About State Strategies for Preventing Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Maternal mortality review committees (MMRCs) across the nation are using shared processes and terminology to understand how to prevent maternal mortality. This guide helps MMRCs and their partners facilitate implementation of data-informed strategies to prevent pregnancy-related deaths.
Resource
How to use State Strategies for Preventing Pregnancy-Related Deaths
This guide is best used when an MMRC is ready to identify priority recommendations informed by the review of pregnancy-related deaths. A review committee is now ready to translate that knowledge to move MMRC information from data to action. For example, a review committee may prioritize recommendations related to leading causes of deaths or those that address disproportionately affected populations. This guide outlines how to engage public health, clinical, and community partners with MMRC information. This guide also refines the prioritization process for selecting strategies to move recommendations to action.
What Is in State Strategies for Preventing Pregnancy-Related Deaths
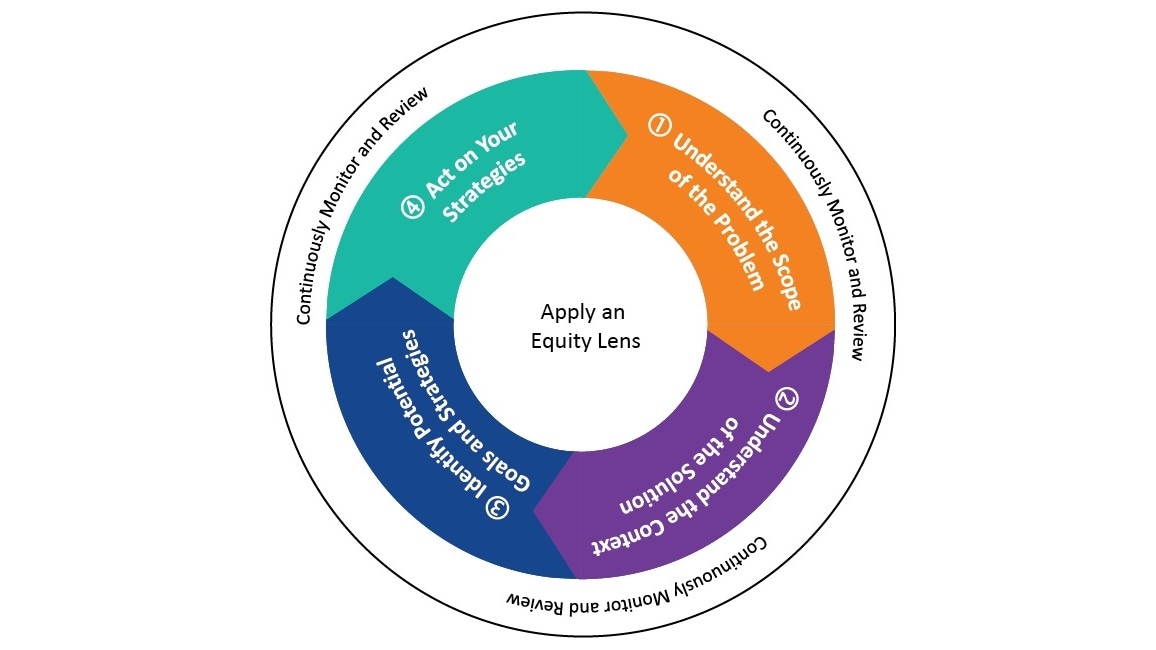
This guide presents translating data into action as a four-step process. Each step is approached through an equity lens and supported by continuous monitoring and review.
Step 1: Understand the scope of the problem. Identify and review complementary data to MMRC data from other population-based sources. This may provide further information for identifying potential actions and associated strategies.
Step 2: Understand the context of the solution to understand what is already being done to address the recommendation. Determine what is being done to address organizational and community factors, partnerships with key decision makers, and available resources. For instance, financial resources.
Step 3: Identify potential goals and strategies based on best practices and successful examples. These goals, while not exhaustive, are illustrative and may include:
- Eliminate racial and ethnic disparities in maternal mortality.
- Invest in and partner with communities.
- Ensure access to care for all pregnant and postpartum persons.
- Ensure quality care for all pregnant and postpartum persons.
- Strengthen maternal mortality data.
Step 4: Act on strategies and discuss important considerations for implementation. This may include assessing potential strategies for fit, developing an implementation plan and timeline, and planning to evaluate strategies.
Integrating Equity
Each step of moving MMRC prioritized recommendations to action should integrate equity. An equity lens includes taking deliberate steps to be sure every mother's life is valued equally. These steps include understanding the impacts of historical trauma, the role of inequitable institutional structures, and patient and community perspectives.
It is important to consider how approach, design, and implementation of strategies may impact disproportionately affected populations. Prioritizing leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths among these populations can help promote progress toward equity and eliminate disparities in maternal mortality.
Continuous Monitoring and Review
Throughout the process, it is important to systematically examine progress to identify facilitators and barriers to success. Information gathered for each step informs continuous monitoring and review. It is important to assess whether selected strategies for action are having the intended effect (evaluation).
Evaluation contributes to the evidence base for maternal health programs and identifies additional actions that may be necessary to achieve success. Continuous monitoring and review of strategy implementation, together with evaluation of outcomes, are important for tracking progress to ensure equitable implementation.
