Key points
- Dengue viruses are usually spread to people through the bites of infected Aedes species mosquitoes.
- A woman infected with dengue during pregnancy can pass the virus to her fetus.
- Rarely, dengue can be spread through other routes.

Through mosquito bites
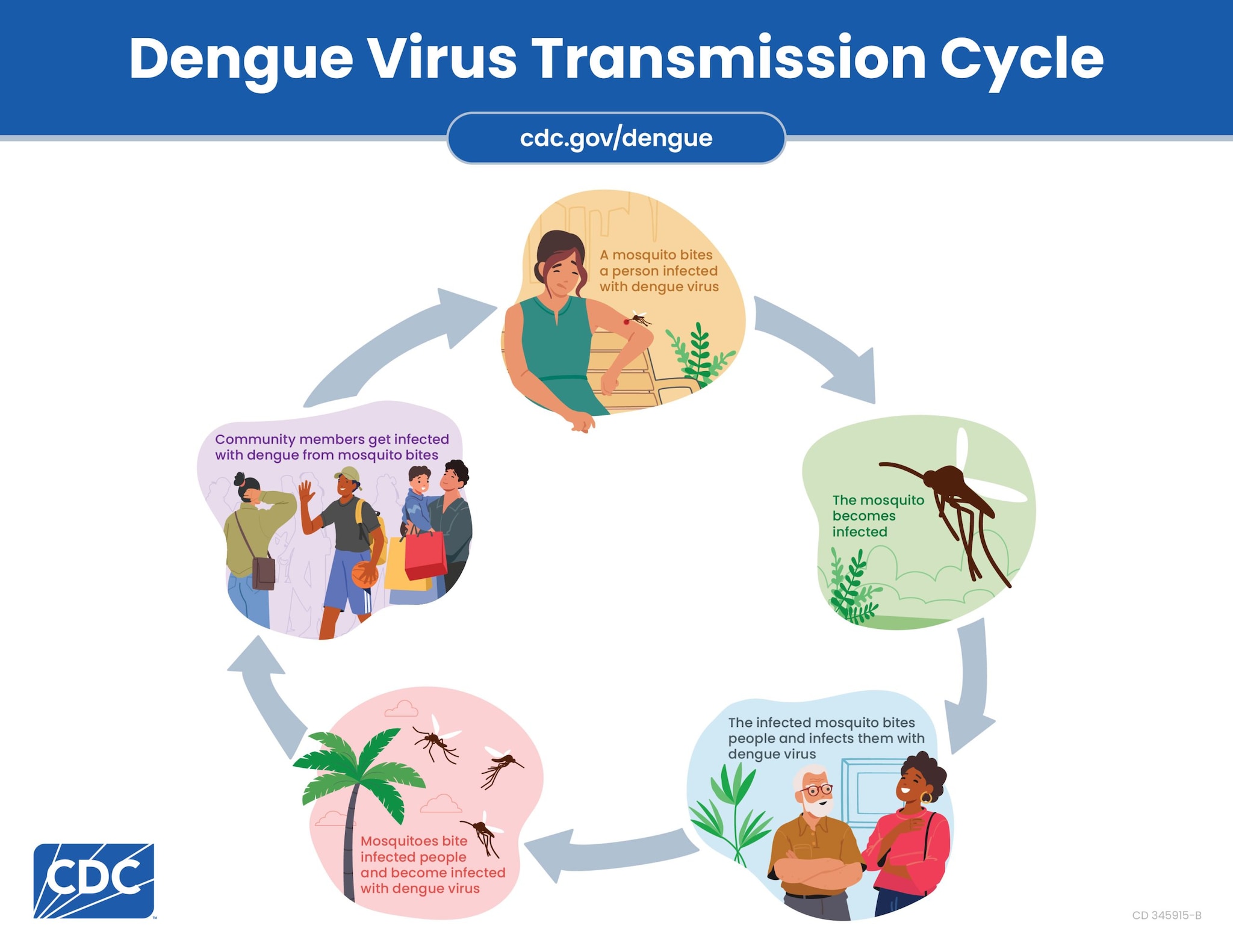
Dengue viruses are spread to people through the bites of infected Aedes species mosquitoes (Ae. aegypti or Ae. albopictus). These are the same types of mosquitoes that spread Zika and chikungunya viruses.
- These mosquitoes typically lay eggs in containers that hold water, like buckets, bowls, animal dishes, flowerpots, and vases.
- These mosquitoes prefer to bite people, and live both indoors and outdoors near people.
- Aedes species mosquitoes can bite during the day and night.
- Mosquitoes become infected with dengue virus when they bite a person infected with the virus. Infected mosquitoes can then spread the virus to other people through bites.
From pregnant woman to fetus
- A woman who is infected with dengue virus during pregnancy can pass the virus to her fetus during pregnancy or around the time of birth.
- Dengue can have harmful effects, including death of the fetus, low birth weight, and premature birth.
Through other routes
- Rarely, dengue is spread in laboratory or healthcare setting exposures through blood transfusions, organ transplants, or needlestick injuries.
- Some evidence suggests that dengue can be spread through sexual contact.
- Dengue virus has been found in breast milk but transmission through breast milk has not been confirmed. Because of the low risk of transmission and the benefits of breastfeeding, women are encouraged to breastfeed even if dengue infection is suspected or confirmed.
