Key points
- Molluscum contagiosum is a benign superficial skin disease caused by a poxvirus.
- The disease is found worldwide but is more common in developing countries.
- Molluscum contagiosum has traditionally been considered a pediatric disease but can infect anyone.
- Adult illnesses often result from sexual activity.
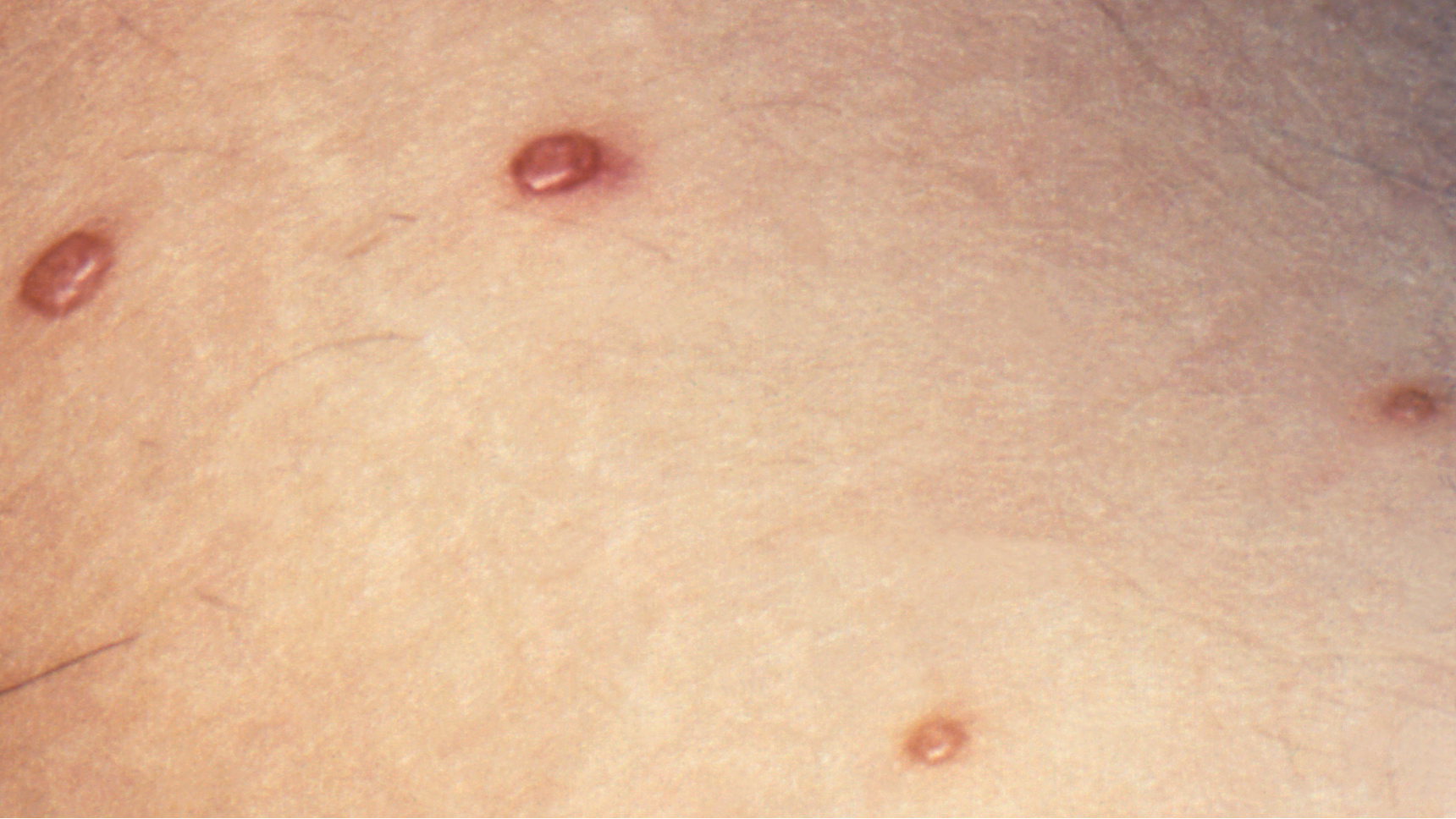
Clinical features
Molluscum contagiosum is characterized by small, pearly papules. The papules typically have a central depression whose core may be expressed, producing a white cheesy material. The lesions average 2 to 5 mm in size. Though they are usually painless, they may become inflamed, red, and swollen.
