Key points
- Most people with Strongyloides infection have no symptoms.
- Some people can experience stomach pain, rash, and a cough.
- People with weakened immune systems may get severely ill.
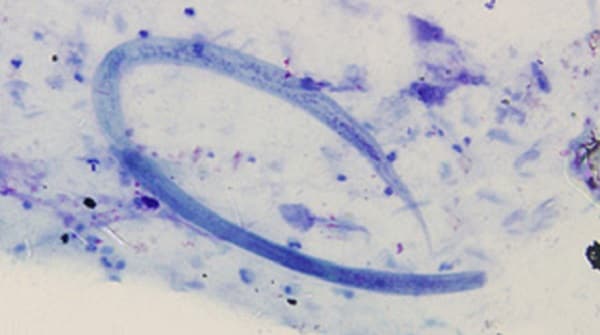
Signs and symptoms
Most people infected with Strongyloides do not have any symptoms. And of those who do, many of them have non-specific or generalized complaints.
In people with more severe infection, symptoms may include
- Stomachache
- Bloating
- Heartburn
- Occasional diarrhea and constipation
- Dry cough
- Sore throat
- Itchy, red rash where the parasite entered the skin
- Red, raised rash typically on the thighs and buttocks
A rash may occur immediately after infection at the site where the parasite entered the body. Coughing usually occurs several days later. Abdominal symptoms take about two weeks to appear.
In rare cases, chronic strongyloidiasis can cause
- Arthritis
- Kidney problems
- Heart conditions
Strongyloidiasis can be severe or even life-threatening in people who
- Take corticosteroids (oral or intravenous) for asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lupus, gout, or other conditions requiring steroids for immunosuppression or symptom relief;
- Are infected with Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)
- Have leukemia or lymphoma; or
- Have had an organ transplant.
