Key points
- A tuberculosis (TB) blood test helps to find out if you have TB germs in your body.
- A TB blood test requires only one visit with a health care provider.
- A TB blood test is recommended for people who have received the TB vaccine.
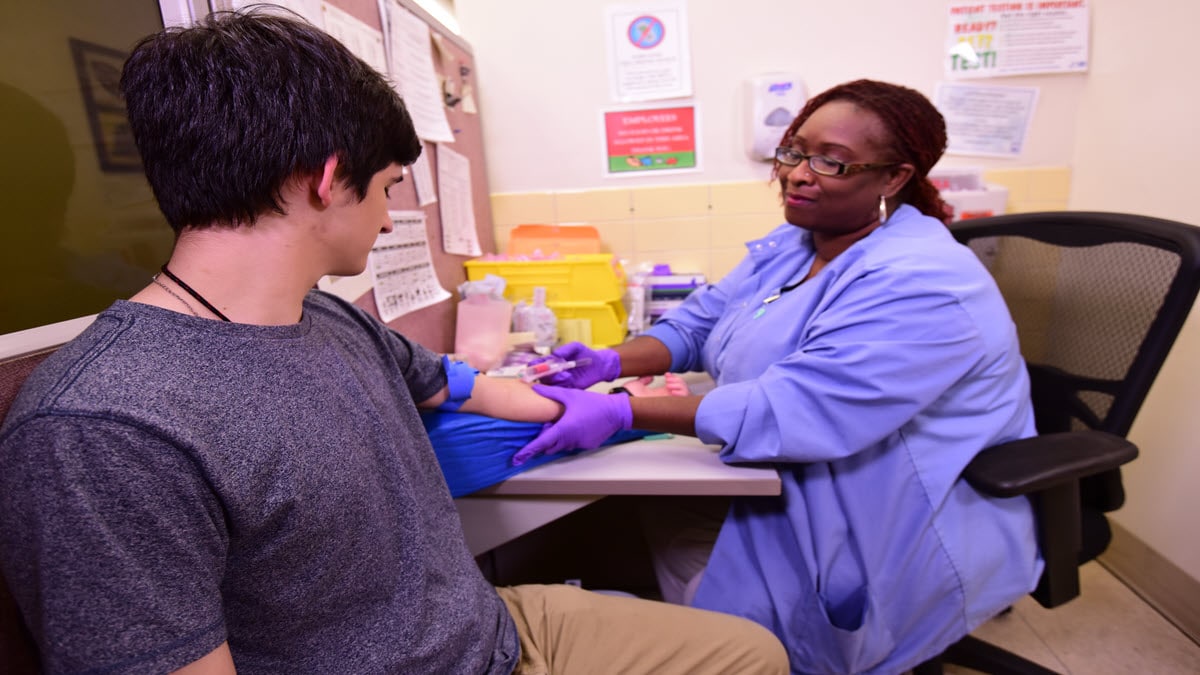
TB blood test
TB blood tests (also called interferon-gamma release assays or IGRAs) use a blood sample to find out if you are infected with TB germs. The tests measure how your immune system reacts when a small amount of your blood is mixed with TB proteins.
Your health care provider will use one of the two TB blood tests approved for use in the United States:
- QuantiFERON®-TB Gold Plus (QFT-Plus)
- T-SPOT®.TB test (T-Spot)
Who can get the TB blood test
Anyone can get a TB blood test. TB blood tests are preferred for people who:
- Have received the TB vaccine, also called bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG).
- Have a difficult time returning for a second appointment.
TB blood tests are safe to use during pregnancy. TB blood tests have not been evaluated for diagnosing inactive TB, also called latent TB infection, in pregnant women.
If you received BCG
BCG is a vaccine for TB disease. The vaccine is not generally used in the United States. It is given to infants and small children in countries where TB is common. It protects children from getting severe forms of active TB disease, such as TB meningitis.
Tell your health care provider if you have received the TB vaccine, especially if you are getting tested for TB infection. The vaccine can cause a false positive TB skin test reaction. TB blood tests are the preferred tests for people who have received the BCG TB vaccine.
How to get tested
You can get tested for TB at the health department or at your health care provider's office. Your health care provider will choose the TB test that is best for you. Public and private health care plans may cover TB testing costs.
Testing results
Positive TB blood test
A positive blood test result for TB infection means you have TB germs in your body.
Negative TB blood test
A negative blood test result for TB infection means inactive TB or active TB disease is unlikely, but your health care provider may do more tests, especially if:
After you get your results
If you have a positive TB blood test result, you have TB germs in your body. Your health care provider will do other tests to determine if you have inactive TB or active TB disease. These tests may include a chest x-ray, and a test of the sputum (phlegm) you cough up.
Your health care provider will discuss your diagnosis with you and recommend treatment.
