What to know
Summary
Viruses
Illness
All data are preliminary and may change as more reports are received.
Directional arrows indicate changes between the current week and the previous week. Additional information on the arrows can be found at the bottom of this page.
A description of the CDC influenza surveillance system, including methodology and detailed descriptions of each data component is available on the surveillance methods page.1
Additional information on the current and previous influenza seasons for each surveillance component are available on FluView Interactive.
U.S. virologic surveillance
Nationally, the percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza virus in clinical laboratories remained stable (change of ≥ 0.5 percentage points) compared to the previous week. Although percent positivity remained stable nationally, this could be due to changes in healthcare seeking or reporting during the holidays rather than an indication that influenza activity has peaked. Percent positivity varied by region, with Region 6 at the highest percent (23.7%) and Region 4 at the lowest (14.4%). Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and A(H3N2) were the predominant viruses reported this week. For regional and state level data and age group distribution, please visit FluView Interactive. Viruses known to be associated with recent receipt of live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) or found upon further testing to be a vaccine virus are not included, as they are not circulating influenza viruses.
Clinical Laboratories
The results of tests performed by clinical laboratories nationwide are summarized below. Data from clinical laboratories (the percentage of specimens tested that are positive for influenza virus) are used to monitor whether influenza activity is increasing or decreasing.
| Week 1 | Data Cumulative since September 29, 2024 (Week 40) |
|
|---|---|---|
| No. of specimens tested | 116,253 | 1,224,789 |
| No. of positive specimens (%) | 21,652 (18.6%) | 85,175 (7.0%) |
| Positive specimens by type | ||
| Influenza A | 21,089 (97.4%) | 82,170 (96.5%) |
| Influenza B | 563 (2.6%) | 3,005 (3.5%) |

Public Health Laboratories
The results of tests performed by public health laboratories nationwide are summarized below. Data from public health laboratories are used to monitor the proportion of circulating influenza viruses that belong to each influenza subtype/lineage.
| Week 1 |
Data Cumulative since September 29, 2024 (Week 40) |
|
|---|---|---|
| No. of specimens tested | 2,658 | 30,352 |
| No. of positive specimens | 1,783 | 14,950 |
| Positive specimens by type/subtype | ||
| Influenza A | 1,743 (97.8%) | 14,460 (96.7%) |
| Subtyping Performed | 1,403 (80.5%) | 12,657 (87.5%) |
| (H1N1)pdm09 | 625 (44.5%) | 5,693 (45.0%) |
| H3N2 | 778 (55.5%) | 6,887 (54.4%) |
| H3N2v† | 0 | 0 |
| H5* | 0 | 77 (0.6%) |
| Subtyping not performed | 340 (19.5%) | 1,803 (12.5%) |
| Influenza B | 40 (2.2%) | 490 (3.3%) |
| Lineage testing performed | 18 (45.0%) | 260 (53.1%) |
| Yamagata lineage | 0 | 0 |
| Victoria lineage | 18 (100%) | 260 (100%) |
| Lineage not performed | 22 (55.0%) | 230 (46.9%) |
*These data reflect specimens tested, and the number determined to be positive for influenza viruses at the public health labs (specimens tested is not the same as cases). The data do not reflect specimens tested only at CDC and could include more than one specimen tested per person. The guidance for influenza A(H5) virus testing recommends testing both a conjunctival and respiratory swab for people with conjunctivitis which has resulted in more specimens testing positive for influenza A(H5) virus than the number of human A(H5) cases. For more information on the number of people infected with A(H5) viruses, please visit the "How CDC is monitoring influenza data among people to better understand the current avian influenza A (H5N1) situation"
†When an influenza virus that normally circulates in swine (but not people) is detected in a person, it is called a "variant" influenza virus. Most human infections with variant influenza viruses occur following exposure to swine, but human-to-human transmission can occur. It is important to note that in most cases, variant influenza viruses have not shown the ability to spread easily and sustainably from human-to-human.

*This graph reflects the number of specimens tested and the number determined to be positive for influenza viruses at the public health lab (specimens tested is not the same as cases). It does not reflect specimens tested only at CDC and could include more than one specimen tested per person. Specimens tested as part of routine influenza surveillance as well as those tested as part of targeted testing for people exposed to influenza A(H5) are included.
