Key points
- Most people get ehrlichiosis from the bite of an infected tick.
- Ehrlichiosis can be spread through blood transfusion and organ transplant.
- Ehrlichiosis is most frequently reported from the southeastern and south-central United States, from the East Coast extending westward to Texas.

Causes
Ehrlichiosis is the general name used to describe diseases caused by the bacteria Ehrlichia chaffeensis, E. ewingii, or E. muris eauclairensis in the United States. The majority of reported cases are due to infection with E. chaffeensis.
How it spreads
Ticks
Most people get ehrlichiosis from the bite of an infected tick.
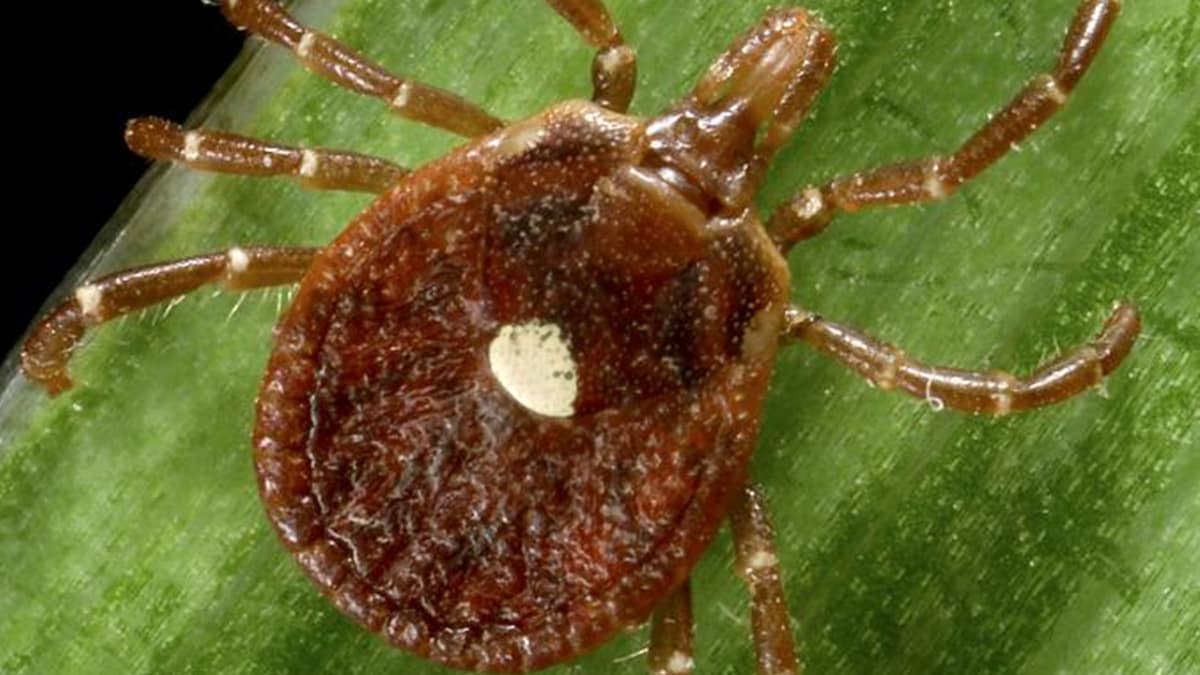
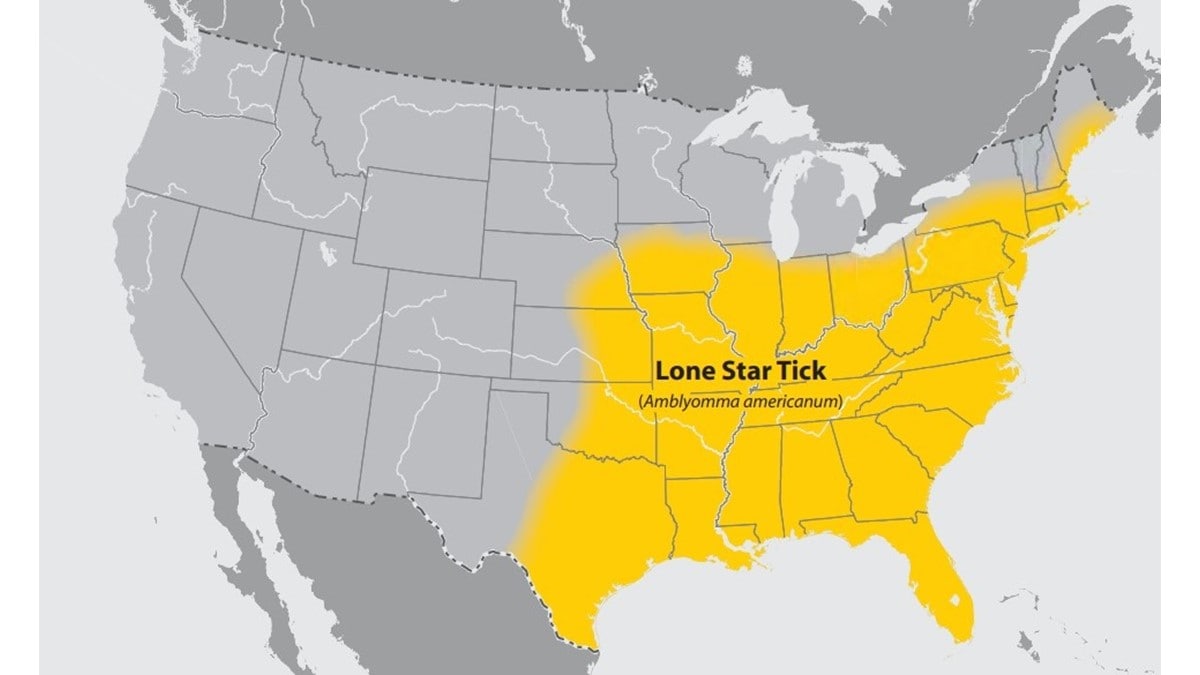
