About
The Viral Hepatitis National Progress Report provides information on progress toward 2025 goals for new viral hepatitis infections and viral hepatitis–related deaths, overall and for key populations.

Progress
Ten objective indicators assess progress toward achieving key viral hepatitis goals. Select the indicator from the table below for more information.

Met or exceeded current annual target

Moving toward annual target, but annual target was not fully met

Annual target was not met and has not changed or moved away from annual target
| Baseline 2017 data year |
2022 Observed (Annual target*) |
2025 Goal 2023 data year |
Trend | 2022 Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis A | |||||
| Reduce estimated† new hepatitis A virus infections by ≥40% | 6,700 | 4,500 (4,450) |
4,000 | 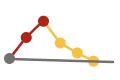 |
|
| Hepatitis B | |||||
| Reduce estimated† new hepatitis B virus infections by ≥20% | 22,200 | 13,800 (18,700) |
18,000 | 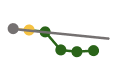 |
|
| Reduce reported rate‡ of new hepatitis B virus infections among persons who inject drugs¶ by ≥25% | 1.4 | 0.6 (1.1) |
1.0 |  |
|
| Reduce reported rate‡ of hepatitis B-related deaths by ≥20% | 0.46 | 0.44 (0.39) |
0.37 |  |
|
| Reduce reported rate‡ of hepatitis B-related deaths among non-Hispanic Asian/Pacific Islander persons by ≥25% | 2.45 | 2.30 (1.94) |
1.84 |  |
|
| Hepatitis C | |||||
| Reduce estimated† new hepatitis C virus infections by ≥20% | 44,700 | 67,400 (36,617) |
35,000 | 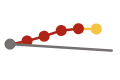 |
|
| Reduce reported rate‡ of new hepatitis C virus infections among persons who inject drugs¶ by ≥25% | 2.3 | 2.7 (1.8) |
1.7 |  |
|
| Reduce reported rate‡ of hepatitis C-related deaths by ≥20% | 4.13 | 2.89 (3.19) |
3.00 |  |
|
| Reduce reported rate‡ of hepatitis C-related deaths among non-Hispanic American Indian/Alaska Native persons by ≥30% | 10.24 | 9.08 (7.68) |
7.17 |  |
|
| Reduce reported rate‡ of hepatitis C-related deaths among non-Hispanic Black persons by ≥30% | 7.03 | 4.75 (5.27) |
4.92 |  |
|
| * Annual targets assume a constant (linear) rate of change from the observed baseline (2017) to the 2025 goal (2023 data year). † The number of estimated viral hepatitis infections was determined by multiplying the number of reported cases by a factor that adjusted for underascertainment and underreporting (CDC 2022 Viral Hepatitis Surveillance Report and Klevens et al., 2014). ‡ Per 100,000 population. ¶ Persons aged 18–40 years were used as a proxy for persons who inject drugs. |
|||||
