Key points
- Ringworm can affect skin, hair, and nails.
- Skin infections cause itchy, ring-shaped rashes.
- Ringworm of the hair can cause hair loss.
- Nail infections can cause the nail to be thick, cracked, and discolored.
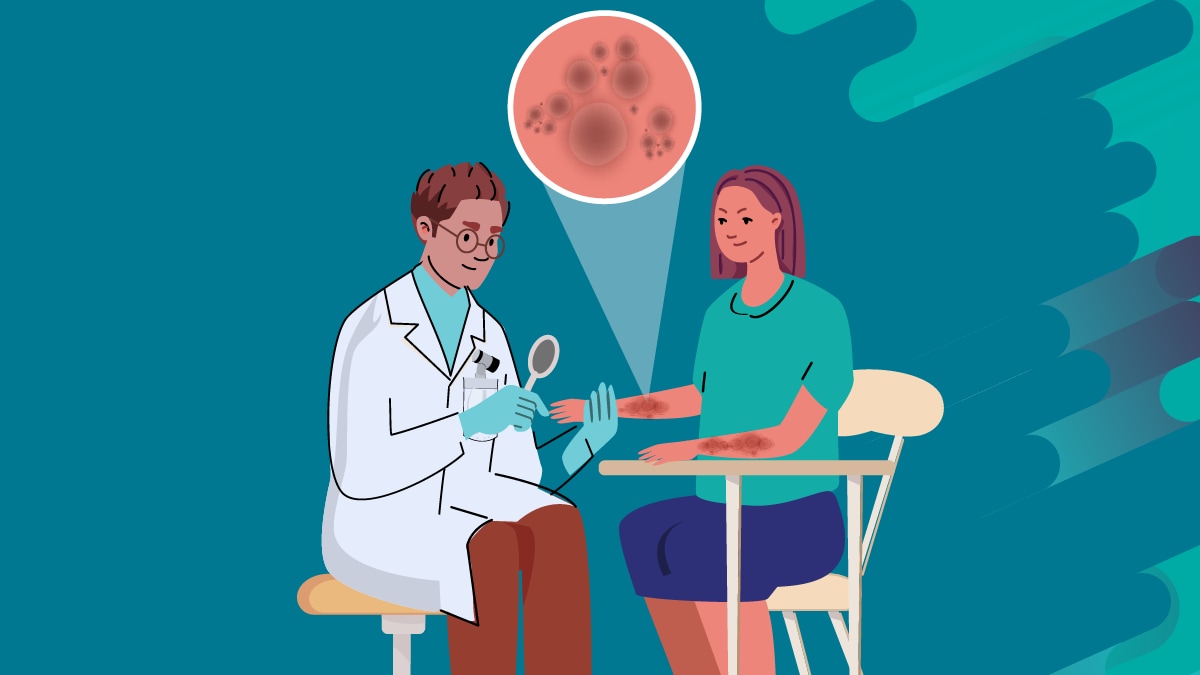
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of ringworm can be a little different depending on the part of the body that is infected. Symptoms typically appear between 4 and 14 days after the skin comes in contact with the fungi that cause ringworm.
Skin on most parts of the body (tinea corporis)
Symptoms include a red, itchy ring-shaped rash that can:
- Have a clear or scaly area inside the ring.
- Have scattered bumps inside the ring that
- appear red on white skin.
- appear red-purple, brown, gray, or black on brown skin.
- appear red on white skin.
- Be slightly raised.
- Have overlapping rings.
Feet (tinea pedis or athlete's foot)
Symptoms include red, swollen, peeling, itchy skin between the toes that:
- Is most common in the pinky toe and the one next to it
- Can affect the sole and heel of the foot.
- Can cause blisters in severe cases.
