Key points
- CDC has unique expertise in establishing systems for emergency operations and response and using public health data.
- CDC's Global Public Health Data Innovation aims to address key barriers to the effective use of data in public health responses.

Overview
CDC enhances global health security by partnering with countries to improve their ability to respond to disease threats. CDC has unique expertise in establishing systems for emergency operations and response and using public health data to inform decisions.
CDC’s Global Public Health Data Innovation (GPHDI) initiative strives to overcome barriers to the effective use of data in public health responses, including:
- Issues with data systems or data-intensive public health processes.
- Workforce limitations that inhibit rapid deployment of digital health solutions at scale.
- Gaps in data systems governance and policy that inhibit digital health strategy and response planning.
This three-year initiative is supported by investment from the 2021 U.S. American Rescue Plan Act.
Priorities
GPHDI funds activities that allow CDC’s work through the Data Modernization Initiative to be leveraged in 10 target countries in the Americas, Africa, and Asia.
These activities support projects that:
- Strengthen national data analytics infrastructure and computational platforms.
- Bolster capabilities for public health decision-making.
- Enable scalable and timely public health response through Public Health Data Automation.
- Enhance data availability and use through data integration and Health Information Exchange.
- Increase capacity building in digital health.
- Extend coordination and leadership in digital health.
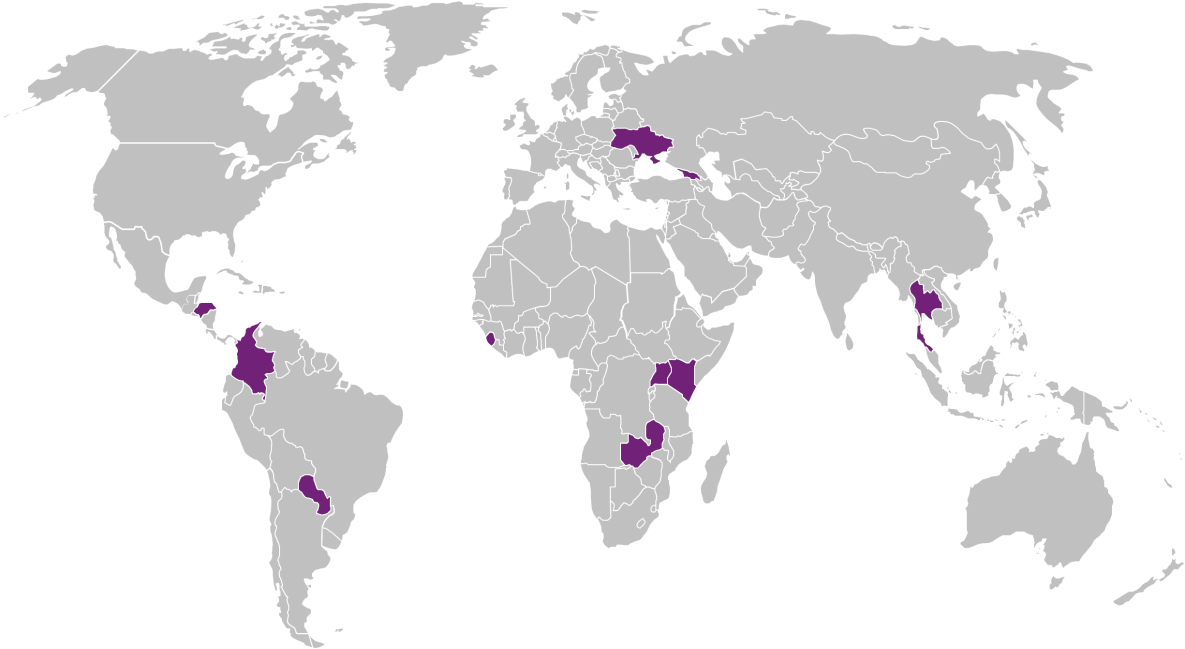
GPHDI's target countries include:
- Colombia
- Georgia
- Honduras
- Kenya
- Paraguay
- Sierra Leone
- Thailand
- Uganda
- Ukraine
- Zambia
Implementation strategies
- Establish or expand scalable platforms for national data linkage, repository, and analytics, and the human resources capable of designing and using them. Enable their use by public health authorities to rapidly respond to evolving public health events.
- Enable data automation and reporting to authorize secure transfer of service delivery data for public health use. This minimizes data collection burden, reduces report delay, and accelerates implementation of new or revised public health reporting when needed.
- Establish data integration, allowing public health authorities to access, compile, and exchange data from different sources. Use common architecture, data standards, cloud technology, and aligned business processes.
- Empower the public health workforce at all levels through coaching and mentorship, training materials, and programs in public health informatics. This builds the leadership and core competencies in informatics and digital health needed to operationalize data modernization.
- Coordinate global, regional, and national partners to implement or improve interoperable systems to facilitate data sharing and decision making. Support global networks to review and disseminate best practices in global digital health.
Core Components
Cloud Infrastructure
Establish roadmaps for adoption of cloud services models that prioritize data sovereignty and governance.
Data Automation and Reporting
Support digital enablement and business transformation for electronic laboratory and case reporting.
Data Standards
Promote and provide technical assistance to harmonize and adopt messaging and content standards for health data.
Data Analytics Platforms
Develop and implement global health use cases for integrated data analytics platforms.
Data Integration
Establish process and architecture for integration of data from multiple sources to improve decision making and situational awareness.
Governance, Leadership, and Policy
Draft policy and governance documents for adoption at the country level and provide coordinated technical assistance.
Workforce
Enable workforce development through development of training materials and programs in public health informatics.
Success story spotlight
Honduras Launches Digital Health Transformation Roadmap
In July 2024, the Honduras Ministry of Health (MoH) launched a Digital Health Transformation Roadmap. This achievement was possible with participation from the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) and other partners.
Through PAHO, CDC currently provides financial support and technical collaboration in key areas of public health in the Americas. Collaboration while working on Global Public Health Data Innovation helped guide strategic conversations with the government of Honduras and the MoH as the digital transformation roadmap was developed.
The roadmap ratifies Honduras' commitment and political will to join countries that have a strategic and technical framework for strengthening health information systems. It prioritizes access to good quality data, strategic information, and digital health tools for decision-making and well-being.
Centralized leadership and strong stakeholder engagement were crucial during this process. This effort has provided important guidance for countries that are contemplating or currently working on a similar project:
- Invest in training and cultural change to support mindset shifts, especially within central levels and health regions.
- Be adaptable to different contexts, recognizing that what works in one area may not work in another due to varying complexities.
- Have dedicated champions who can drive the initiative and provide continuous follow-up because this is essential for maintaining momentum and achieving success.
