At a glance
Smallpox dates back at least 3,000 years. Efforts to eradicate the disease began in the mid-20th century, with the last naturally occurring case reported in 1977.
Origin

The origin of smallpox is unknown. The finding of smallpox-like rashes on Egyptian mummies suggests that smallpox has existed for at least 3,000 years. The earliest written description of a disease like smallpox appeared in China in the 4th century CE (Common Era). Early written descriptions also appeared in India in the 7th century and in Asia Minor in the 10th century.
Spread
Historians trace the global spread of smallpox to the growth of civilizations and exploration. Expanding trade routes over the centuries also led to the spread of the disease.
Highlights from history
- 6th Century: Increased trade with China and Korea brings smallpox to Japan.
- 7th Century: Arab expansion spreads smallpox into northern Africa, Spain, and Portugal.
- 11th Century: Crusades further spread smallpox in Europe.
- 15th Century: Portugal occupies part of western Africa, bringing smallpox.
- 16th Century: European settlers and the African slave trade import smallpox into the Caribbean and Central and South America.
- 17th Century: European settlers bring smallpox to North America.
- 18th Century: Explorers from Great Britain bring smallpox to Australia.
Early control efforts
Smallpox was a terrible disease. On average, 3 out of every 10 people who got it died. People who survived usually had scars, which were sometimes severe.
One of the first methods for controlling smallpox was variolation, a process named after the virus that causes smallpox (variola virus). During variolation, people who had never had smallpox were exposed to material from smallpox sores (pustules) by scratching the material into their arm or inhaling it through the nose. After variolation, people usually developed the symptoms associated with smallpox, such as fever and a rash. However, fewer people died from variolation than if they had acquired smallpox naturally.
The basis for vaccination began in 1796 when the English doctor Edward Jenner noticed that milkmaids who had gotten cowpox were protected from smallpox. Jenner also knew about variolation and guessed that exposure to cowpox could be used to protect against smallpox. To test his theory, Dr. Jenner took material from a cowpox sore on milkmaid Sarah Nelmes' hand and inoculated it into the arm of James Phipps, the 8-year-old son of Jenner's gardener. Months later, Jenner exposed Phipps several times to variola virus, but Phipps never developed smallpox. More experiments followed, and, in 1801, Jenner published his treatise "On the Origin of the Vaccine Inoculation." In this work, he summarized his discoveries and expressed hope that "the annihilation of the smallpox, the most dreadful scourge of the human species, must be the final result of this practice."