Novel Influenza A Virus Infections
No cases of influenza A(H5) were reported to CDC this week. To date, human-to-human transmission of influenza A(H5) virus has not been identified in the United States.
The Louisiana Department of Health has reported that the adult patient, aged ≥ 18 years, who had been hospitalized with H5N1 in Louisiana has died. This is the first person in the United States who has died as a result of an H5 infection. Additional information is available here: https://ldh.la.gov/news/H5N1-death.
The CSTE position statement, which includes updated case definitions for confirmed, probable, and suspected cases is available at http://www.cste.org/resource/resmgr/position_statements_files_2023/24-ID-09_Novel_Influenza_A.pdf
An up-to-date human case summary during the outbreak by state and exposure source is available at www.cdc.gov/bird-flu/situation-summary/index.html
Information about avian influenza is available at https://www.cdc.gov/flu/avianflu/index.htm.
Interim recommendations for Prevention, Monitoring, and Public Health Investigations are available at https://www.cdc.gov/bird-flu/prevention/hpai-interim-recommendations.html.
The latest case reports on avian influenza outbreaks in wild birds, commercial poultry, backyard or hobbyist flocks, and mammals in the United States are available from the USDA at https://www.aphis.usda.gov/aphis/ourfocus/animalhealth/animal-disease-information/avian/avian-influenza/2022-hpai.
Influenza Virus Characterization
CDC performs genetic and antigenic characterization of U.S. viruses submitted from state and local public health laboratories according to the Right Size Roadmap submission guidance. These data are used to compare how similar the currently circulating influenza viruses are to the reference viruses representing the current influenza vaccines. The data are also used to monitor evolutionary changes that continually occur in influenza viruses circulating in humans. CDC also tests susceptibility of circulating influenza viruses to antiviral medications including the neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir, zanamivir, and peramivir) and the polymerase acidic protein (PA) endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir. The HA clade and subclades were assigned using Nextclade (https://clades.nextstrain.org).
CDC has genetically characterized 803 influenza viruses collected since September 29, 2024.
| Virus Subtype or Lineage | Genetic Characterization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total No. of Subtype/Lineage Tested |
HA Clade |
Number (% of subtype/lineage tested) |
HA Subclade |
Number (% of subtype/lineage tested) |
|
| A/H1 | 316 | ||||
| 5a.2a | 180 (57.0%) | C.1.9 | 180 (57.0%) | ||
| 5a.2a.1 | 136 (43.0%) | D | 6 (1.9%) | ||
| D.1 | 2 (0.6%) | ||||
| D.3 | 15 (4.7%) | ||||
| D.5 | 113 (35.8%) | ||||
| A/H3 | 428 | ||||
| 2a.3a | 5 (1.2%) | G.1.3.1 | 5 (1.2%) | ||
| 2a.3a.1 | 423 (98.8%) | J.1 | 1 (0.2%) | ||
| J.1.1 | 3 (0.7%) | ||||
| J.2 | 383 (89.5%) | ||||
| J.2.1 | 8 (1.9%) | ||||
| J.2.2 | 28 (6.5%) | ||||
| B/Victoria | 59 | ||||
| 3a.2 | 59 (100%) | C.3 | 1 (1.7%) | ||
| C.5 | 7 (11.9%) | ||||
| C.5.1 | 37 (62.7%) | ||||
| C.5.6 | 8 (13.6%) | ||||
| C.5.7 | 6 (10.2%) | ||||
| B/Yamagata | 0 | ||||
| Y3 | 0 | Y3 | 0 | ||
CDC antigenically characterizes influenza viruses by hemagglutination inhibition (HI) (H1N1pdm09, H3N2, and B/Victoria viruses) or neutralization-based HINT (H3N2 viruses) using antisera that ferrets make after being infected with reference viruses representing the 2024-2025 Northern Hemisphere recommended cell or recombinant-based vaccine viruses. Antigenic differences between viruses are determined by comparing how well the antibodies made against the vaccine reference viruses recognize the circulating viruses that have been grown in cell culture. Ferret antisera are useful because antibodies raised against a particular virus can often recognize small changes in the surface proteins of other viruses. In HI assays, viruses with similar antigenic properties have antibody titer differences of less than or equal to 4-fold when compared to the reference (vaccine) virus. In HINT, viruses with similar antigenic properties have antibody neutralization titer differences of less than or equal to 8-fold. Viruses selected for antigenic characterization are a subset of the recent genetically characterized viruses and are chosen based on the genetic changes in their surface proteins and may not be proportional to the number of such viruses circulating in the United States.
