Key points
- All adults can benefit from being physically active.
- Healthcare providers can help adults with disabilities find activities to match their abilities and preferences.
- Find ideas to help adults with disabilities improve their physical activity.
Format: PDF
Language: English (US)
Infographic: Increasing Physical Activity Among Adults with Disabilities
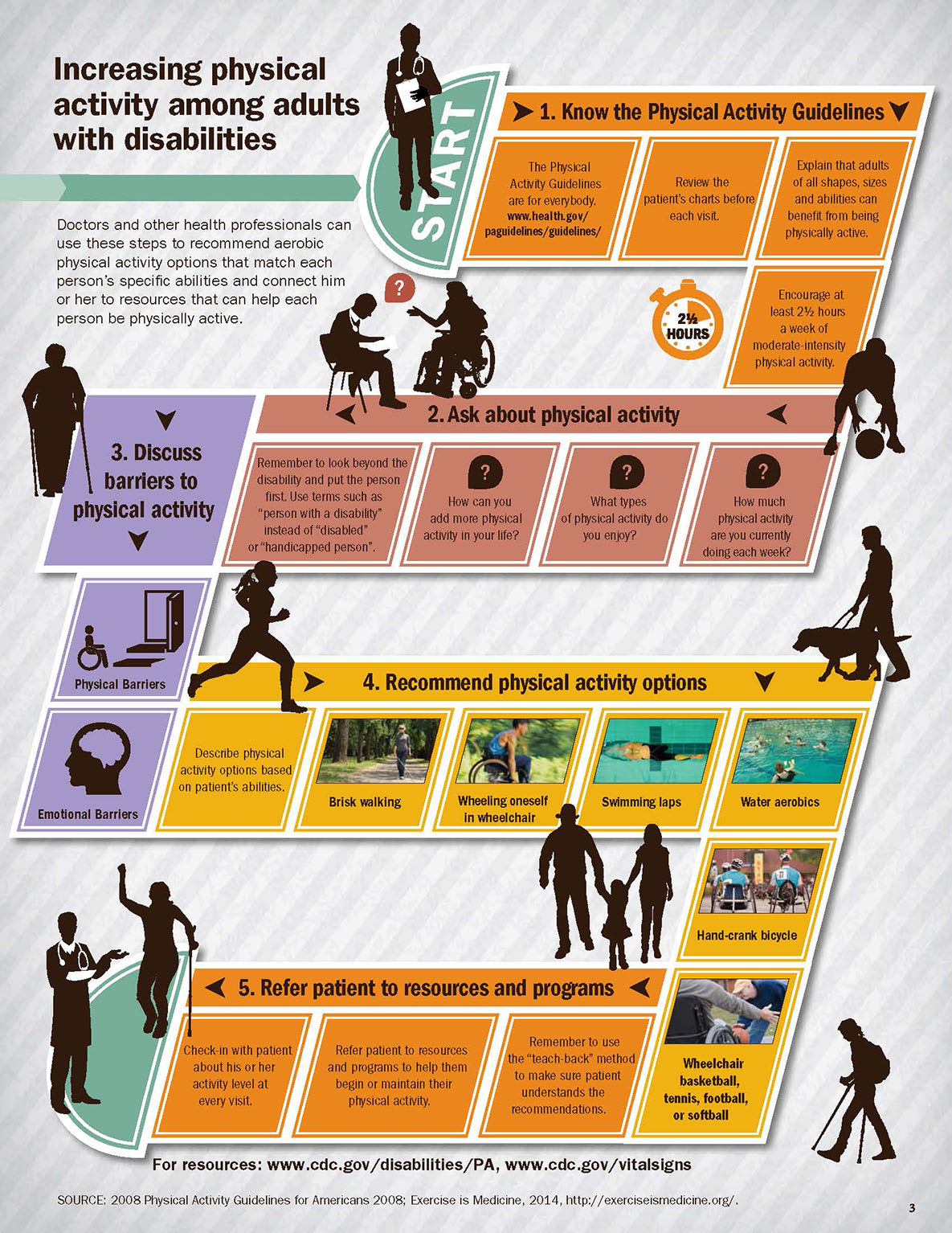
Description
Title: Increasing physical activity among adults with disabilities
Doctors and other health professionals can use these steps to recommend aerobic physical activity options that match each person’s specific abilities and connect him or her to resources that can help each person be physically active.
1. Know the Physical Activity Guidelines
- The Physical Activity Guidelines are for everybody. www.health.gov/paguidelines/guidelines/
- Review the patient's charts before each visit.
- Explain that adults of all shapes, sizes, and abilities can benefit from being physically active.
- Encourage at least 2½ hours a week of moderate-intensity physical activity.
2. Ask about physical activity
- How much physical activity are you currently doing each week?
- What types of physical activity do you enjoy?
- How can you add more physical activity in your life?
- Remember to look beyond the disability and put the person first. Use terms such as "person with a disability" instead of "disabled" or "handicapped person".
3. Discuss barriers to physical activity
- Physical barriers
- Emotional barriers
4. Recommend physical activity options
- Describe physical activity options based on patient's abilities.
- Brisk walking
- Wheeling oneself in wheelchair
- Swimming laps
- Water aerobics
- Hand-crank bicycle
- Wheelchair basketball, tennis, football, or softball
- Brisk walking
5. Refer patient to resources and programs
- Remember to use the "teach-back" method to make sure patient understands the recommendations.
- Refer patient to resources and programs to help them begin or maintain their physical activity.
- Check-in with patient about his or her activity level at every visit.
Content Source:
Disability and Health; National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities
- 2008 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans 2008; Exercise is Medicine, 2014, http://exerciseismedicine.org/.
