Key points
- Strep throat is a bacterial infection in the throat and tonsils.
- Healthcare providers can do a quick test to see if a sore throat is strep throat.
- Antibiotics can help people with strep throat feel better faster.
- Speak with a healthcare provider if you have concerns about strep throat.

Symptoms
It usually takes 2 to 5 days after exposure to become ill with strep throat.
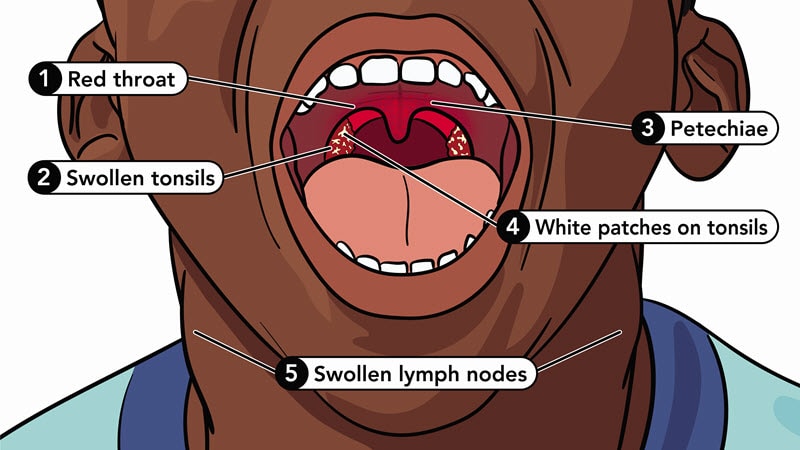
Common symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Pain when swallowing
- Red and swollen tonsils
- Sore throat that started very quickly and may look red
- Swollen lymph nodes in the front of the neck
- Tiny, red spots on the roof of the mouth, called petechiae
- White patches or streaks of pus on the tonsils

Less common symptoms, especially for children, may include:
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Rash (scarlet fever)
- Stomach pain
Complications
Complications can occur after a strep throat infection if the bacteria spread to other parts of the body.
Complications can include:
- Abscesses (pockets of pus) around the tonsils or in the neck
- Ear infections
- Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (a kidney disease)
- Rheumatic fever (a disease affecting the heart, joints, brain, skin)
- Sinus infections
Risk factors
Anyone can get strep throat, but some factors increase the risk of getting it.
Age
Strep throat is more common in children than adults.
- Most common: Children 5 through 15 years old
- Rare: Children younger than 3 years old
Close contact
Close contact with another person with strep throat is the most common risk factor for illness. For example, if someone has strep throat, the bacteria often spread to other people in their household.
Contact with children: Parents of school-age children and adults who are often in contact with children are at increased risk.
Crowded settings can increase the risk of getting any group A strep infection including strep throat. These settings include:
- Daycare centers and schools
- Detention or correctional facilities
- Homeless shelters
- Military training facilities
Causes
Group A Streptococcus (group A strep bacteria) cause strep throat and are contagious.
Prevention
People can take steps to help protect themselves and others from group A strep infections, including strep throat. These steps include:
- Wash hands often with soap and water
- Avoid sharing cups, utensils, and bites of food with people who are sick
- Wash cups, utensils, and plates after someone who's sick uses them
- Cover coughs and sneezes
- Keep wounds clean and bandaged
- Seek health care if you think you have a group A strep infection
Testing and diagnosis
Healthcare providers can use several types of tests to diagnose strep throat.
Treatment and recovery
Healthcare providers treat strep throat with antibiotics.
