What to know
CDC-developed tools can help TB program staff manage and analyze data collected during TB contact, large cluster, and outbreak investigations in order to characterize transmission networks.
Overview
TB contact, cluster, and outbreak investigations are frequently complicated by challenges associated with managing and analyzing large volumes of diverse data.
For example, it is not uncommon for location-based contact investigations to identify multiple potential exposure locations and hundreds of potential contacts. Manually organizing and comparing large amounts of location and date data to identify overlaps between persons at locations and prioritize contacts of concern can be an extremely tedious and error-prone task.
During investigations of large TB clusters or outbreaks, public health practitioners routinely attempt to characterize transmission networks by evaluating:
- Surveillance data, epidemiologic links, and other data from contact investigations,
- Chronology data related to the timing of symptom onset and infectious periods, and
- Genomic data used to estimate the relatedness of isolates collected from patients.
Systematically and iteratively synthesizing and analyzing these disparate data as an investigation proceeds can be exceedingly time consuming and computationally difficult. These videos provide information on CDC-developed tools to help TB programs manage and analyze data.
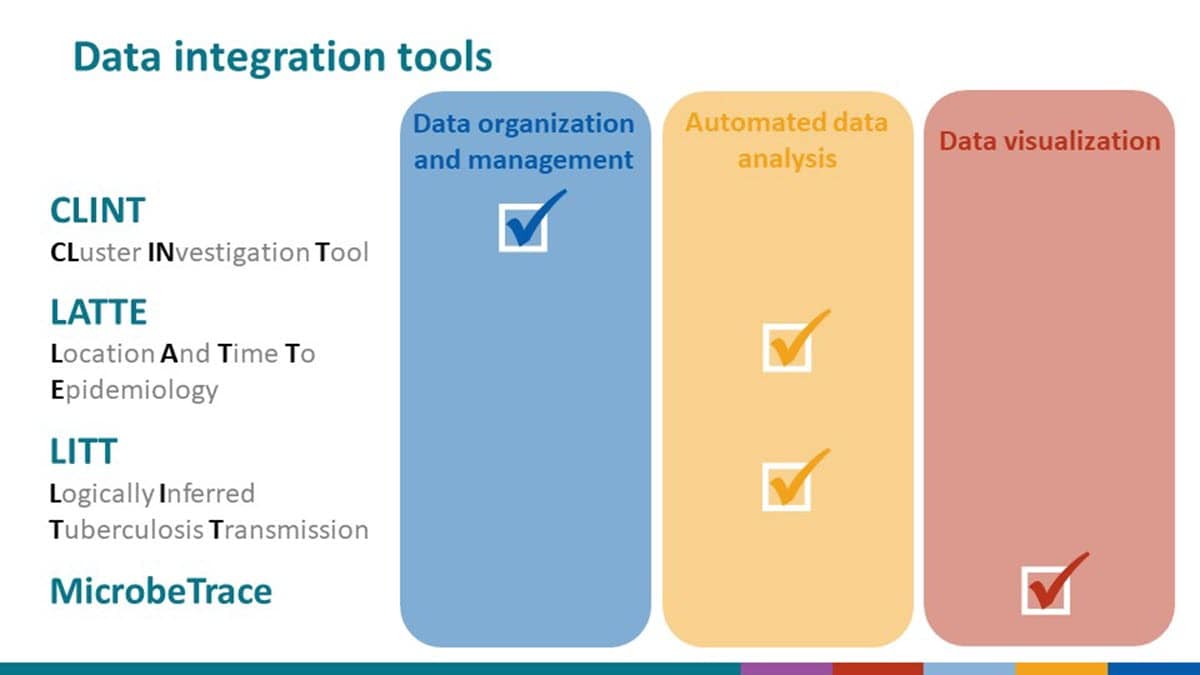
Cluster Investigation Tool (CLINT)
The Cluster INvestigation Tool (CLINT) helps users organize and summarize genotyping and surveillance data routinely collected as part of TB cluster investigations and uploaded to the TB Genotyping Information System (TB GIMS).
Logically Inferred Tuberculosis Transmission (LITT)
The Logically Inferred Tuberculosis Transmission (LITT) algorithm automates the integration and analysis of surveillance data, epidemiologic link data, data on estimated infectious period dates, and whole genome sequencing data collected from pathogen isolates to characterize TB transmission networks.
LITT Resources:
- Manuscript, user's manual, training presentation, input file templates, training datasets, and R code are available on GitHub.
- Online user interface available in TB GIMS and through CDC Office of Advanced Molecular Detection portal. Send access requests to TBGenotyping@cdc.gov.
Location And Time To Epidemiology (LATTE)
The Location And Time To Epidemiology (LATTE) algorithm automates the comparison and visualization of date data collected during location-based contact investigations (dates of stays in locations, estimated dates of infectious periods) to identify and prioritize contacts of concern for follow-up.
LATTE Resources:
- User's manual, training presentation, input file templates, training datasets, and R code are available on GitHub.
- Online user interface available through CDC Office of Advanced Molecular Detection portal. Send access requests to TBGenotyping@cdc.gov.
MicrobeTrace
MicrobeTrace, a browser-based, standalone tool built by the CDC Molecular Epidemiology and Bioinformatics team in the HIV Laboratory Branch, helps integrate, visualize, and explore demographic, genomic and contact tracing data collected during investigations of outbreaks and transmission clusters.
MicrobeTrace Resources:
- User's manual and other resources available on GitHub
- Training presentation
- Access MicrobeTrace
- Questions can be sent to the MicrobeTrace Help Desk at microbetrace@cdc.gov
- Questions can be sent to the MicrobeTrace Help Desk at microbetrace@cdc.gov
