What to know
- Acanthamoeba keratitis occurs when the Acanthamoeba ameba infects the eye.
- The disease can lead to permanent vision loss.
- See your eye doctor right way if you have symptoms of Acanthamoeba keratitis.
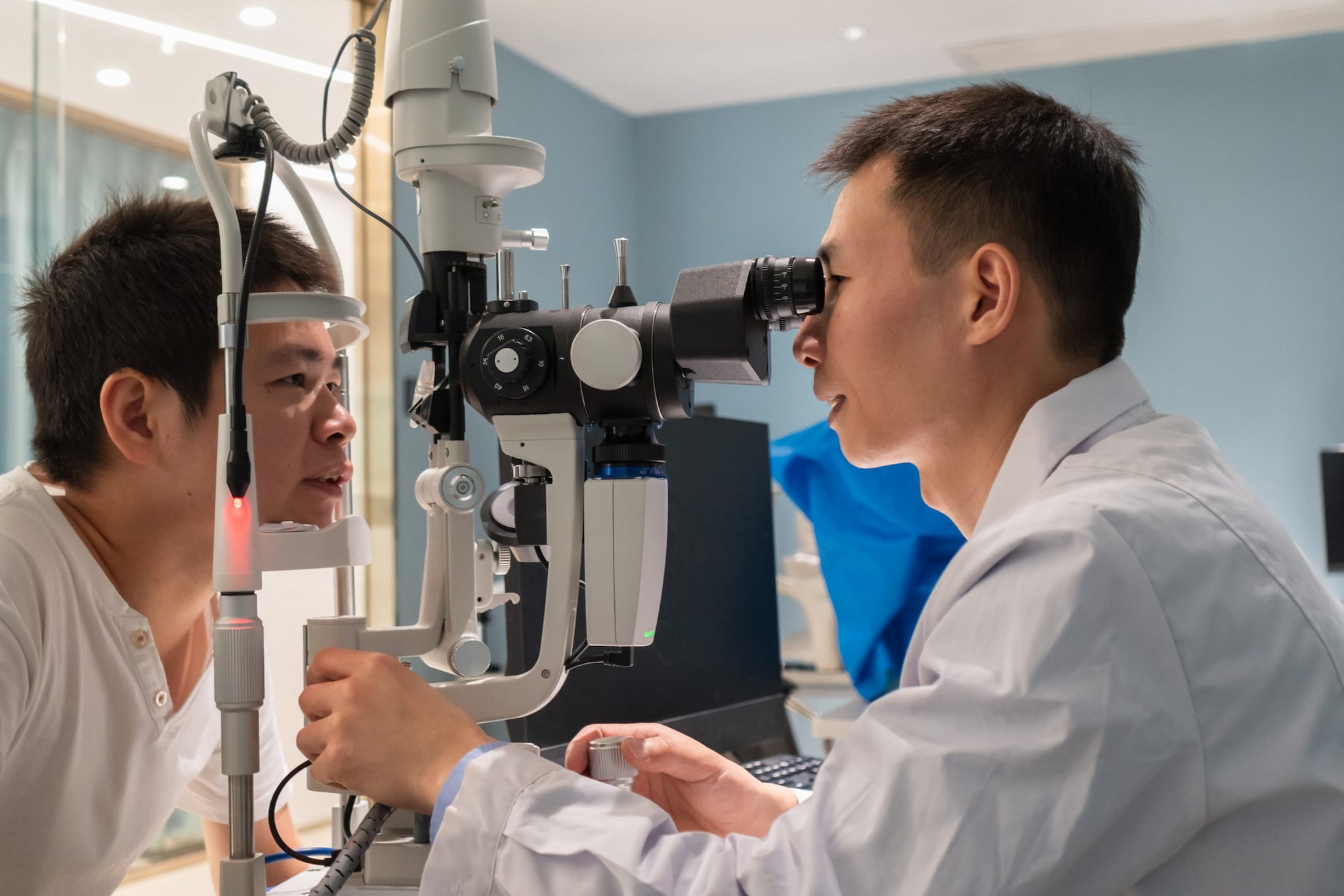
Overview
Acanthamoeba can be found in water, soil, and dust. Acanthamoeba keratitis is a rare disease that occurs when the ameba infects the cornea, the transparent outer covering of the eye. If untreated, the disease can cause severe pain and permanent vision loss.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of Acanthamoeba keratitis can appear like symptoms of other more common eye infections. Symptoms also can differ from person to person, last several weeks or months, and include:
- Eye pain
- Eye redness
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Sensation of having something in your eye
- Excessive tearing
Exposure risks
Anyone can get Acanthamoeba keratitis, but it's most common among people who wear contact lenses. Poor contact lens hygiene or wearing contact lenses while swimming, using a hot tub, or showering may increase the risk of Acanthamoeba entering the eye. However, some contact lens users who practice proper hygiene can also develop an Acanthamoeba infection.
Prevention

To protect against Acanthamoeba keratitis and other eye infections, contact lens wearers should follow healthy habits, including:
- Washing your hands with soap and water and drying them before handling contacts
- Removing contact lenses before showering, using a hot tub, or swimming
- Cleaning, rubbing, and rinsing lenses every time you take them out
- Storing lenses properly
