At a glance
- Report possible or confirmed cases of C. auris immediately.
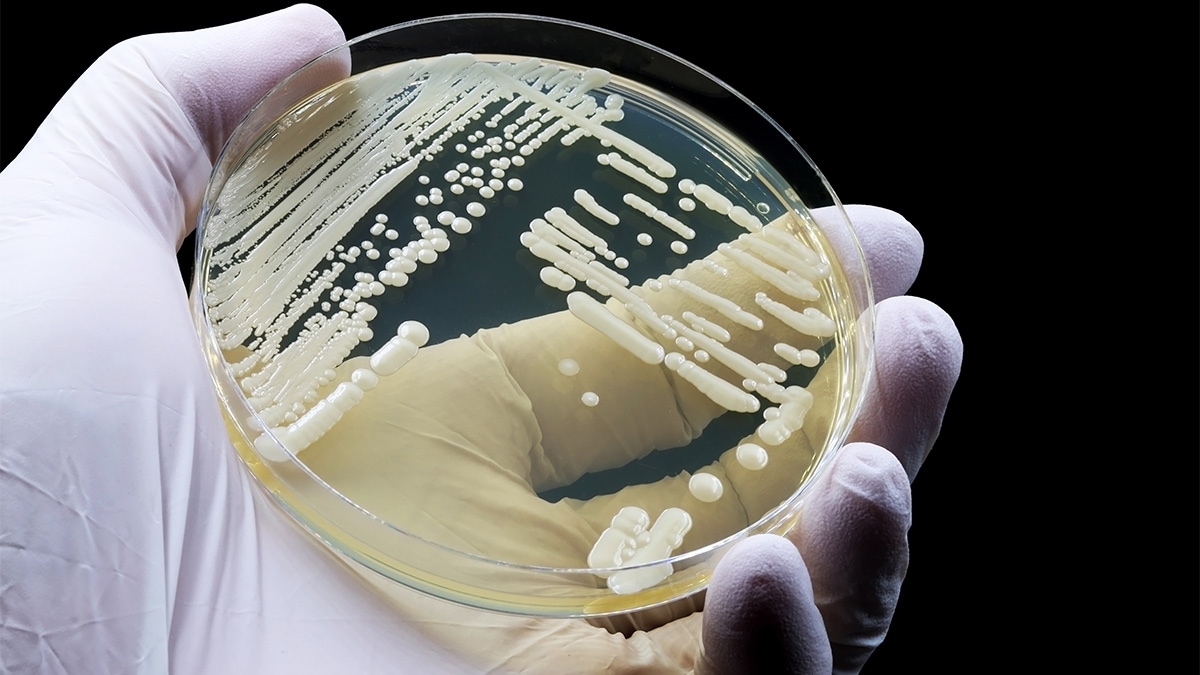
- There are no phenotypic characteristics to easily distinguish C. auris from other Candida species.
- The most reliable way to identify C. auris is MALDI-TOF MS.
- Real-time PCR is the preferred method for detecting colonization.

Laboratory processes and resources
Report possible or confirmed cases
Early detection of C. auris is critical to limiting its spread. Report any possible or confirmed cases immediately to the facility's infection control and prevention department. Follow facility processes for reporting to the state or local public health department.
Confirming C. auris
There are no phenotypic characteristics that can easily distinguish C. auris from other Candida species. The most reliable way to identify C. auris is matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). There are several alternative methods to identify C. auris.
Antifungal susceptibility testing
Perform antifungal susceptibility testing for C. auris following Infectious Disease Sociate of America (IDSA) guidelines. The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) has not yet defined breakpoints for C. auris but CDC has established tentative breakpoints based on expert opinion and breakpoints established for closely related species that can be used in the interim.
Surveillance
Healthcare facilities are encouraged to begin screening patients for C. auris after the initial case is identified. Typically skin swab specimens are tested. There are several methods to detect colonization but Real-time PCR is preferred.