Vaccination became widely accepted and gradually replaced the practice of variolation. At some point in the 1800s, the virus used to make the smallpox vaccine changed from cowpox to vaccinia virus.
Global smallpox eradication program
In 1959, the World Health Organization (WHO) started a plan to rid the world of smallpox. Unfortunately, this global eradication campaign suffered from a lack of funds, personnel, and commitment from countries, and a shortage of vaccine donations. Despite their best efforts, smallpox was still widespread in 1966, causing regular outbreaks across South America, Africa, and Asia.
The Intensified Eradication Program began in 1967 with a promise of renewed efforts. Laboratories in many countries where smallpox occurred regularly were able to produce more, higher-quality freeze-dried vaccine. Other factors that played an important role in the success of the intensified efforts included the development of the bifurcated needle, the establishment of a case surveillance system, and mass vaccination campaigns.
By the time the Intensified Eradication Program began in 1967, smallpox was already eliminated in North America (1952) and Europe (1953). Cases were still occurring in South America, Asia, and Africa (smallpox was never widespread in Australia). The Program made steady progress toward ridding the world of this disease, and by 1971 smallpox was eradicated from South America, followed by Asia (1975), and finally Africa (1977).
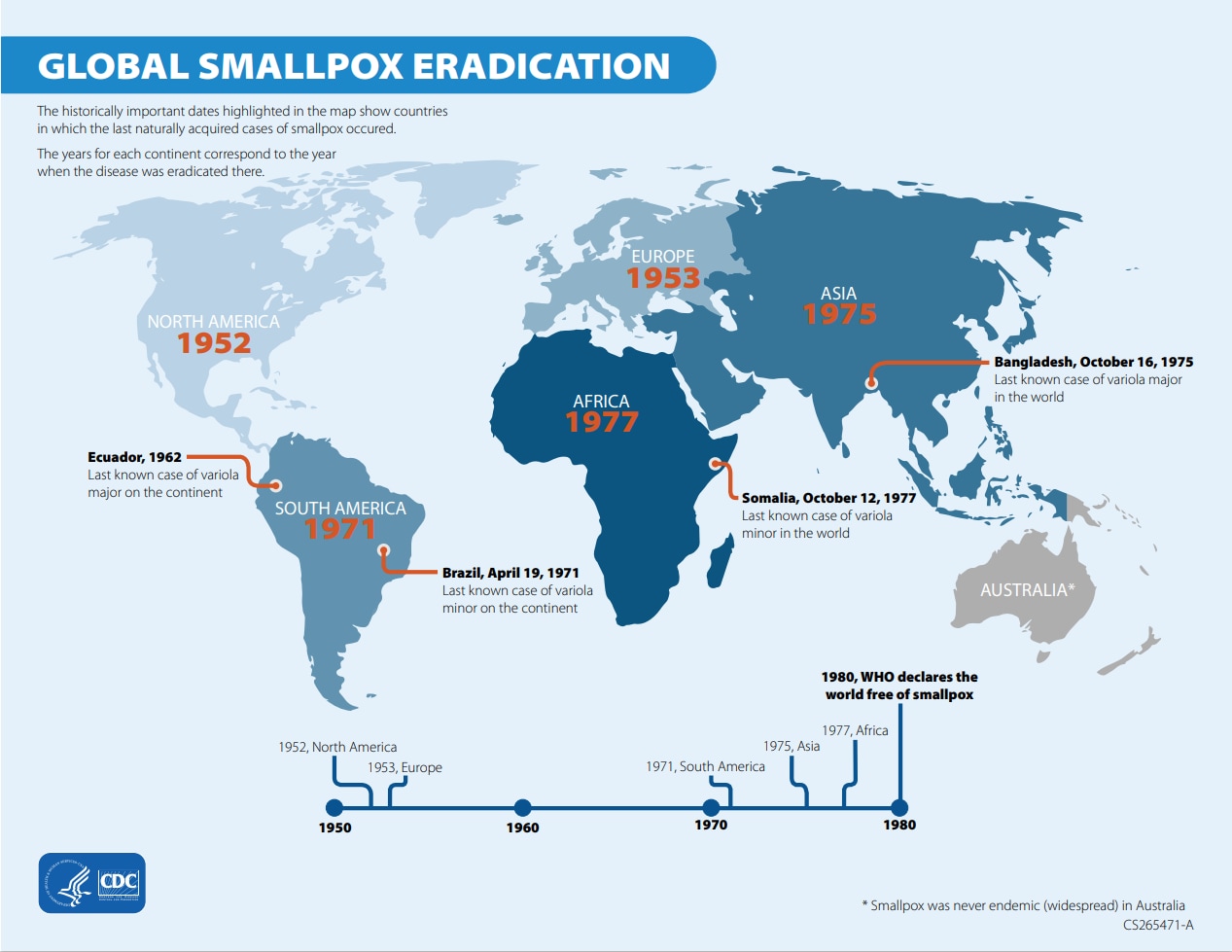
Last cases

In late 1975, three-year-old Rahima Banu from Bangladesh was the last person in the world to have naturally acquired variola major. She was also the last person in Asia to have active smallpox. She was isolated at home with house guards posted 24 hours a day until she was no longer infectious. A house-to-house vaccination campaign within a 1.5-mile radius of her home began immediately. A member of the Smallpox Eradication Program team visited every house, public meeting area, school, and healer within 5 miles to ensure the illness did not spread. They also offered a reward to anyone who reported a smallpox case.
Ali Maow Maalin was the last person to have naturally acquired smallpox caused by variola minor. Maalin was a hospital cook in Merca, Somalia. On October 12, 1977, he rode with two smallpox patients in a vehicle from the hospital to the local smallpox office. On October 22, he developed a fever. At first healthcare workers diagnosed him with malaria, and then chickenpox. The smallpox eradication staff then correctly diagnosed him with smallpox on October 30. Maalin was isolated and made a full recovery. Maalin died of malaria on July 22, 2013, while working in the polio eradication campaign.
Janet Parker was the last person to die of smallpox. In 1978, Parker was a medical photographer at England's Birmingham University Medical School. She worked one floor above the Medical Microbiology Department where staff and students conducted smallpox research. She became ill on August 11 and developed a rash on August 15 but was not diagnosed with smallpox until 9 days later. She died on September 11, 1978. Her mother, who was providing care for her, developed smallpox on September 7, despite having been vaccinated two weeks earlier. An investigation suggested that Janet Parker had been infected either via an airborne route through the medical school building's duct system or by direct contact while visiting the microbiology corridor.
World free of smallpox

Almost two centuries after Jenner hoped that vaccination could annihilate smallpox, the 33rd World Health Assembly declared the world free of this disease on May 8, 1980. Many people consider smallpox eradication to be the biggest achievement in international public health.
Stocks of variola virus
Following the eradication of smallpox, scientists and public health officials determined there was still a need to perform research using the variola virus. They agreed to reduce the number of laboratories holding stocks of variola virus to only four locations. In 1981, the four countries that either served as a WHO collaborating center or were actively working with variola virus were the United States, England, Russia, and South Africa. By 1984, England and South Africa had either destroyed their stocks or transferred them to other approved labs. There are now only two locations that officially store and handle variola virus under WHO supervision: the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, Georgia, and the State Research Center of Virology and Biotechnology (VECTOR Institute) in Koltsovo, Russia.