Influenza A Viruses
- A(H1N1)pdm09: 40 A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses were antigenically characterized by HI, and all were well-recognized (reacting at titers that were within 4-fold of the homologous virus titer) by ferret antisera to cell-grown A/Wisconsin/67/2022-like reference viruses representing the A(H1N1)pdm09 component for the cell- and recombinant-based influenza vaccines.
- A(H3N2): 63 A(H3N2) viruses were antigenically characterized by HI or HINT, and 25 (39.7%) were well-recognized (reacting at titers that were within 4-fold of the homologous virus titer in HI or reacting at titers that were less than or equal to 8-fold of the homologous virus in HINT) by ferret antisera to cell-grown A/Massachusetts/18/2022-like reference viruses representing the A(H3N2) component for the cell- and recombinant-based influenza vaccines.
Influenza B Viruses
- B/Victoria: 7 influenza B/Victoria-lineage virus were antigenically characterized by HI, and all were well-recognized (reacting at titers that were within 4-fold of the homologous virus titer) by ferret antisera to cell-grown B/Austria/1359417/2021-like reference viruses representing the B/Victoria component for the cell- and recombinant-based influenza vaccines.
- B/Yamagata: No influenza B/Yamagata-lineage viruses were available for antigenic characterization.
Assessment of Virus Susceptibility to Antiviral Medications
CDC assesses susceptibility of influenza viruses to the antiviral medications including the neuraminidase inhibitors (oseltamivir, zanamivir, and peramivir) and the PA endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir using next generation sequence analysis supplemented by laboratory assays. Information about antiviral susceptibility test methods can be found at U.S. Influenza Surveillance: Purpose and Methods.
Viruses collected in the U.S. since September 29, 2024, were tested for antiviral susceptibility as follows:
| Antiviral Medication | Total Viruses | A/H1 | A/H3 | B/Victoria | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuraminidase Inhibitors | Oseltamivir | Viruses Tested | 803 | 322 | 423 | 58 |
| Reduced Inhibition | 1 (0.1%) | 1 (0.3%) | 0 | 0 | ||
| Highly Reduced Inhibition | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Peramivir | Viruses Tested | 803 | 322 | 423 | 58 | |
| Reduced Inhibition | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Highly Reduced Inhibition | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Zanamivir | Viruses Tested | 803 | 322 | 423 | 58 | |
| Reduced Inhibition | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Highly Reduced Inhibition | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| PA Cap-Dependent Endonuclease Inhibitor | Baloxavir | Viruses Tested | 776 | 262 | 454 | 60 |
| Decreased Susceptibility | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
One A(H1N1)pdm09 virus had NA-I223V and NA-S247N amino acid substitutions and showed reduced inhibition by oseltamivir.
High levels of resistance to the adamantanes (amantadine and rimantadine) persist among influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and influenza A(H3N2) viruses (the adamantanes are not effective against influenza B viruses). Therefore, use of these antivirals for treatment and prevention of influenza A virus infection is not recommended and data from adamantane resistance testing are not presented.
Outpatient and Emergency Department Illness Surveillance
Outpatient respiratory illness visits
The U.S. Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network (ILINet) monitors outpatient visits for respiratory illness referred to as influenza-like illness [ILI (fever plus cough or sore throat)], not laboratory-confirmed influenza, and will therefore capture respiratory illness visits due to infection with any pathogen that can present with similar symptoms, including influenza virus, SARS-CoV-2, and RSV. It is important to evaluate syndromic surveillance data, including that from ILINet, in the context of other sources of surveillance data to obtain a complete and accurate picture of influenza, SARS-CoV-2, and other respiratory virus activity.
