About
Key Highlights
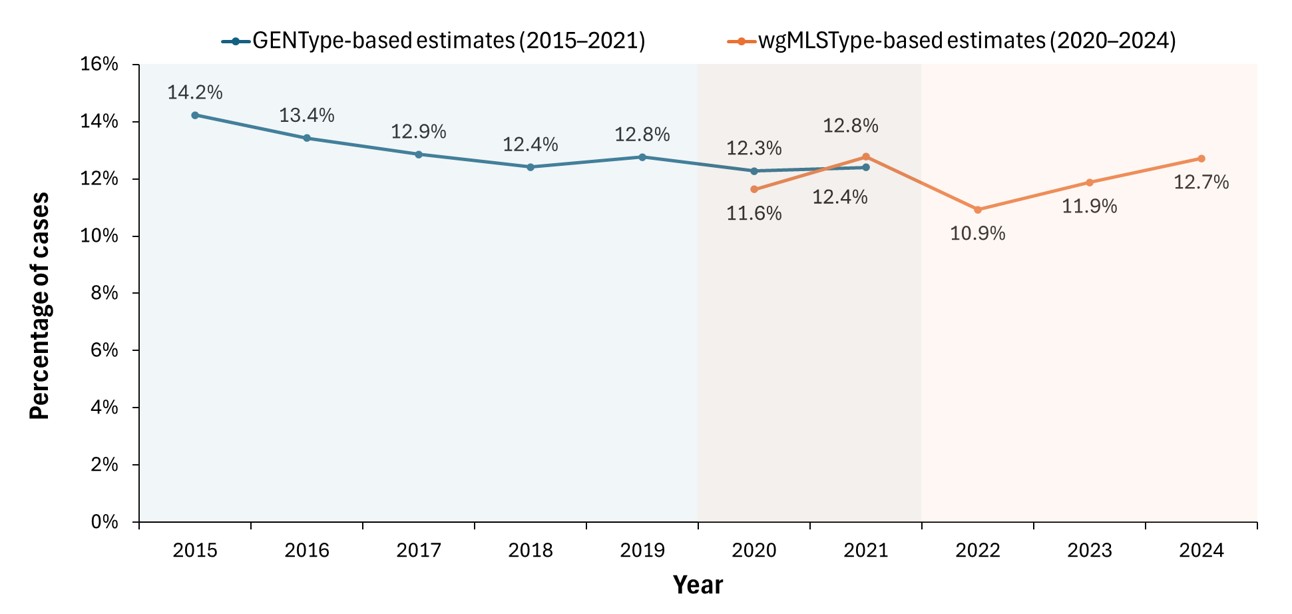
- Based on conventional genotyping (GENType), the percentage of cases attributed to recent transmission declined from 14% in 2015 to 12% in 2021.
- The updated estimate for 2021 based on whole-genome multilocus sequence typing (wgMLSType) was 13%.
- After a decline in 2022 to 11%, the estimated percentage of cases attributed to recent transmission increased to 12% in 2023 and 13% in 2024.
Data map
Figure 2. Percentage of Tuberculosis Cases Estimated to be Attributed to Recent Transmission: United States, 2015–2024
Notes
A case is attributed to recent transmission if a plausible source case can be identified in a person who had an M. tuberculosis isolate with the same GENType (GENType-based estimates) or the same wgMLSType and differed by ≤5 single nucleotide polymorphisms (wgMLSType-based estimates), had an infectious form of TB, was 10 years of age or older, resided within 10 miles (GENType-based estimates) or 100 miles (wgMLSType-based estimates) of the case, and was diagnosed within 2 years before the case.
Data for all years are updated through July 10, 2025.
See Technical Notes.
