Key points
- Over 200 types of mosquitoes live in the continental United States and U.S. territories. About 12 types spread germs that can make people sick.
- Nuisance mosquitoes bother people but do not spread germs.
- Because you can’t tell if a mosquito is spreading germs when it bites, protect yourself from bites.
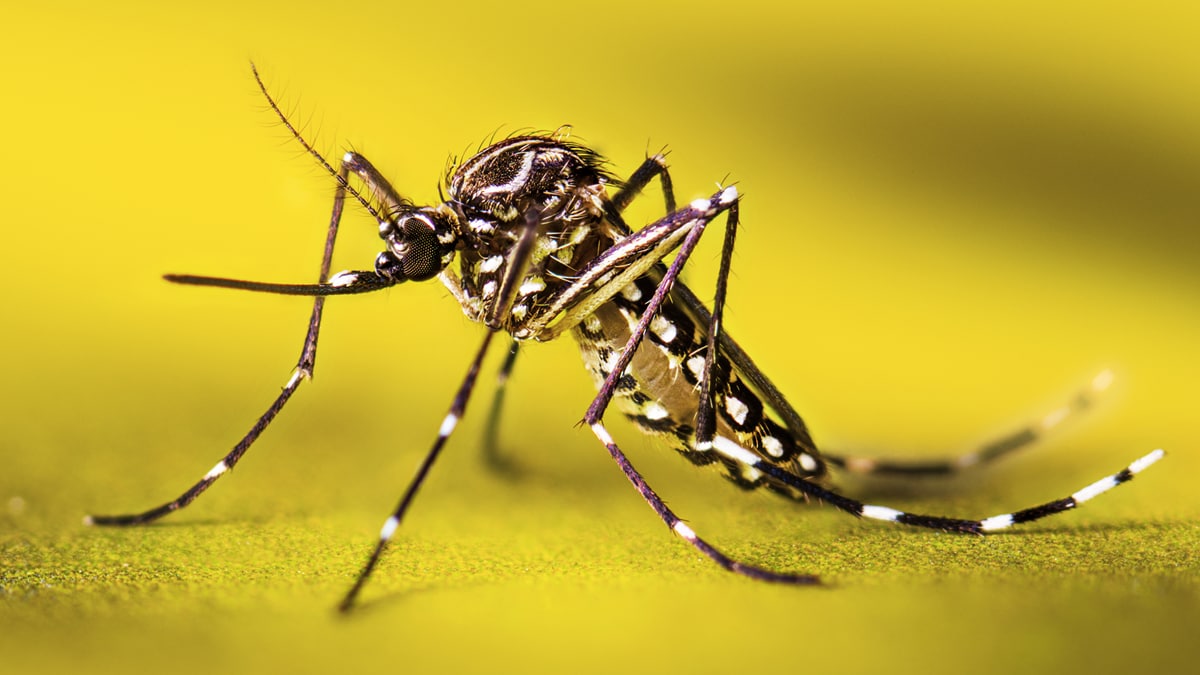

Mosquitoes that spread germs
Only some types of mosquitoes can spread germs (viruses and parasites) to people and animals. In the United States, the most common types of mosquitoes that can spread germs include:
- Aedes species mosquitoes (Ae. aegypti)
- Culex species mosquitoes (Cx. pipiens, Cx. tarsalis, Cx. quinquefasciatus)
- Anopheles species mosquitoes (An. freeborni and An. quadrimaculatus)
A person who gets bitten by an infected mosquito and gets sick has a mosquito-borne disease.
- West Nile is one of the most common mosquito-borne diseases in the continental United States.
- Other mosquito-borne diseases in the United States include:
- Dengue, chikungunya, and Zika outbreaks have occurred in U.S. states and territories, including Florida, Hawaii, Texas, Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and American Samoa.
Prevent Mosquito Bites
About malaria in the United States
Malaria was common in the United States into the 20th century. Most of the continental United States has Anopheles mosquitoes (particularly An. freeborni and An. quadrimaculatus), which can spread malaria.