Nationally, during Week 1, 6.1% of patient visits reported through ILINet were due to respiratory illness that included fever plus a cough or sore throat, also referred to as ILI. This week's percentage decreased slightly (change of > 0.1 percentage points) compared to Week 52 and is above the national baseline of 3.0% for the sixth consecutive week. The percentage of visits for ILI increased (change of > 0.1 percentage points) in HHS Region 1, remained stable in regions 2 and 3 (change of ≤ 0.1 percentage points), and decreased in all other regions (4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10) this week compared to last. All regions are above their respective baselines and ILI activity remains elevated across the country. The decrease this week compared to last could be due to changes in healthcare seeking or reporting during the holidays rather than an indication that influenza activity has peaked. Multiple respiratory viruses are co-circulating, and the relative contribution of influenza virus infections to ILI varies by location.

Outpatient respiratory illness visits by age group
About 70% of ILINet participants provide both the number of patient visits for respiratory illness and the total number of patient visits for the week broken out by age group. Based on these data, the percentage of visits for respiratory illness decreased (change of > 0.1 percentage point) in the 0-4 years and 5-24 years age groups, remained stable in the 25-49 years age group (change of ≤ 0.1 percentage points), and increased (change of > 0.1 percentage point) in the 50-64 years and 65+ years age groups in Week 1 compared to Week 52.

Outpatient respiratory illness activity map
Data collected in ILINet are used to produce a measure of ILI activity* by state/jurisdiction and Core Based Statistical Areas (CBSA).
| Activity Level | Number of Jurisdictions | Number of CBSAs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 (Week ending Jan. 4, 2025) |
Week 52 (Week ending Dec. 28, 2024) |
Week 1 (Week ending Jan. 4, 2025) |
Week 52 (Week ending Dec. 28, 2024) |
|
| Very High | 19 | 25 | 68 | 77 |
| High | 24 | 17 | 189 | 191 |
| Moderate | 5 | 6 | 136 | 135 |
| Low | 2 | 4 | 169 | 158 |
| Minimal | 5 | 3 | 141 | 133 |
| Insufficient Data | 0 | 0 | 226 | 235 |
*Data collected in ILINet may disproportionally represent certain populations within a jurisdiction or CBSA, and therefore, may not accurately depict the full picture of influenza activity for the entire jurisdiction or CBSA. Differences in the data presented here by CDC and independently by some health departments likely represent differing levels of data completeness with data presented by the health department likely being the more complete.
National Syndromic Surveillance System (NSSP)
The overall percentage of emergency department (ED) visits with a discharge diagnosis of influenza reported in NSSP was 4.8% during Week 1, a slight decrease (change of > 0.1 percentage points) from 5.3% the previous week. The percentage increased in regions 1 and 2, remained stable (change of ≤ 0.1 percentage points) in regions 3 and 5, and decreased (change of > 0.1 percentage points) in all other HHS regions in Week 1 compared to the previous week. The percentage increased among the 65+ years age group, remained stable (change of ≤ 0.1 percentage points) among the 18-64 years age group, and decreased among all other age groups in Week 1 compared to the previous week. The decreases this week compared to last could be due to changes in healthcare seeking or reporting during the holidays rather than an indication that influenza activity has peaked.

Hospitalization surveillance
FluSurv-NET
The Influenza Hospitalization Surveillance Network (FluSurv-NET) conducts population-based surveillance for laboratory-confirmed influenza-related hospitalizations in select counties in 14 states and represents approximately 9% of the U.S. population. FluSurv-NET hospitalization data are preliminary. As data are received each week, prior case counts and rates are updated accordingly.
A total of 7,096 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations were reported by FluSurv-NET sites between October 1, 2024, and January 4, 2025. The weekly hospitalization rate observed in Week 1 was 6.8 per 100,000 population. The cumulative hospitalization rate observed in Week 1 was 23.2 per 100,000 population.
Among all hospitalizations, 6,869 (96.8%) were associated with influenza A virus, 186 (2.6%) with influenza B virus, 8 (0.1%) with influenza A virus and influenza B virus co-infection, and 33 (0.5%) with influenza virus for which the type was not determined. Among those with influenza A subtype information, 574 (43.3%) were A(H1N1) pdm09 and 753 (56.7%) were A(H3N2).
When examining rates by age, the highest cumulative hospitalization rate per 100,000 population was among adults aged 65 years and older (68.4), followed by adults aged 50-64 years (25.9), children aged 0-4 years (22.3), adults aged 18-49 (11.0), and children aged 5-17 (7.7).
