Key points
A Maternal Death Surveillance and Response (MDSR) system collects and analyzes data on individual maternal deaths. Recommendations can then be followed to improve maternity care systems and prevent future maternal deaths. MDSR is used in many low- and middle-income countries to reduce maternal deaths.

Investigating and reducing maternal deaths
A Maternal Death Surveillance and Response (MDSR) system is a continuous cycle intended to prevent future maternal deaths by learning from previous deaths. This is done by identifying and studying each death, then developing and following recommendations to prevent future deaths from similar causes.
MDSR is especially helpful in countries where official data systems may not record many of the births and deaths and where the risk of maternal death is high.
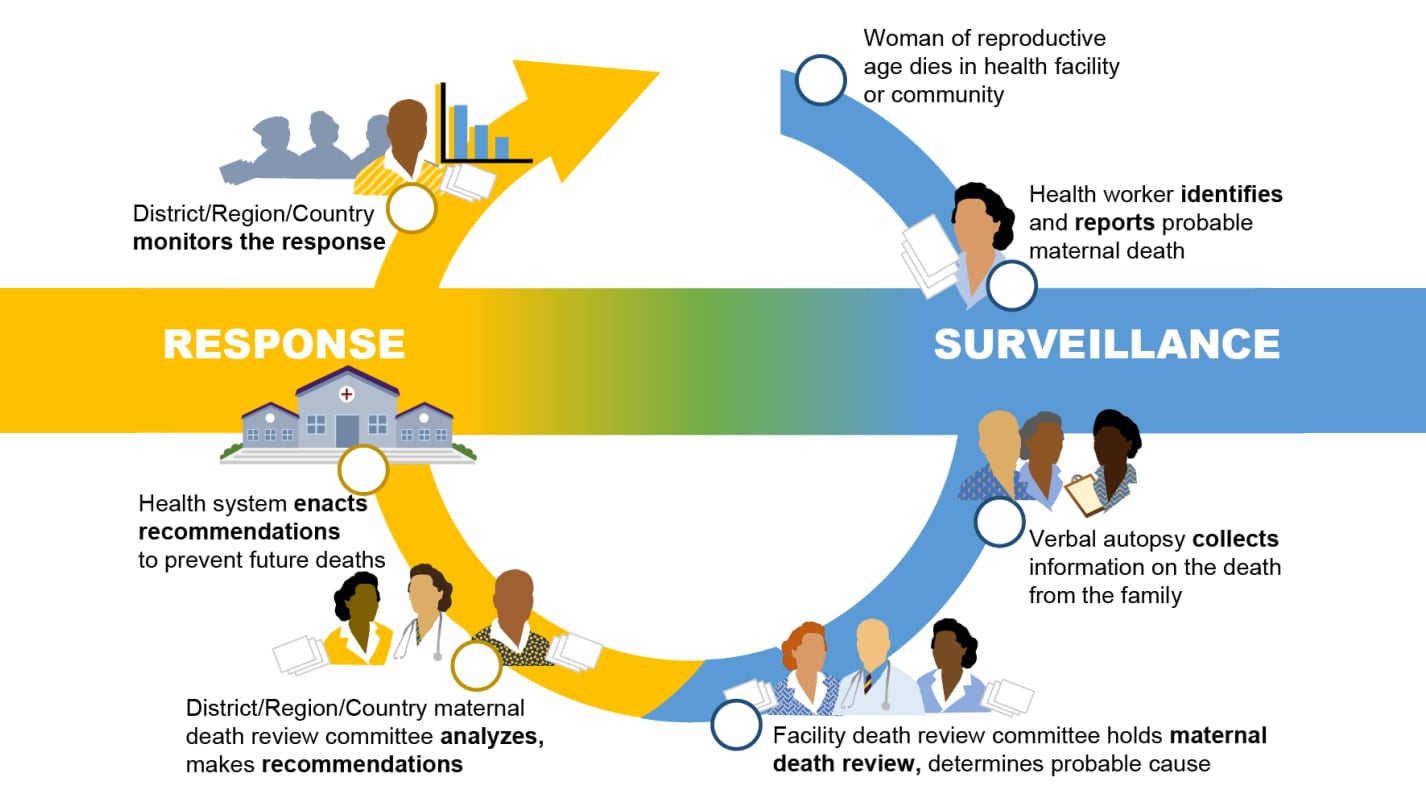
The steps in MDSR include the following:
- The cycle begins with health workers identifying a maternal death (death due to pregnancy-related causes).
- The health workers report (or "notify") that death through the MDSR system.
- More detailed information on the death is collected by health workers and using a verbal autopsy.
- The health facility's Maternal Death Review Committee meets to review the information on the death and determine the likely cause of death.
- A higher-level Maternal Death Review Committee meets periodically to review all the maternal deaths in the area and make recommendations to prevent future maternal deaths from those causes.
- The health system enacts those recommendations.
- A higher level (for example, national) entity reviews the MDSR reports, recommendations, and data to monitor the effect of the response to prevent future deaths.
Using MDSR to improve maternal health programs
CDC has worked with Ministries of Health and local health staff to adopt or improve MDSR systems, and to adapt them to the local conditions and needs. This collaborative work has been focused in the following areas:
Working in new areas of MDSR
- Developing improved indicators for monitoring MDSR systems globally.
- Conducting a content analysis from 56 MDSR reports published between 2011 and 2020 by low- and middle-income countries to identify core themes and indicators.
Improving MDSR data accuracy and analysis for better understanding and decision-making
- Improving the identification and reporting of deaths, resulting in more accurate data on the number and causes of maternal deaths.
- Analyzing and interpreting MDSR data to identify and enact facility-based actions to reduce maternal deaths.
- Compiling and analyzing MDSR data to show the effect of program activities on reducing maternal deaths.
- Mapping locations of maternal deaths using Geographic Information Systems (GIS).
Preparing to implement MDSR
- Informing national MDSR guidelines in Uganda, Haiti, Cameroon, and Zambia.
- Training health staff at all levels of the health system to carry out each stage of the MDSR cycle.
- Developing a checklist to determine MDSR implementation readiness in humanitarian and vulnerable settings, such as refugee camps.
