COVID-19
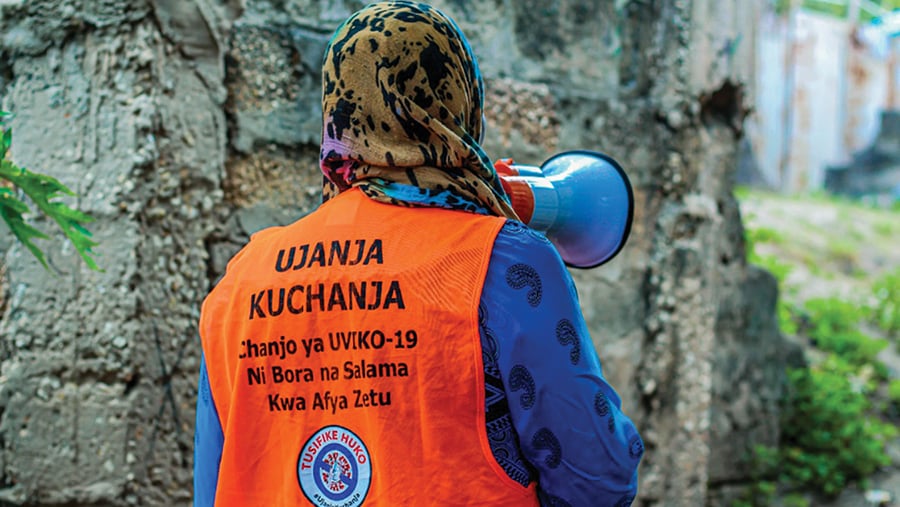


The first case of COVID-19 in Tanzania was confirmed in March 2020, and CDC was on the frontlines supporting the Government of Tanzania (GOT) response with surveillance, infection prevention and control (IPC), border health efforts, activation of rapid response teams, and mobilization of disease detectives from the supported Field Epidemiology and Laboratory Training Program. As cases of COVID-19 surged, CDC helped the GOT decentralize COVID-19 testing from the National Public Health Laboratory in Dar es Salaam to laboratories across the country. This work included establishing COVID-19 molecular testing in Zanzibar, Arusha, Dodoma, Mwanza and introducing COVID-19 rapid antigen tests in country. CDC support for COVID-19 diagnostics in Tanzania improved the turn-around time of COVID-19 test results and helped health care providers recommend appropriate care to further reduces the mortality rate and complications related to COVID-19.
In June 2021, Tanzania joined COVAX, a global partnership dedicated to establishing fair and equal access to COVID-19 vaccines for every country in the world. The first 1 million COVID-19 vaccine doses – donated by the U. S. government and delivered by COVAX – arrived in Tanzania on July 24, 2021. CDC Tanzania leveraged existing President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) service delivery platforms and resources from the Global Health Security Agenda (GHSA) to expand vaccine coverage. These targeted efforts greatly accelerated vaccinations of people living with HIV (PLHIV), healthcare workers, and community health workers and the training, orientation, and data entry for COVID-19 vaccinators. Seventeen CDC Tanzania staff deployed to supported regions to provide a hands-on six-week surge of technical assistance around vaccine distribution planning, service delivery, the establishment of vaccination points in HIV clinics and other clinics to increase vaccine access, strengthening vaccination confidence, and increasing vaccination demand by using influential local leaders, religious leaders, and community healthcare workers. Through these initial efforts, more than 40% of people living with HIV and 80-90% of CDC-supported community and health facility workers got at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the six-week surge campaign.
![]()
Strengthening Health Information Systems to Respond to COVID-19:
With extensive technical assistance from CDC and support from other donors, Tanzania developed and integrated electronic health information systems to monitor COVID-19 cases and vaccines administers. The CDC support systems include the COVID-19 Digital App collected information on COVID cases identified within health facilities; PIMA- COVID App managed laboratory COVID-19 test results; Afyamsafiri App captured comprehensive travelers’ surveillance to mitigate the importation and exportation of cases; and Chanjocovid, provided COVID-19 vaccine information system to track vaccines administered. CDC continues to support their integration to the national surveillance systems to support real time data analyses for action and inform policy.
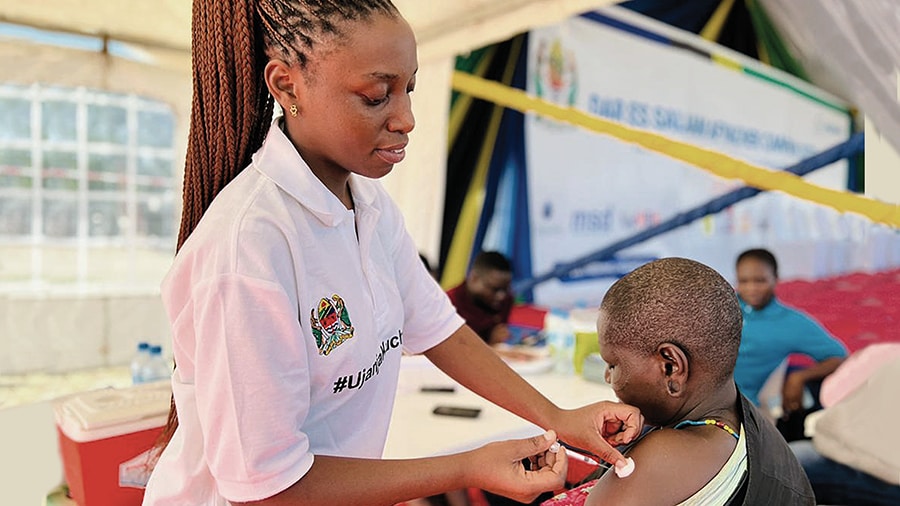
After six weeks of fast-moving vaccination efforts and more vaccines arriving in the country, CDC’s Tanzania office focused on long- range vaccination plans. In February 2022, the office expanded its support for COVID-19 vaccination to the general population after receiving resources from the U.S. government through the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA). With the addition of ARPA funds, CDC was able to vaccinate more than 500,000 people in one month and continued to see a rise in vaccination.
By March 2022 it was announced that Tanzania would be a priority country in the Global Vaccine Access (Global VAX) initiative. This support included $25 million provided by USAID and $5.3 million provided by CDC to expand vaccination coverage in Tanzania. CDC utilized political will and community engagement of local leaders at all levels to jointly design region-specific COVID-19 plans for short- term surge campaigns, and innovative individual and community outreach approaches. Through these concentrated and ongoing efforts, vaccination in CDC-supported regions quickly increased. Tanzania’s COVID-19 vaccination rate skyrocketed from 15% in June 2022 to more than 80% in October 2022, only four months later surpassing the national target.


CDC Tanzania’s extensive efforts to reach a larger part of the general population continue to have a significant impact. Through CDC support:
- More than 10.9 million people were fully vaccinated against COVID-19 in the 11 CDC-supported regions and Zanzibar. This includes 98% of CDC-supported people living with HIV.
- More than 1,500 COVID-19 vaccination stations were created in HIV
- More than 3,000 people were trained to administer
- More than 1,000 lab reagents and supplies procured for COVID-19 genomic sequencing
- More than 120,000 COVID-19 educational materials were printed and distributed
- Up to 8,000 health facilities and community vaccination sites were supported weekly
- Worked with 296 religious community leaders and 9,791 community members on COVID-19 advocacy
1Data as of November 2022