Key points
- Influenza viruses are constantly changing, and some changes can make antiviral drugs less effective or ineffective against influenza viruses.
- Influenza viruses can become less susceptible to antiviral drugs during or after antiviral treatment or emerge spontaneously.
- CDC continually monitors influenza viruses to detect viruses with antiviral resistance.
Understanding Reduced Susceptibility and Antiviral Resistance
When an antiviral drug is fully effective against a virus, that virus is said to be susceptible to that antiviral drug. Influenza viruses are constantly changing, and some changes can make antiviral drugs work less well or not work at all against these viruses. Antiviral drugs work by targeting a specific location or site found on an influenza virus. When an influenza virus develops changes to the virus site that an antiviral drug targets, that virus may show reduced or no susceptibility to that antiviral drug. Influenza viruses can show reduced susceptibility to one or more influenza (flu) antiviral drugs. Reduced susceptibility that is detected using laboratory methods can be a sign of potential antiviral drug resistance in clinical settings. Typically, an influenza virus is called resistant after sufficient laboratory evidence is available to show that the antiviral drug lacks activity against the virus.
In the United States, there are four FDA-approved antiviral drugs recommended by CDC this season. Three are neuraminidase inhibitor antiviral drugs: oseltamivir (available as a generic version or under the trade name Tamiflu®) for oral administration, zanamivir (trade name Relenza®) for oral inhalation using an inhaler device, and peramivir (trade name Rapivab®) for intravenous administration. The fourth is a cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor, baloxavir marboxil (trade name Xofluza®) for oral administration. Baloxavir marboxil was approved for use in the United States by FDA in 2018.
There is another class of FDA-approved antiviral drugs, M2 ion channel blockers amantadine and rimantadine, also called the adamantanes, that have activity against influenza A viruses (but not influenza B viruses). However, the adamantane antiviral drugs have not been recommended for use to treat flu in the United States for many years because of widespread antiviral resistance to this class of antivirals among circulating seasonal influenza A viruses.
Status of Reduced Susceptibility and Antiviral Resistance in the United States
In the United States, nearly all recently circulating seasonal influenza A and B viruses have been susceptible to the neuraminidase inhibitors and to baloxavir. However, nearly all circulating seasonal influenza A viruses have been resistant to adamantanes, which is why they are not recommended for treatment of seasonal influenza A virus infections.
Development of Reduced Susceptibility and Antiviral Resistance
Influenza viruses are constantly changing; they can change in significant ways from one season to the next and can even change within the course of one flu season. As an influenza virus replicates (i.e., makes copies of itself), its genetic makeup may change in a way that results in the virus becoming less susceptible to one or more of the antiviral drugs used to treat or prevent flu. Influenza viruses can become less susceptible to antiviral drugs during or after antiviral treatment. In addition, genetic changes in the virus that result in reduced susceptibility or antiviral resistance can emerge spontaneously. Antiviral resistant influenza viruses vary in their ability to infect people and are not necessarily more or less transmissible than susceptible influenza viruses.
Detecting Reduced Susceptibility and Antiviral Resistance
CDC routinely analyzes influenza viruses collected through domestic and global surveillance to see if they have genetic changes that are known to cause resistance. Influenza viruses are also analyzed for changes that are suspected to reduce susceptibility to any flu antiviral drug. Such changes in the virus can make an antiviral drug become less effective or ineffective at treating or preventing flu illness. Additionally, CDC collaborates with the Wadsworth Center public health laboratory of New York State's Department of Health (NYSDOH), a National Influenza Reference Center (NIRC), that conducts extended antiviral susceptibility monitoring. This designated laboratory receives influenza viruses from state public health laboratories during influenza season. The combined data inform public health policy recommendations about the use of flu antiviral medications.
CDC is continuously improving testing algorithms and methods used for monitoring antiviral susceptibility in circulating infuenza viruses. Analysis starts with using molecular techniques (i.e., next generation sequence analysis) to look for genetic changes that have previously been associated with reduced antiviral susceptibility or antiviral resistance. This is followed by other laboratory methods where viruses are tested in the presence of an antiviral drug (e.g., neuraminidase inhibition assay).
Testing Susceptibility to Baloxavir
CDC's Influenza Division took specific laboratory actions to incorporate the antiviral drug baloxavir into routine virologic surveillance. This included the creation and validation of new assays to determine baloxavir susceptibility to circulating seasonal influenza A and B viruses, and training of laboratorians to conduct baloxavir susceptibility testing.