When examining age-adjusted rates by race and ethnicity, the highest cumulative hospitalization rate per 100,000 population was among non-Hispanic Black persons (36.9), followed by American Indian/Alaska Native persons (33.6), Hispanic persons (23.0), non-Hispanic White persons (18.6), and Asian/Pacific Islander persons (16.0).

**In this figure, weekly rates for all seasons prior to the 2024-2025 season reflect end-of-season rates. For the 2024-2025 season, rates for recent hospital admissions are subject to reporting delays and are shown as a dashed line for the current season. As hospitalization data are received each week, prior case counts and rates are updated accordingly.
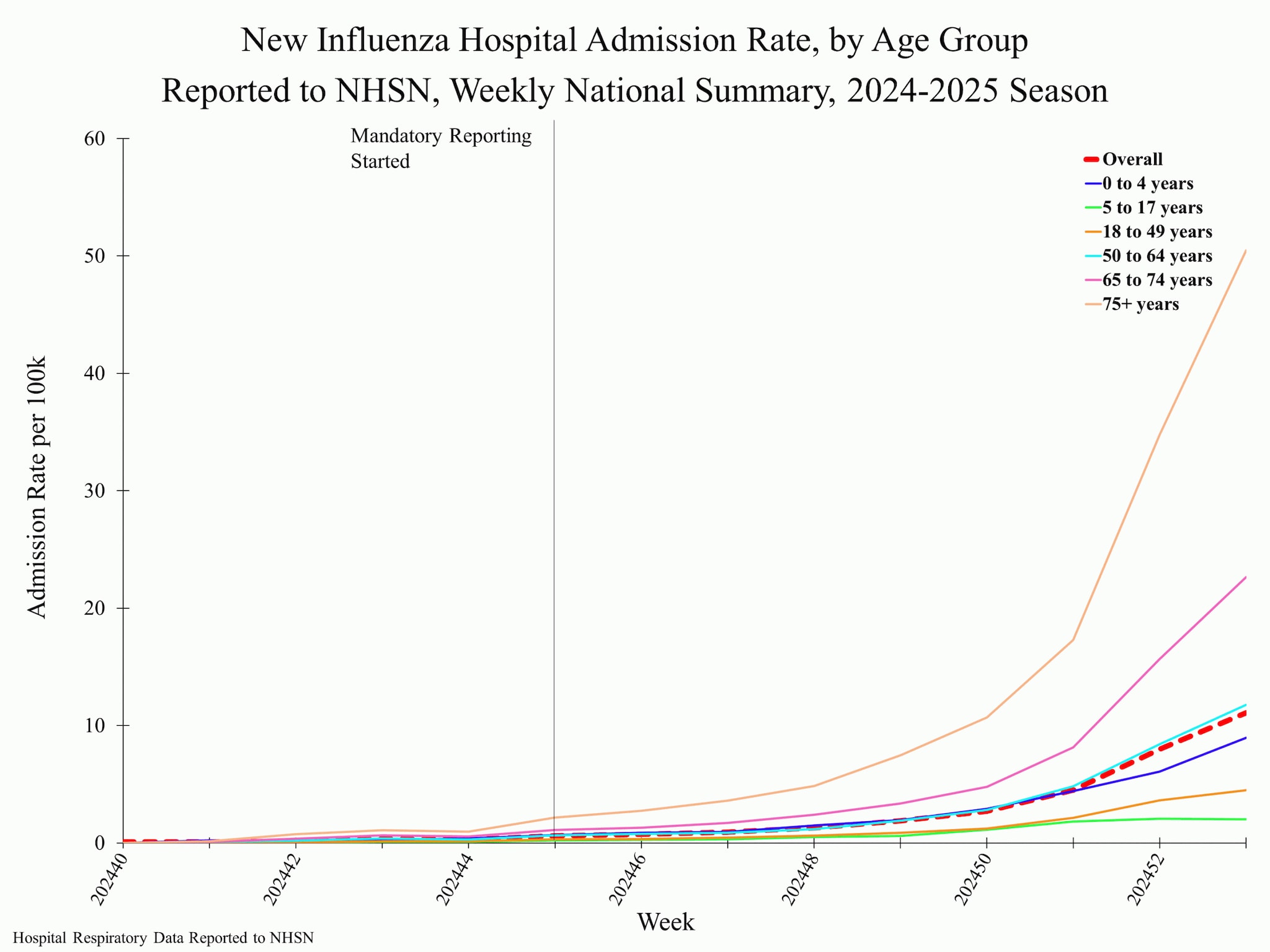
National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Hospital Respiratory Data
Hospitals report to NHSN the weekly number of patients with laboratory-confirmed influenza who were admitted to the hospital. Nationally, during Week 1, 37,434 laboratory confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations were reported. This is an increase (change of > 5%) compared to Week 52.