- Local U.S. mosquito-borne spread has resulted in more than 150 locally acquired cases and more than 60 limited outbreaks in the United States over the past 50 years.
- In addition, more than 2,000 cases of malaria are reported annually in the United States, with most cases occurring in returned travelers.
How mosquitoes get infected
For a mosquito to get infected with a germ and then spread that germ to people or animals is a complex process.
- A mosquito takes a blood meal from a person or animal.
- If the blood meal contains a germ, then the germ must pass from the mosquitoes' gut into its body. Mosquitoes do not transmit all kinds of germs, only those that can grow or multiply in the body of the mosquito.
- The germ multiplies in the body of the mosquito. Then the germ moves from the body into the salivary glands where saliva is made. This process takes 2–3 weeks.
- The next time a mosquito bites a person or animal, the germ passes from the salivary glands into the blood of the person or animal being bitten.
- The person or animal can get sick.
Ability of a mosquito to get infected with and spread a germ depends on:
- The type of germ
- Environmental conditions, like temperature
- The amount of a germ eaten during a blood meal
- The age of the mosquito
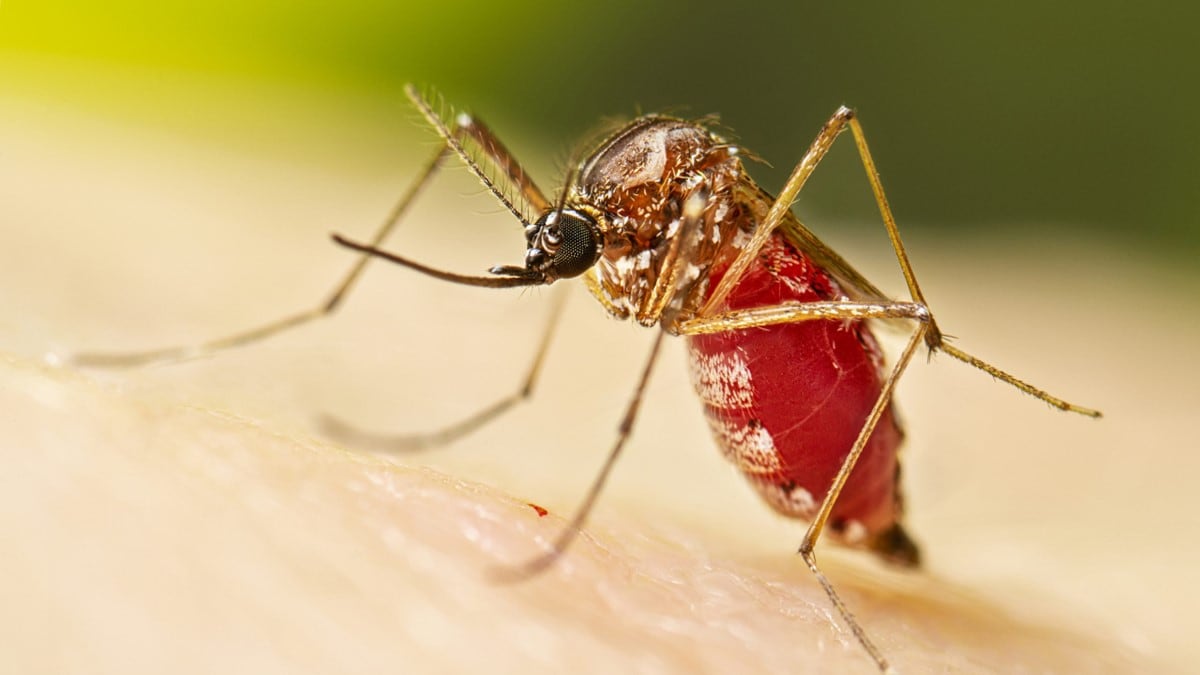
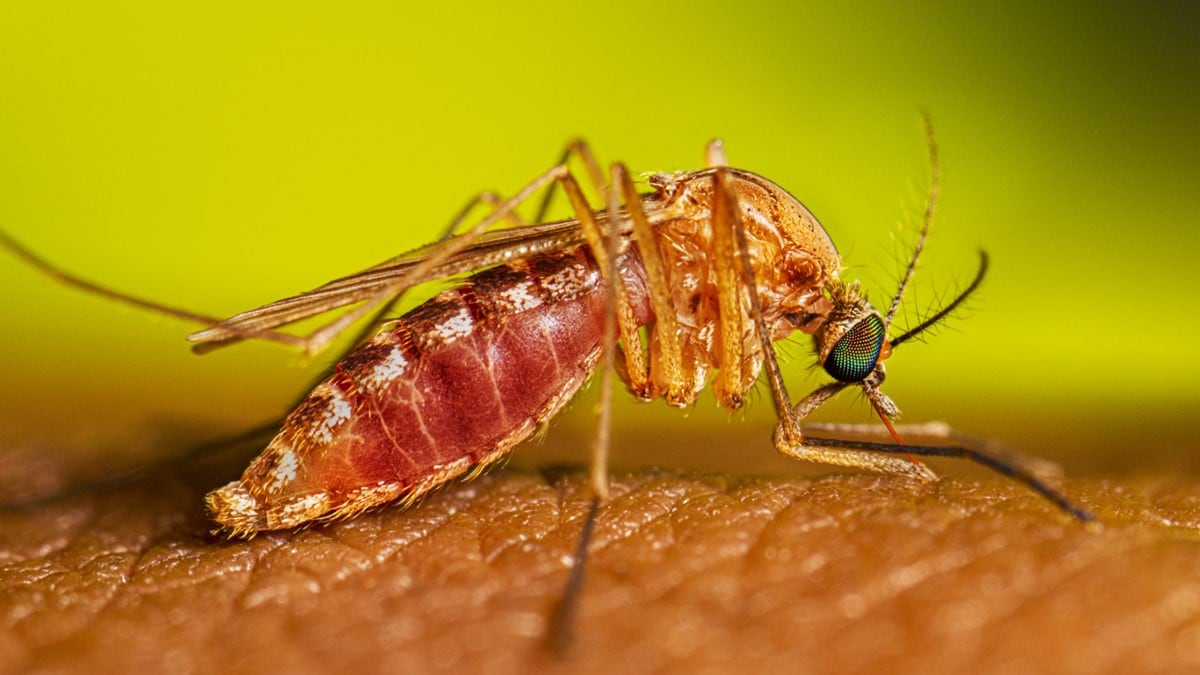
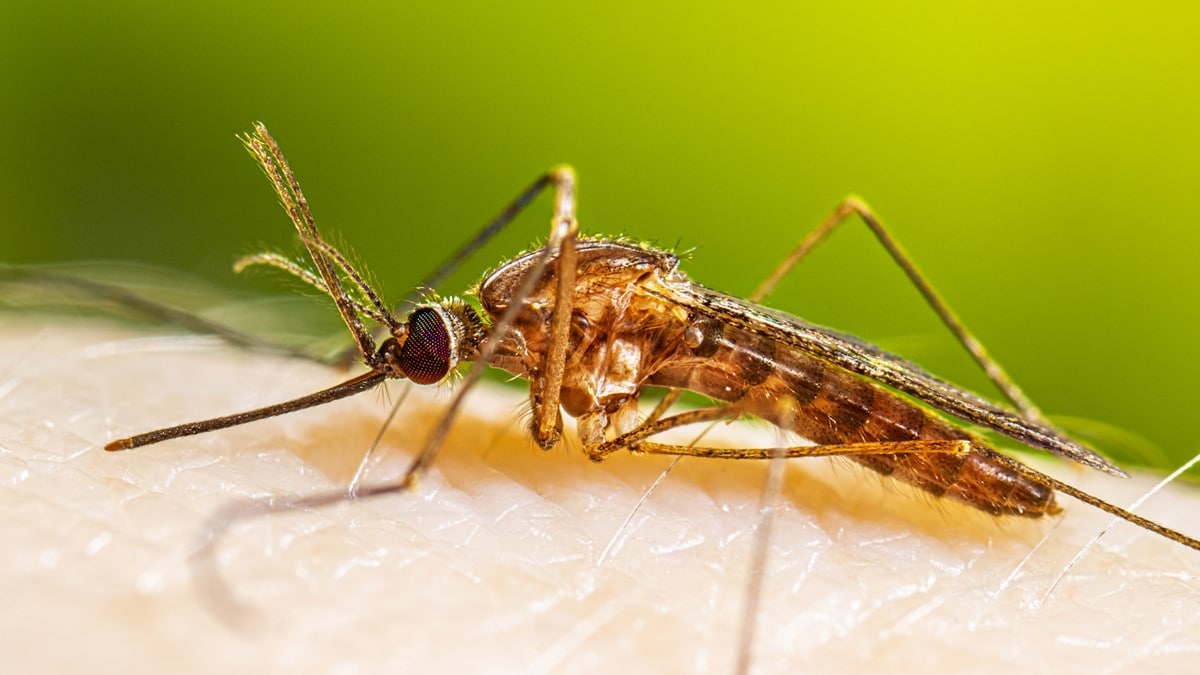
Quick look at some mosquitoes
In the United States, the following mosquitoes can spread germs.