Molluscum contagiosum is a self-limited infection. The papules usually disappear spontaneously within 6 to 12 months. However, they may take as long as 4 years to resolve.
Patients who are immunosuppressed may have more and larger lesions.
Treatment and recovery
The lesions caused by molluscum are usually benign and resolve without scarring if left alone. Trying to remove lesions by scraping and scooping increases the risk of scarring and is not recommended for otherwise healthy people.
Physical removal
Physical removal such as cryotherapy, curettage and laser therapy require a trained healthcare provider and often local anesthesia. These procedures can result in post-procedural pain, irritation, and scarring.
Oral therapy
Gradual removal of lesions may be achieved by oral therapy with cimetidine. This option is often preferred for pediatric patients because:
- It is less painful.
- Parents can administer it at home.
- It has less chance of leaving scars.
While cimetidine is safe, painless, and well tolerated, facial mollusca do not respond as well as lesions elsewhere on the body. In patients with facial mollusca, consider other treatment options, such as topical therapy.
Topical therapy
There are a number of topical treatments that are available for molluscum infections. These treatments must be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Podophyllotoxin cream (0.5%) is a reliable home therapy for women who are not pregnant. Each lesion must be treated individually as the therapeutic effect is localized. It is not recommended during pregnancy due to the potential risk to the fetus.
Other options for topical therapy include iodine and salicylic acid, potassium hydroxide and tretinoin. Another therapy, the blistering agent cantharidin, is available but must be applied in a healthcare provider's office.
Imiquimod (a T-cell modifier) is available for adults. It has not been proven effective in children and is not recommended for children due to possible adverse events.
Therapy for immunocompromised people
Patients with HIV/AIDS or other immunosuppressing conditions often do not respond to traditional treatments.
Thus far, the most effective therapy for immunocompromised people who have molluscum are those that boost their immune systems.
In extreme cases, intralesional interferon has been used to treat facial lesions in these patients. However, interferon can cause severe and unpleasant side effects (flu-like symptoms, site tenderness, depression, and lethargy). These side effects make interferon a less desirable treatment.
Radiation therapy is also of little benefit.
Complications
The most common complication of molluscum is a bacterial secondary infection. Secondary infections may be a significant problem in patients who are immunocompromised. This includes those with HIV/AIDS or those taking immunosuppressing drugs. In these cases, treatment to prevent further spread of the infection is recommended.
Resources
American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology provides information on skin related conditions and diseases.
Toll-free: 866-509-SKIN (7546)
1-888-462-DERM (3376) for information on finding a dermatologist in your area.
American Sexual Health Association
The American Sexual Health Association'sExternal mission is to stop sexually transmitted diseases, including molluscum contagiosum, and their harmful effects.
Phone: 919-361-8400
Sexually Transmitted Infection Resource Center Hotline: 1-800-227-8922
National AIDS Hotlines
These hotlines provide callers with anonymous, confidential, and reliable answers to questions about HIV/AIDS.
National AIDS Hotline: 1-800-342-2437[English service operates 24 hours per day/7 days per week]
National AIDS Hotline en Español: 1-800-344-7432[Operates 10:00 a.m. to 2:00 a.m. EST, 7 days a week]
National AIDS hotline for the hearing impaired: 1-800-243-7889[Operates 10:00 a.m. to 10:00 p.m. EST, Monday – Friday]
