What to know
CryptoNet is built on common platforms successfully used by national laboratory networks such as PulseNet and CaliciNet. By using these shared platforms, CryptoNet is able to more efficiently use existing infrastructure and harmonize laboratory workflows with these other programs to facilitate the collection and DNA fingerprinting of Cryptosporidium (or "Crypto" for short).

CryptoNet laboratory methods
Molecular methods, such as those developed and used by CryptoNet, are the only methods able to differentiate Crypto species, genotypes, and subtypes. These are used in epidemiological investigations and genetic typing and not for clinical diagnosis. Multiple individual protocols comprise the standardized method for Crypto genotyping and subtyping.
CryptoNet genotyping and subtyping
CryptoNet laboratories use a uniform DNA fingerprinting test called genotyping to identify the Crypto species that infect a person. The most common Crypto species that infect and make people sick are C. hominis and C. parvum. Microbiologists look at parts of the DNA of these Crypto species to identify differences and categorize the Crypto into subtypes. CryptoNet laboratories use DNA sequencing of the 18S ribosomal RNA gene to differentiate Crypto species and genotypes and the 60 kDa glycoprotein (gp60) gene to determine C. parvum or C. hominis subtypes.
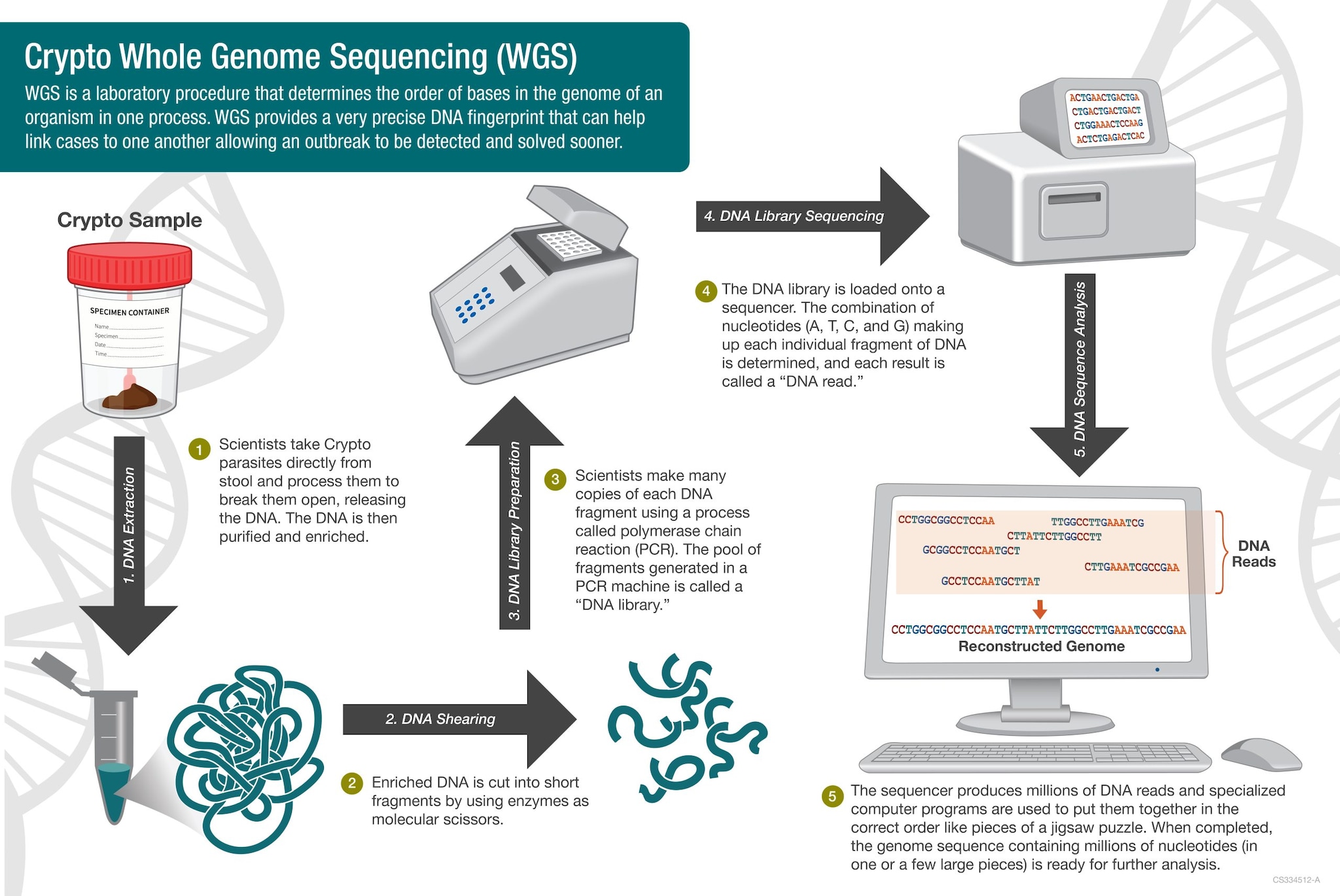
CryptoNet whole genome sequencing
CryptoNet developed whole genome sequencing and whole genome multi-locus sequence typing (wgMLST) methods to better differentiate C. hominis and C. parvum subtypes that reoccur or persist in cryptosporidiosis cases and outbreaks. Whole genome sequencing (WGS) is an advanced DNA fingerprinting technique where all the Crypto genetic material is used to make a complete DNA fingerprint or genome. In wgMLST, CDC scientists look at the entire Crypto genome to find regions of the DNA (or loci) that are different enough to better tell subtypes apart. More detailed Crypto DNA fingerprinting can identify connections between people infected with Crypto (for example eating the same contaminated food) that would otherwise be missed. If connections between infected people are not identified, outbreaks can go undetected and Crypto can continue to spread and cause illness.
DNA isolation
Since Crypto cannot be cultured, an enrichment technique is used to obtain enough genomic DNA for WGS.
Whole genome sequencing
Common sequencing platforms are used following validated WGS protocols, often harmonized with PulseNet.
wgMLST
Analysis of WGS data is performed using CryptoNet’s wgMLST pipeline.
CryptoNet Data
In addition to Crypto DNA fingerprinting, information on Crypto cases is collected in all participating CryptoNet states. This information is collected using a standard form and completed by a state or local health department. The Crypto case investigation form includes questions about travel, recreational water exposures, such as swimming, drinking water sources, raw or unpasteurized food and drinks, animal contact, and contact with people more likely to get infected (e.g., day care attendees and staff).
