At a glance
- View hearing loss statistics among wholesale and retail trade (WRT) workers.
- Approximately 9% of all Wholesale Trade workers and 9% of all Retail Trade workers have hearing difficulty.
- About 6% of all Wholesale Trade workers and 7% of all Retail Trade workers have tinnitus.
- 51% of noise-exposed Wholesale Trade workers and 74% of noise-exposed Retail Trade workers report not wearing hearing protection.

Hearing loss and tinnitus
- Approximately 9% of all Wholesale Trade workers and 9% of all Retail Trade workers have hearing difficulty.1
- About 6% of all Wholesale Trade workers and 7% of all Retail Trade workers have tinnitus.3
- About 20% of noise-exposed tested WRT workers have a material hearing impairment.4 Hearing impairment is hearing loss that impacts day-to-day activities.
- 13% of noise-exposed tested WRT workers have hearing impairment in both ears.5
Trends
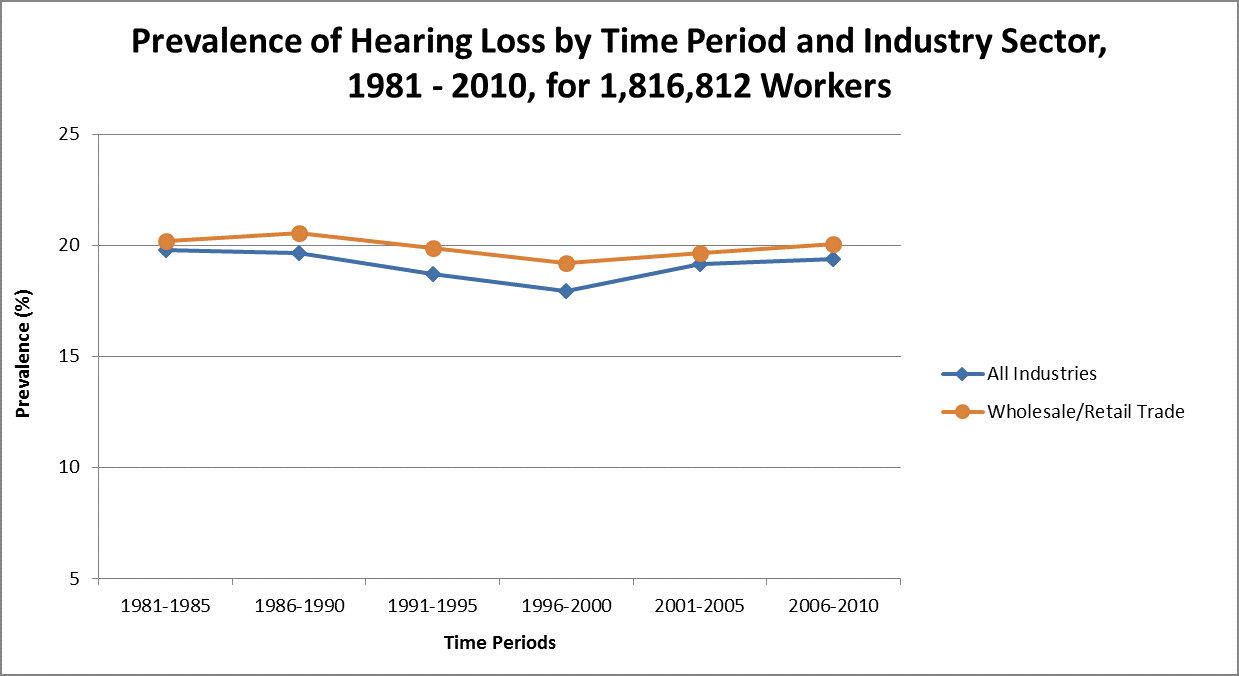
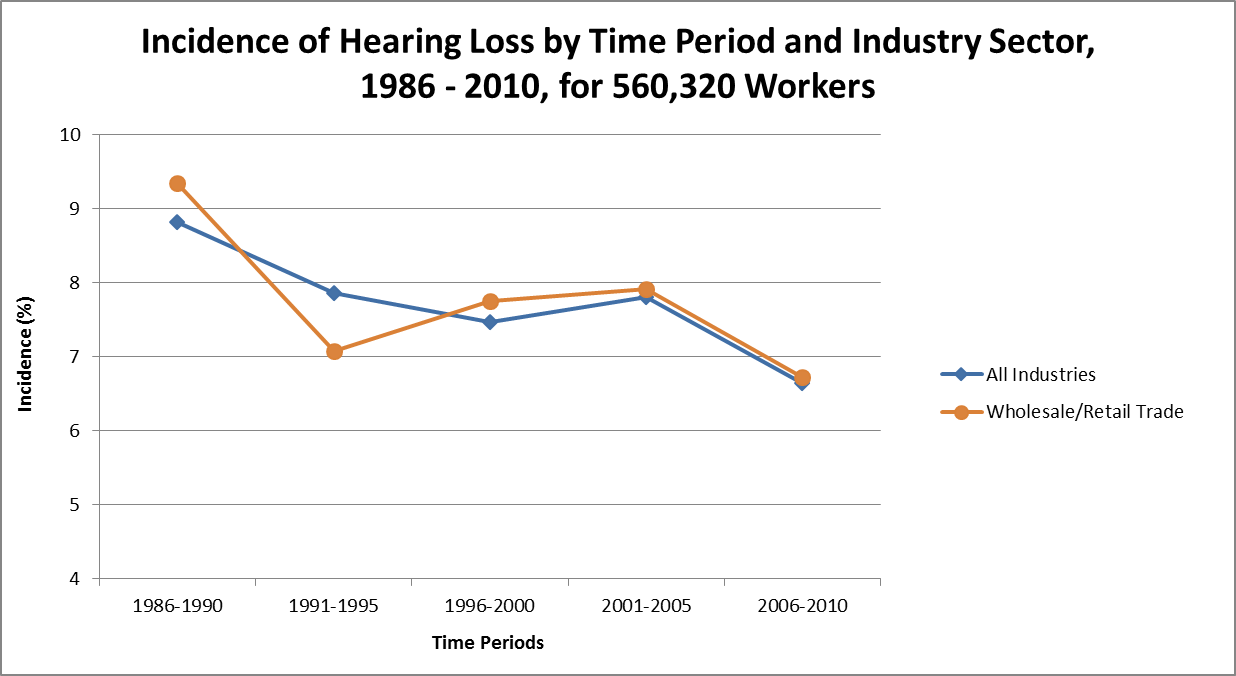
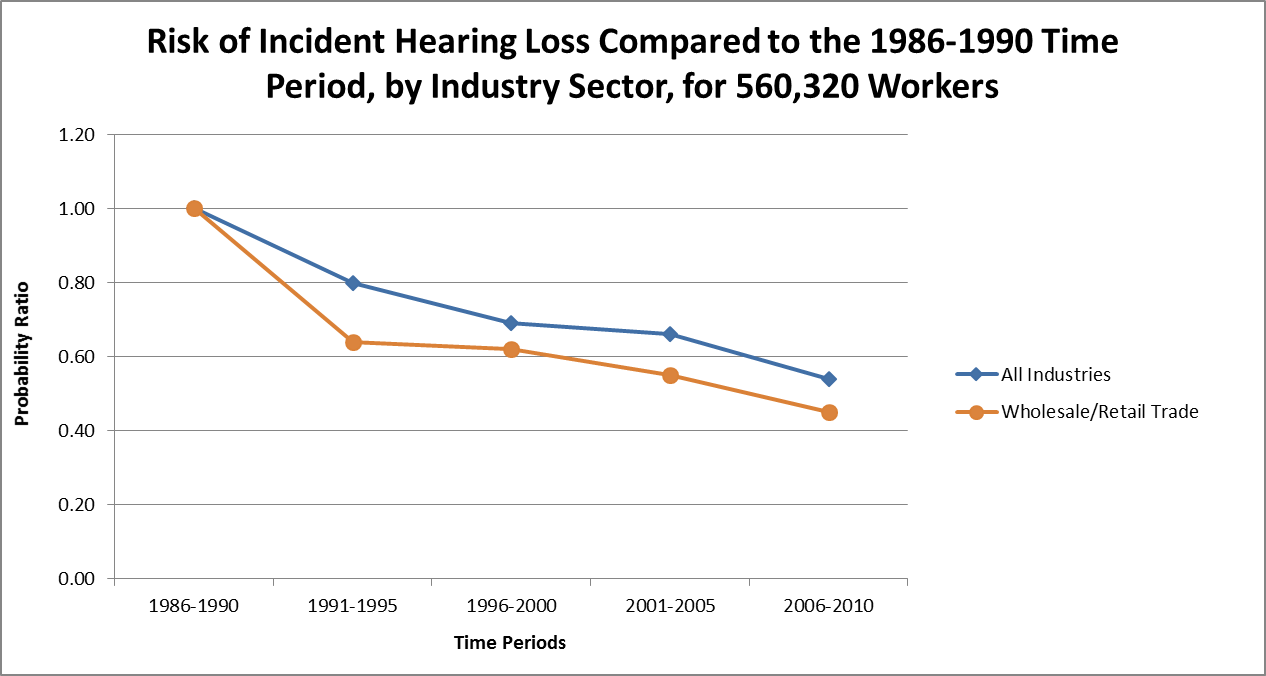
Trends among noise-exposed tested WRT workers (1980-2010)4
- The prevalence for WRT decreased less than 1% over 30 years (1981-2010) as compared with a less than 1% reduction for all industries.
- The incidence for WRT decreased 3% over 25 years (1986-2010) as compared with a 2% reduction for all industries.
- The adjusted risk for WRT decreased 55% over 25 years (1986-2010) as compared with a 46% reduction for all industries.
Return to occupational hearing loss statistics
Go back to select another industry.
Content Source:
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- Kerns E, Masterson EA, Themann CL, Calvert GM. (2018). Cardiovascular conditions, hearing difficulty and occupational noise exposure within U.S. industries and occupations. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 61, 477-491.
- Green DR, Masterson EA, Themann CL. (2021). Prevalence of hearing protection device non-use among noise-exposed U.S. workers in 2007 and 2014. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 64(12), 1002-1017.
- Masterson EA, Themann CL, Luckhaupt SE, Li J. & Calvert GM. (2016). Hearing difficulty and tinnitus among U.S. workers and non-workers in 2007. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 59, 290-300.
- Masterson EA, Deddens JA, Themann CL, Bertke S. & Calvert GM. (2015). Trends in worker hearing loss by industry sector, 1981-2010. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 58, 392-401.
- Masterson EA, Bushnell PT, Themann CL, & Morata TC. (2016). Hearing impairment among noise-exposed workers — United States, 2003–2012. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 65(15), 389-394.
