Key points
- Symptoms of alpha-gal syndrome (AGS) can range from mild to severe, and some may be life-threatening.
- They usually appear 2–6 hours after being exposed to products containing alpha-gal, like red meat or dairy products.
- If you are having a severe allergic reaction, seek immediate emergency care.
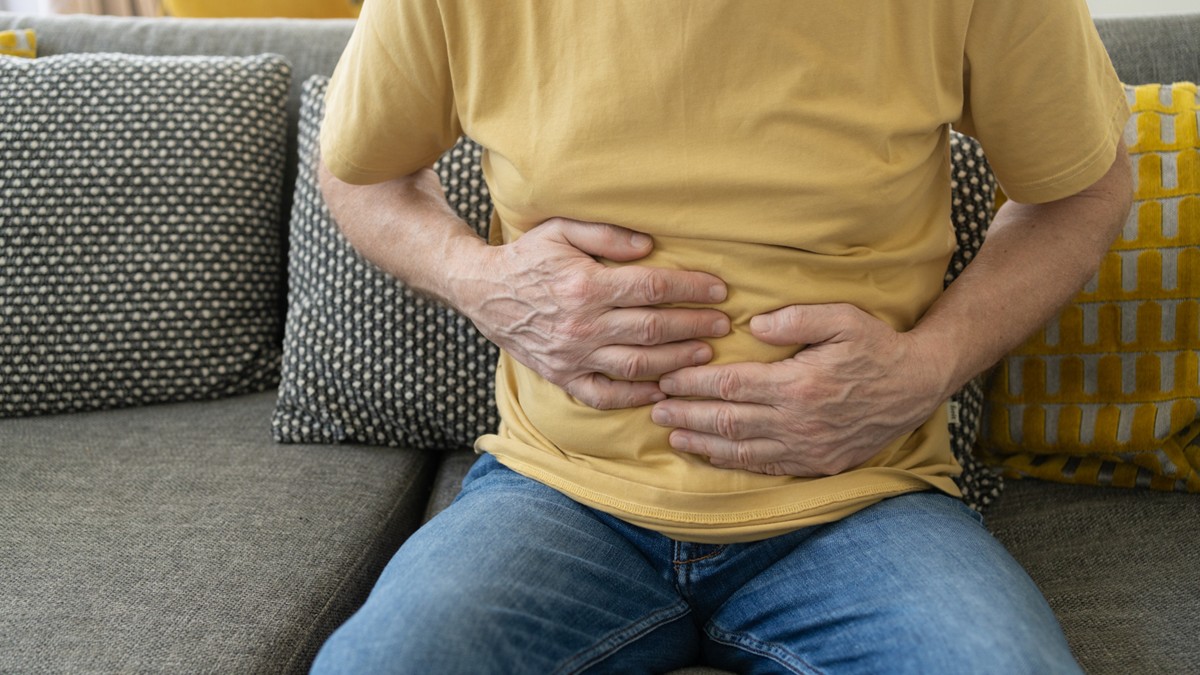
What to look out for
AGS reactions can be different from person to person. They can range from mild to severe, and some may be life-threatening. People with AGS might not react to every product containing alpha-gal, and some people can experience different symptoms or reactions each time they are exposed to alpha-gal, even when it is the same product.
Symptoms usually appear 2–6 hours after eating red meat or dairy products. They also may appear after exposure to products containing alpha-gal (for example, gelatin-coated medications).
When to seek emergency care
AGS reactions can include:
- Hives or itchy rash
- Nausea or vomiting
- Severe stomach pain
- Heartburn or indigestion
- Diarrhea
- Cough, shortness of breath, or difficulty breathing
- Drop in blood pressure
- Swelling of the lips, throat, tongue, or eye lids
- Dizziness or faintness
- A combination of symptoms referred to as anaphylaxis
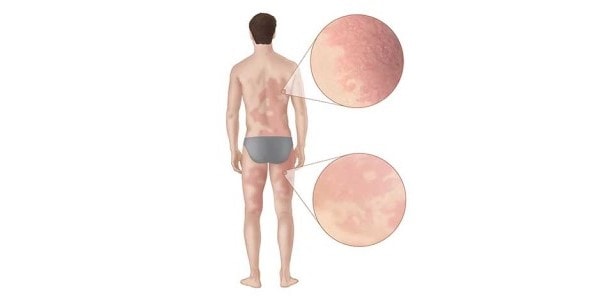
When to seek emergency help
AGS can be severe and even life-threatening. Seek immediate emergency care if you are having a severe allergic reaction.
If you think you may have AGS, talk to your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider may prescribe an epinephrine auto-injector (e.g. "EpiPen") or epinephrine nasal spray. Work with your healthcare provider to learn how to use the products. Ask your healthcare provider how to prepare for an allergic reaction and to recognize anaphylaxis. People who need to use epinephrine auto-injectors or nasal spray should still seek emergency care.