The weekly hospital admission rate observed in Week 1 was 11.1 per 100,000. The weekly rate of hospital admissions in all 10 HHS regions ranged from 8.9 (Region 10) to 16.9 (Region 2). The weekly rate of hospitalizations decreased in Region 10 and increased in all other regions (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9). The decrease in Region 10 this week compared to last week could be due to changes in healthcare seeking or reporting during the holidays rather than an indication that influenza activity has peaked.
When examining rates by age for Week 1, the 5-17-years age group remained stable (change of < 5%) while the remaining age groups (0-4 years, 18-49 years, 50-64 years, 65-74 years, and 75+ years) increased this week (change of > 5%) compared to last. The highest hospital admission rate per 100,000 population was among the 75+ years age group (50.5), followed by 65-74-years (22.6), and 50-64-years (11.8).
Mortality surveillance
National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) Mortality Surveillance
Based on NCHS mortality surveillance data available on January 10, 2025, 1.1% of the deaths that occurred during the week ending January 4, 2025 (Week 1), were due to influenza. This percentage increased (> 0.1 percentage point change) compared to Week 52. The data presented are preliminary and may change as more data are received and processed.

Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality
Six influenza-associated pediatric deaths were reported to CDC during Week 1.
Five deaths occurred during the 2024-2025 season, bringing the total pediatric deaths for this season to 16. The deaths occurred during Week 52 of 2024 (the week ending December 28, 2024) and Week 1 of 2025 (the week ending January 4, 2025). Four of the deaths were associated with influenza A viruses that had subtyping performed; three were A(H1N1) viruses and one was an A(H3) virus. One death was associated with an influenza B virus with no lineage determined.
One death occurring during the 2023-2024 season was also reported, which brings the total number of pediatric deaths for last season to 207. This death was associated with an influenza B virus with no lineage determined and occurred during Week 14 of 2024 (the week ending April 6, 2024).

Additional National and International Influenza Surveillance Information
Indicators Status by System
Increasing: 
Decreasing: 
Stable: 
Clinical Labs: Up or down arrows indicate a change of greater than or equal to 0.5 percentage points in the percent of specimens positive for influenza compared to the previous week.
Outpatient Respiratory Illness (ILINet): Up or down arrows indicate a change of greater than 0.1 percentage points in the percent of visits due to respiratory illness (ILI) compared to the previous week.
NHSN Hospitalizations: Up or down arrows indicate change of greater than or equal to 5% of the number of patients admitted with laboratory-confirmed influenza compared to the previous week.
NCHS Mortality: Up or down arrows indicate change of greater than 0.1 percentage points of the percent of deaths due to influenza compared to the previous week.
Additional surveillance information
FluView Interactive: FluView includes enhanced web-based interactive applications that can provide dynamic visuals of the influenza data collected and analyzed by CDC. These FluView Interactive applications allow people to create customized, visual interpretations of influenza data, as well as make comparisons across flu seasons, regions, age groups and a variety of other demographics.
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health: Monthly surveillance data on the prevalence of health-related workplace absenteeism among full-time workers in the United States are available from NIOSH.
U.S. State and local influenza surveillance: Select a jurisdiction below to access the latest local influenza information.
Public Health Agency of Canada:
The most up-to-date influenza information from Canada is available in Canada's weekly FluWatch report.
Public Health England:
The most up-to-date influenza information from the United Kingdom is available from Public Health England.
Any links provided to non-Federal organizations are provided solely as a service to our users. These links do not constitute an endorsement of these organizations or their programs by CDC or the Federal Government, and none should be inferred. CDC is not responsible for the content of the individual organization web pages found at these links.
A description of the CDC influenza surveillance system, including methodology and detailed descriptions of each data component is available on the surveillance methods page.
