Key points
- Acanthamoeba is a free-living ameba, a kind of one-celled organism that lives in water, soil, and dust.
- Most people will come into contact with Acanthamoeba at some point, but most won't get sick. Although rare, some people develop serious Acanthamoeba infections that are often fatal.
- See a healthcare provider right away if you have symptoms of an Acanthamoeba infection.

Overview
Most people will be exposed to Acanthamoeba during their lifetime. The ameba is found in soil and dust as well fresh water and saltwater. It can also be found in swimming pools, hot tubs, drinking water systems, humidifiers, and in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
Most people exposed to Acanthamoeba won't get sick. For others, it can cause serious infections of the brain, skin, eyes, and sinuses. Acanthamoeba can infect parts of the body through cuts or skin wounds or from being inhaled into the lungs or nostrils. It can get into the eyes through contact lens use.
Types
Non-keratitis Acanthamoeba infections
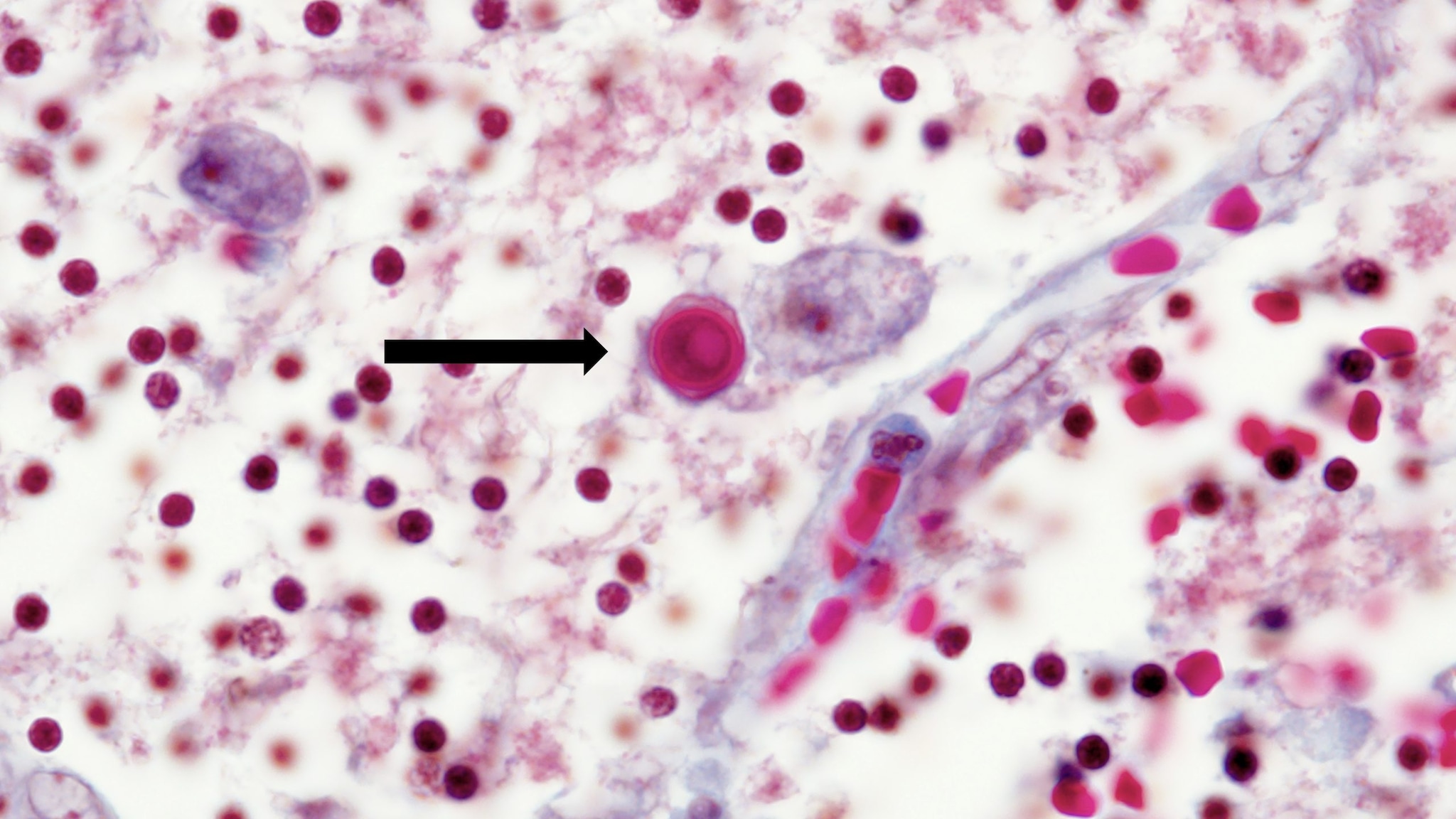
Non-keratitis Acanthamoeba infections are rare but serious infections that can affect one or many parts of the body. These infections usually occur in people with weakened immune systems and include:
- Granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE), which affects the brain and is almost always fatal
- Cutaneous acanthamoebiasis, a skin infection
- Acanthamoeba rhinosinusitis, an infection of the nasal cavity and sinuses
- Disseminated infection, which affects multiple parts of the body. GAE, cutaneous acanthamoebiasis, and Acanthamoeba rhinosinusitis can all spread to cause disseminated infections.
Acanthamoeba keratitis
Acanthamoeba keratitis is an eye infection that typically occurs in healthy people and can cause permanent vision loss. Most people in the United States who get this infection wear contact lenses. The infection usually doesn't spread to other parts of the body.
Free-living amebas
A free-living ameba is a kind of one-celled organism that lives in water and soil around the world. Most people will come into contact with these amebas during their lives but won't get sick. Others will develop rare but serious infections.
Although there are several types of free-living amebas that live in the environment, three are known to cause severe disease in people:
- Acanthamoeba
All of these amebas can cause life-threatening brain infections. Some can also cause infections of the eyes, skin, sinuses, and other parts of the body.