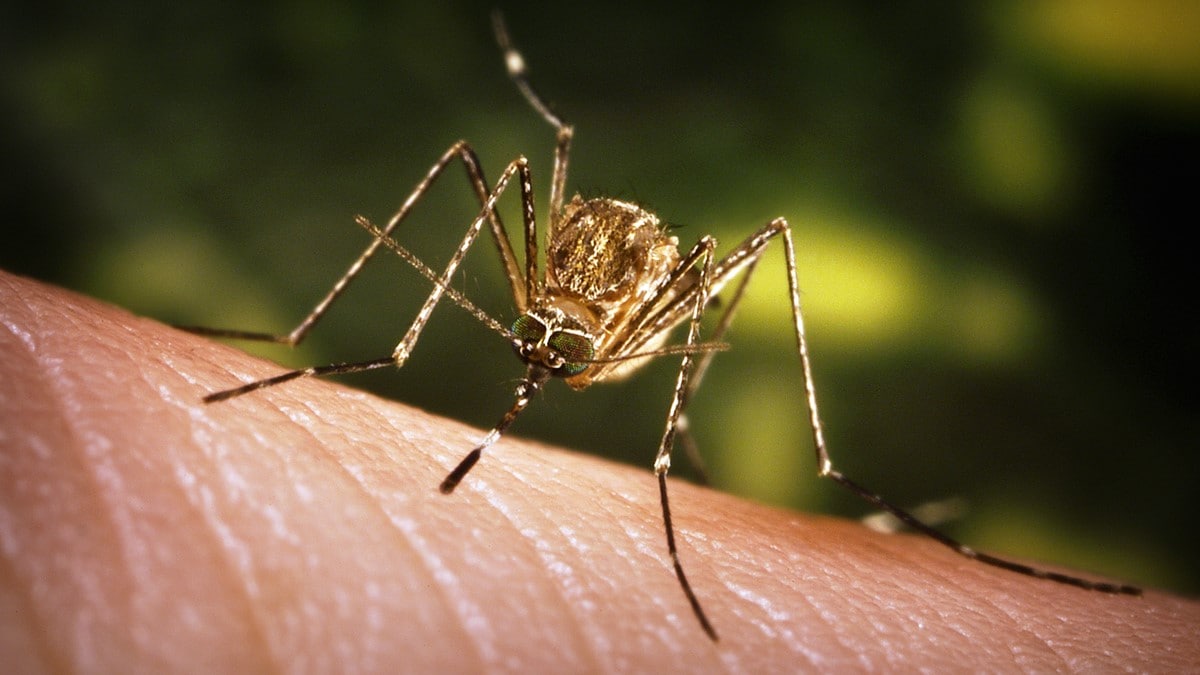

Nuisance mosquitoes
Most types of mosquitoes in the United States are nuisance mosquitoes. These mosquitoes can become a problem immediately following heavy rains, or natural disasters, such as hurricanes or floods.
Nuisance mosquitoes do not spread germs that can make people sick.