In the United States, E. chaffeensis and E. ewingii are carried by the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum), found primarily in the south-central and eastern United States.
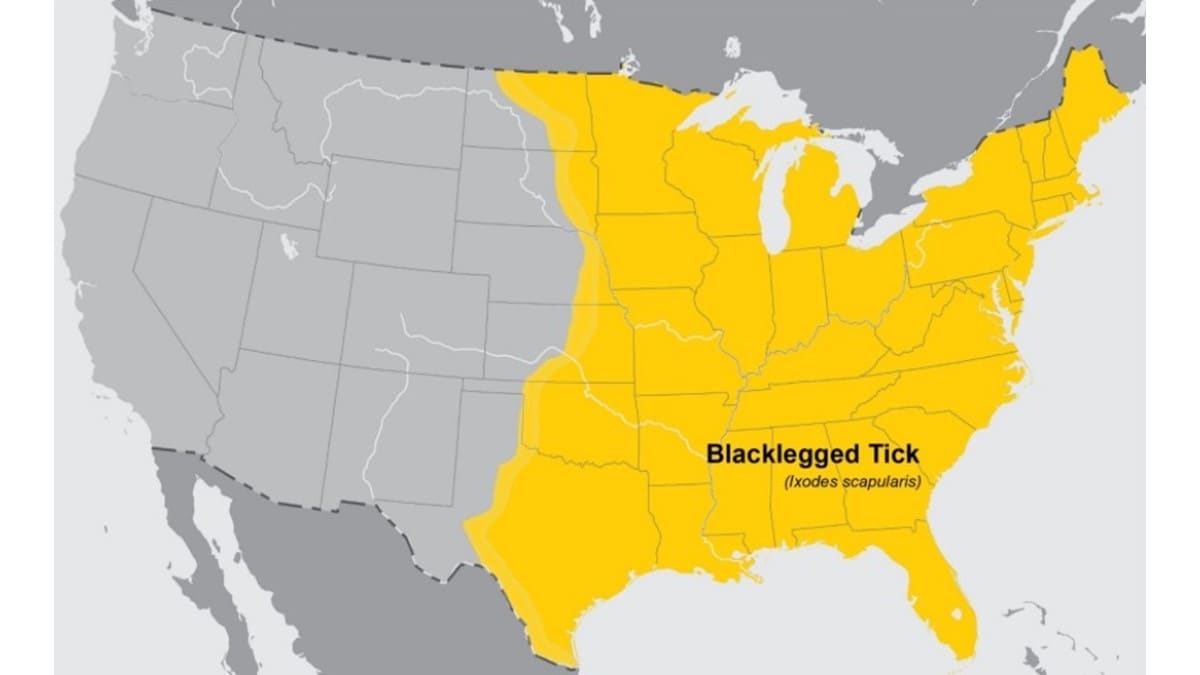
E. muris eauclairensis is carried by the blacklegged tick (Ixodes scapularis). While the blacklegged tick is widely distributed in the eastern United States, E. muris eauclairensis cases have only been reported from Wisconsin and Minnesota.
Blood transfusion and organ transplant
In rare cases, Ehrlichia species have been spread through blood transfusion and organ transplant.
Range
Ehrlichiosis caused by E. chaffeensis and E. ewingii is most frequently reported from the southeastern and south-central United States, from the East Coast extending westward to Texas.