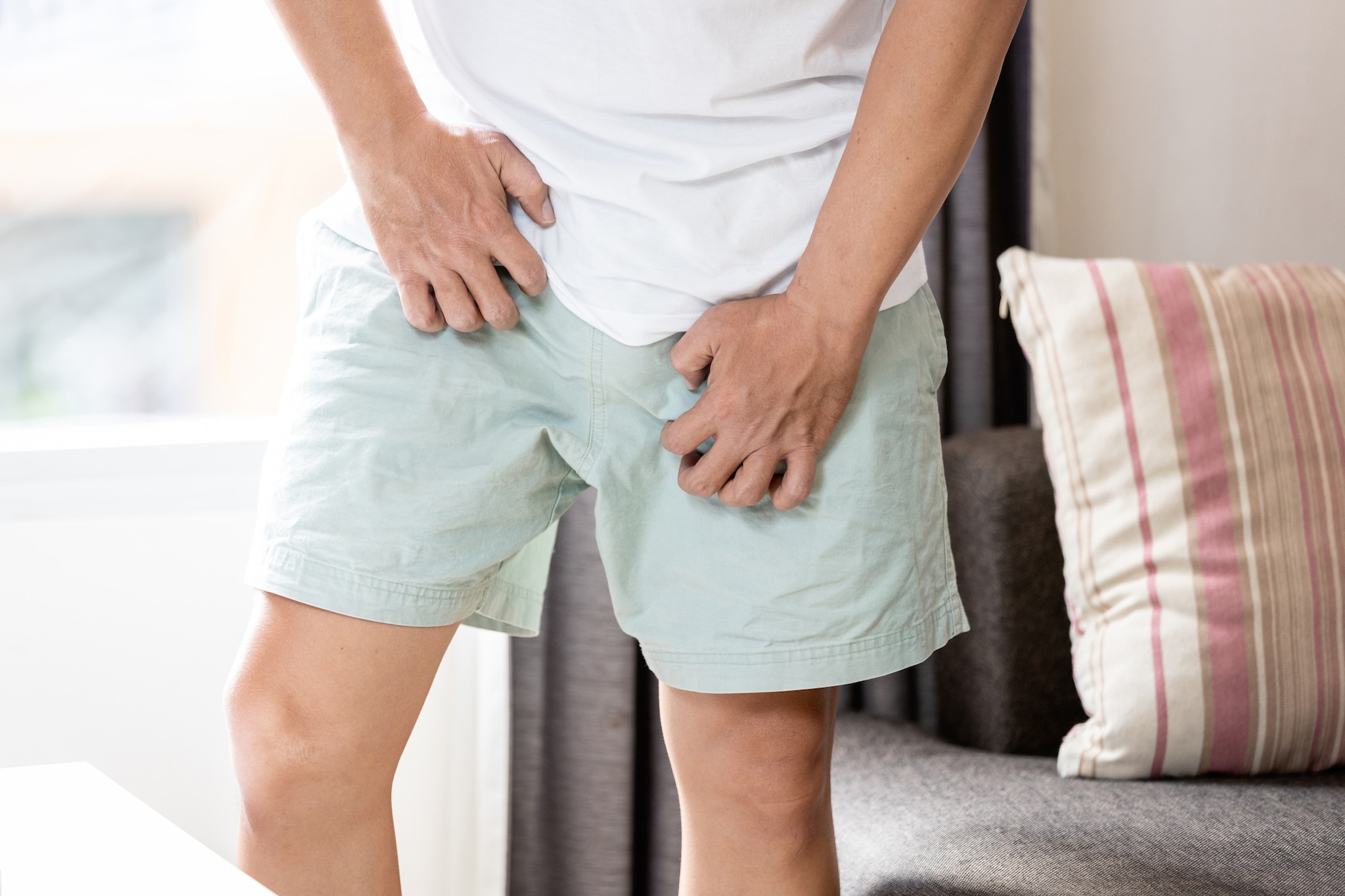
Groin (tinea cruris or jock itch)
Ringworm on the groin causes itchy, scaly, red spots. It is usually on the inner sides of the skin folds of the thigh.
Scalp (tinea capitis)
Ringworm on the scalp causes a scaly, itchy, circular, red bald spot. Without treatment the spot can grow larger and more can appear.
Ringworm of the scalp is more common in children than it is in adults.
Beard (tinea barbae)
Symptoms of ringworm on the beard include:
- Scaly, itchy, red spots on the cheeks, chin, and upper neck
- Spots might become crusted over or filled with pus

Nail infections
Nails (onychomycosis):
May affect up to 14% of the population. Finger and toe nails can be affected but toe nail infections are much more common. People with toenail infections often have infections in the skin of their foot too.
Nails can become:
- Discolored, thick, fragile, or cracked.
- Separated from the nail bed.
