
† Hospitals that recruited healthy adult volunteers included Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (Boston, Massachusetts), Vanderbilt University Medical Center (Nashville, Tennessee), and Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center (Winston-Salem, North Carolina).
Suggested citation for this article: Self WH, Tenforde MW, Rhoads JP, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) Vaccines in Preventing COVID-19 Hospitalizations Among Adults Without Immunocompromising Conditions — United States, March–August 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021;70:1337–1343. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7038e1.
MMWR and Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report are service marks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of
Health and Human Services.
References to non-CDC sites on the Internet are
provided as a service to MMWR readers and do not constitute or imply
endorsement of these organizations or their programs by CDC or the U.S.
Department of Health and Human Services. CDC is not responsible for the content
of pages found at these sites. URL addresses listed in MMWR were current as of
the date of publication.
All HTML versions of MMWR articles are generated from final proofs through an automated process. This conversion might result in character translation or format errors in the HTML version. Users are referred to the electronic PDF version (https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr) and/or the original MMWR paper copy for printable versions of official text, figures, and tables.
Questions or messages regarding errors in formatting should be addressed to mmwrq@cdc.gov.