What to know
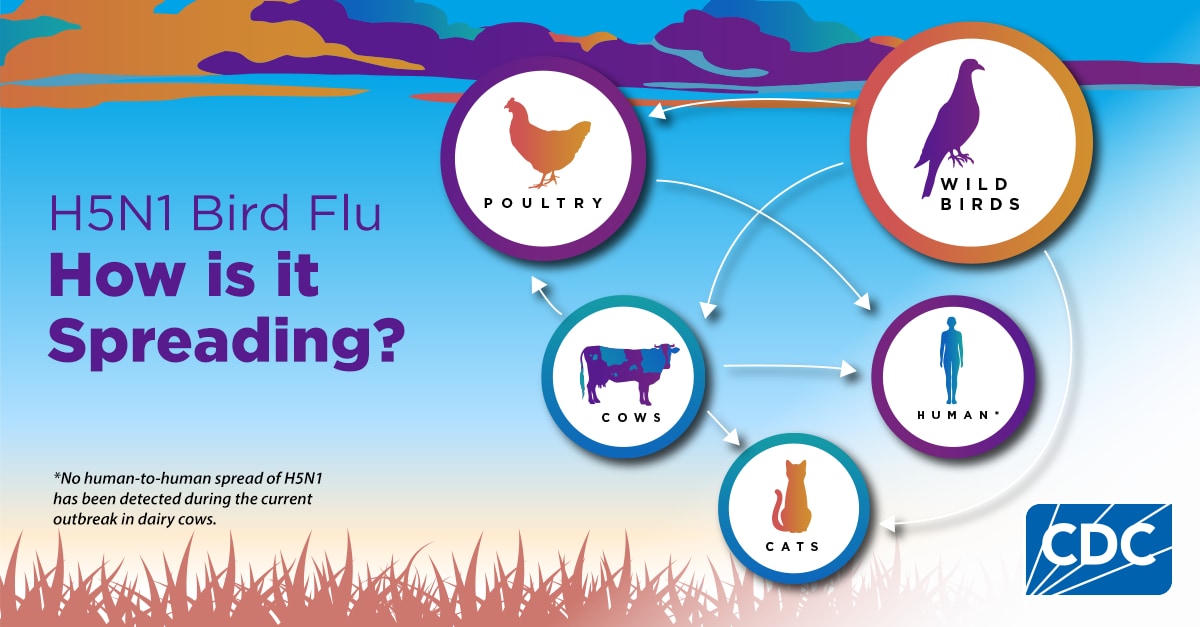
- H5 bird flu is widespread in wild birds worldwide and is causing outbreaks in poultry and U.S. dairy cows with several recent human cases in U.S. dairy and poultry workers.
- While the current public health risk is low, CDC is watching the situation carefully and working with states to monitor people with animal exposures.
- CDC is using its flu surveillance systems to monitor for H5 bird flu activity in people.
Current situation
Confirmed human case summary during the 2024 outbreak, by state and exposure source
Exposure Source
| State | Exposure Associated with Commercial Agriculture and Related Operations | Other Animal Exposure† | Exposure Source Unknown‡ | State Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy Herds (Cattle) | Poultry Farms and Culling Operations |
||||
| California | 36 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 37 |
| Colorado | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| Iowa | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Louisiana | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Michigan | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Missouri | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Oregon | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Texas | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Washington | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Wisconsin | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Source Total | 40 | 23 | 1 | 2 | 66 |
NOTE: One additional case was previously detected in a poultry worker in Colorado in 2022.
†Exposure was related to other animals such as backyard flocks, wild birds, or other mammals
‡Exposure source was not able to be identified
Probable human case summary during the 2024 outbreak, by state and exposure source
When a case tests positive for H5 at a public health laboratory but testing at CDC is not able to confirm H5 infection, per Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists (CSTE) guidance, a case is reported as probable.
- Probable cases with commercial poultry exposure (e.g., poultry farms or culling operations):
- Washington (3)
- Arizona (2)
- Washington (3)
- Probable cases with commercial dairy (cattle) exposure:
- California (1)
- California (1)
- Probable cases with exposure source unknown:
- Delaware (1)
- Delaware (1)
Confirmed and probable cases are typically updated by 5 PM EST on Mondays (for cases confirmed by CDC on Friday, Saturday, or Sunday), Wednesdays (for cases confirmed by CDC on Monday or Tuesday), and Fridays (for cases confirmed by CDC on Wednesday and Thursday). Affected states may report cases more frequently.
National flu surveillance (since February 25, 2024)
Targeted H5 surveillance (since March 24, 2024)
Detections in Animals
- 10,922 wild birds detected as of 1/3/2025 | Full Report
- 51 jurisdictions with bird flu in wild birds
- 129,795,101 poultry affected as of 1/2/2024 | Full Report
- 50 states with outbreaks in poultry
- 915 dairy herds affected as of 1/2/2024 | Full Report
- 16 states with outbreaks in dairy cows
These data will be updated daily, Monday through Friday, after 4 p.m. to reflect any new data.
Cumulative data on wild birds have been collected since January 20, 2022. Cumulative data on poultry have been collected since February 8, 2022. Cumulative data on humans in the U.S. have been collected since April 28, 2022. Cumulative data on dairy cattle have been collected since March 25, 2024.
Protective Actions for People
- Protective actions around wild birds Avoid direct contact with wild birds and observe them only from a distance, if possible. Learn more.
- What to do if you find a dead bird Avoid contact with wild or domestic birds that appear ill or have died and call to report sick or dead birds. Learn more.
- Protective actions around other animals with H5N1 bird flu Avoid unprotected exposure to infected live or dead animals or surfaces contaminated by them. Learn more.
- Protective actions if you work with potentially infected dairy cattle Avoid unprotected direct physical contact or close exposure with cattle and materials potentially infected or confirmed to be infected with HPAI A(H5) virus. Learn more.
- Consuming Milk People should not eat or drink raw milk or products made with raw milk. Choosing pasteurized milk is the best way to keep you and your family safe. Learn more.
- Preparing food It is safe to eat properly handled and cooked poultry in the United States. There are recommendations around products from other animals with H5 virus infections, including cattle and milk. Learn more.
- Traveling to other countries CDC does not currently recommend any travel restrictions related to bird flu to countries affected by bird flu in birds, other animals or people. Learn more.
- If you have contact with infected birds or other animals and become sick Learn what to do if you have contact with infected birds or other animals and become sick. Learn more.
- Clinicians can visit CDC's avian influenza (bird flu) information for health professionals for the latest guidance. Learn more.
- Public health professionals and laboratorians can visit CDC's avian influenza (bird flu) information for public health partners for the latest guidance. Learn more.
- Get a seasonal flu vaccine Seasonal flu vaccination will not prevent infection with bird flu viruses, but can reduce the risk of getting sick with human influenza viruses and thus the risk for seasonal and bird flu co-infection. Learn more.
