Noise and Occupational Hearing Loss
About Occupational Hearing Loss
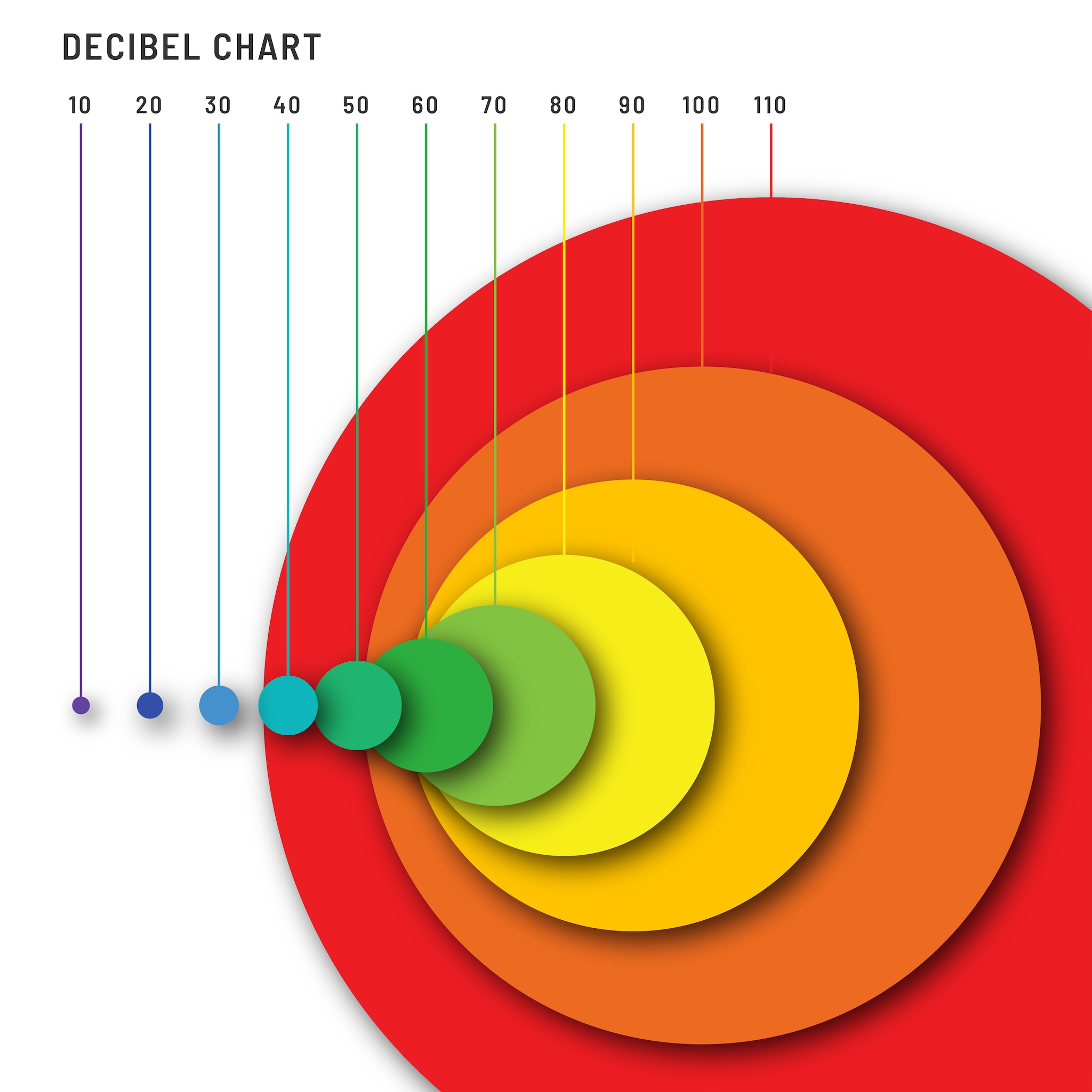
Decibels are a unit of measurement used to describe the amount of sound power present. Standard measurements like pounds or feet have linear relationships, decibels do not. Differences in decibel level represent a logarithmic relationship, for example a sound that is 10 dB louder than another is ten times more intense. This graphic is a visualization of the sound power present at different dB levels.
It is important for everyone to understand how occupational hearing loss can occur and how it can be prevented. Occupational hearing loss can occur when you are exposed to loud noise or ototoxic chemicals while at work.
- Noise is considered loud (hazardous) when it reaches 85 A-weighted decibels (dBA) or higher. A-weighted decibels are a scale for measuring noise. Hazardous noise can cause both hearing loss and tinnitus. Tinnitus is an annoying buzzing, rushing, or ringing noise in your ears or in your head.
- Exposure to certain chemicals can cause damage to different parts of the ear, meaning they are ototoxic. Exposure to ototoxic chemicals can cause hearing loss and make the ears more sensitive to the harmful effects of noise. About 10 million workers are exposed to solvents and an unknown number are exposed to other ototoxicants.
Most hearing loss occurs slowly over time.
Signs of Hearing Loss:
- Having difficulty hearing when there is background noise.
- Thinking people are mumbling when they talk to you.
- Needing to ask others to repeat themselves often.
Often, those close to you will notice that you have hearing trouble before you notice it yourself.
Hearing Loss and Tinnitus Are Common:
- About 22 million workers are exposed to hazardous noise on-the-job each year.
- In the U.S., hearing loss is the third most common chronic physical health condition among adults, after high blood pressure and arthritis.
- About 1 in 8 people in the U.S. working population has hearing difficulty. Among those with hearing difficulty, occupational exposures are the cause for 1 in 4 people.
- About 1 in 13 people in the U.S. working population has tinnitus, and 1 in 25 has both hearing difficulty and tinnitus.
Occupational Hearing Loss Is Permanent but Preventable:
- Employers, health and safety professionals, and workers can take action to prevent hearing loss.
- Employers and health and safety professionals can measure noise, implement noise controls, and establish hearing loss prevention programs.
- Workers should have a yearly hearing test if exposed to hazardous noise or ototoxic chemicals.
Hearing Loss Can Lead To Other Safety and Health Concerns:
Exposure to loud noise and ototoxic chemicals can lead to more than just hearing damage. Research shows that hearing loss is associated with cognitive decline and heart problems. Hearing loss and tinnitus can also impact your mental health, which may result in depression, anxiety, and a feeling of isolation and sadness.
Hearing loss can impact safety at home and on the job. The sound of a smoke detector, the warning beep as a forklift backs up, and the engine of an oncoming car may be missed. Workers with hearing loss are more likely to get injured on the job.
Working in a noisy job when you’re pregnant can increase your stress levels which can impact the health of your developing baby. Very loud sounds may also affect your baby’s hearing. To learn more, visit the NIOSH Noise and reproductive health page.
Learn more about hearing loss as it relates to noise and chemicals and view statistics on occupational hearing loss in different industries on the following pages.
