At a glance
Oral cholera vaccines (OCV) can be used to help prevent and control cholera, in addition to other standard prevention measures including improved access to clean water, adequate sanitation, and good hygiene practices.
Preventing cholera with vaccines
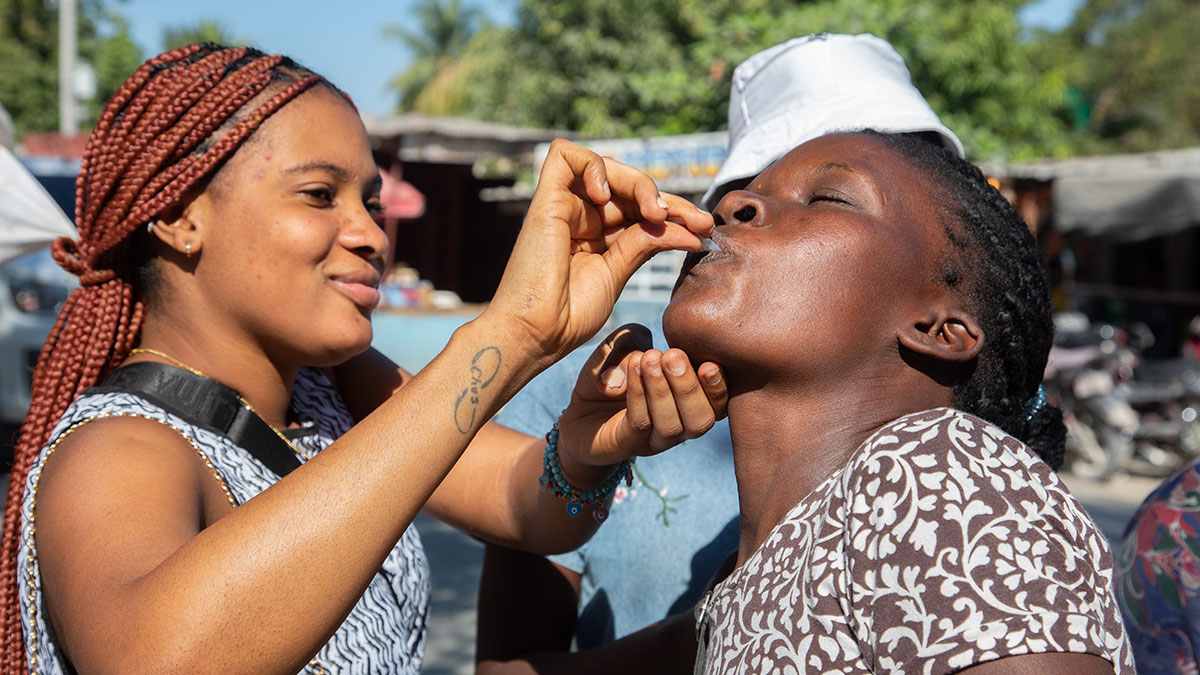
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that countries use cholera vaccines in these circumstances:
- During cholera outbreaks
- During humanitarian crises with a high risk of cholera
- In areas where local transmission of cholera occurs regularly, as part of a national cholera prevention program
Two doses of OCV protects against cholera for at least 3 years, preventing about 2 of 3 cholera infections.
In recent years there has been a surge in cholera outbreaks, and the demand for OCV has greatly outweighed the supply. Since October 2022, only one dose of vaccine is being used in outbreak responses. One dose provides protection for about a year.
Access to oral cholera vaccines
Accessing OCV
After the cholera outbreak in Haiti in 2010, which killed nearly 10,000 people, global partners established an OCV stockpile in 2013 to respond to outbreaks and help save lives.
In January 2023, global partners launched a program for countries to get vaccines for preventive OCV campaigns in countries where cholera regularly occurs.
CDC supports cholera vaccine use
CDC works with countries and global partners to prevent and control cholera with vaccines by supporting and strengthening local capacity so countries can better:
- Use OCV to respond to cholera outbreaks
- Identify areas most at risk of cholera for preventive campaigns
- Plan, implement, monitor, and evaluate OCV campaigns
CDC also conducts research to answer questions about OCV effectiveness and impact.
In partnership with the Global Task Force on Cholera Control, CDC supports the implementation of the vaccine component of Ending Cholera, A Global Roadmap to 2030 by:
- Developing technical guidance on how to request, prioritize, use, and allocate OCVs
- Supporting countries to develop and pre-review their multi-year preventive OCV requests