Seasonal influenza A and B viruses in humans as well as numerous influenza A viruses collected from animals were tested to establish baseline susceptibility to baloxavir. The baloxavir susceptibility of other distantly related influenza viruses was also tested. CDC collaborates with the Association of Public Health Laboratories (APHL) and the Wadsworth Center NYSDOH, a National Influenza Reference Center (NIRC), to include baloxavir susceptibility testing as part of extended (in-state) antiviral susceptibility surveillance starting in the 2025-2026 season. CDC has trained staff within these partner organizations to use CDC's methodology for assessing baloxavir susceptibility.
Oseltamivir Resistance and Causes
Influenza viruses are constantly changing. Changes that occur in circulating influenza viruses typically involve the structures of the viruses' two primary surface proteins: hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) (the image below shows an influenza virus and its HA and NA surface proteins.)
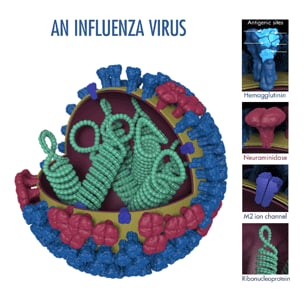
Oseltamivir is the most commonly prescribed antiviral drug of those recommended in the United States to treat flu illness. Oseltamivir is known as a "NA inhibitor" because this antiviral drug binds to NA proteins of an influenza virus and inhibits the enzymatic activity of these proteins. By inhibiting NA activity, oseltamivir reduces the spread of influenza viruses from infected cells to other healthy cells.
Changes in the NA proteins of an influenza virus can reduce the ability of oseltamivir to bind to the virus. As a result, oseltamivir's ability to inhibit the enzyme activity of NA proteins can be diminished, and this may cause "oseltamivir resistance" (non-susceptibility). A particular genetic change known as the "H275Y" mutation in the NA is the mutation that is known to confer oseltamivir resistance in influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses. Influenza viruses that have the "H275Y" mutation show highly reduced inhibition by oseltamivir in laboratory assays (i.e., neuraminidase inhibition assay). The "H275Y' mutation makes oseltamivir ineffective in treating infections with that influenza virus. The "H275Y" mutation also reduces the effectiveness of peramivir to treat infections caused by an influenza virus with this mutation. Other mutations in the NA proteins of circulating viruses have been shown to affect oseltamivir's ability to inhibit the enzyme activity of the viral NA proteins. Such viruses can show 'reduced' or even 'highly reduced' inhibition by oseltamivir and other NA inhibitors in laboratory tests; however, not all are considered "resistant" due to insufficient data to support their antiviral resistance from clinical settings.
CDC's Enhanced Monitoring of Influenza Viruses for Reduced Susceptibility and Antiviral Resistance
CDC continuously works to improve the ability to rapidly detect influenza viruses with antiviral reduced susceptibility and antiviral resistance through improvements in laboratory methods; increasing the number of surveillance sites; and increasing the number of laboratories that can test for reduced susceptibility and antiviral resistance. Enhanced surveillance efforts have provided CDC with the capability to detect antiviral resistant influenza viruses more quickly and enabled CDC to monitor for changing trends over time.
Updated Information on Antiviral Susceptibility Among Circulating Seasonal Influenza A and B Viruses
For the latest information on antiviral susceptibility among circulating seasonal influenza A and B viruses in the United States, please see the current CDC influenza surveillance report.
CDC conducts ongoing surveillance and testing of influenza viruses for antiviral reduced susceptibility and resistance among seasonal and novel influenza A viruses (of animal origin that have infected people), and guidance is updated as needed.
Because there were no drastic changes in antiviral susceptibility patterns during the previous flu season, the guidance on the use of flu antiviral drugs for the upcoming flu season remains unchanged. The latest guidance for clinicians on the use of antiviral drugs for flu is available on the CDC website.
Monitoring Antiviral Susceptibility and Implications for the U.S. Antiviral Stockpile created as part of the United States Pandemic Plan
Monitoring for antiviral susceptibility will be essential to determine the use of specific antivirals during the next influenza pandemic. Available FDA-approved and authorized flu antiviral drugs can be used in the event that a novel influenza A virus, such as avian influenza A(H5N1) virus, gains the ability to spread easily among people in a sustained manner. During the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, neuraminidase inhibitor antiviral drugs were released from the Strategic National Stockpile (SNS) and used to treat infection with the pandemic influenza virus, now referred to as influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus. In addition, an investigational antiviral drug was made available by FDA Emergency Use Authorization for treatment of hospitalized pandemic influenza patients in the United States through clinician requests to CDC. Antivirals in the SNS and state pandemic influenza antiviral stockpiles are for use during public health emergencies in the United States, such as an influenza (flu) pandemic, but are typically not for seasonal flu epidemics. The Administration for Strategic Preparedness & Response (ASPR) overseas the SNS.
