Key points
- Breast cancer is a disease in which cells in the breast grow out of control.
- There are different kinds of breast cancer.

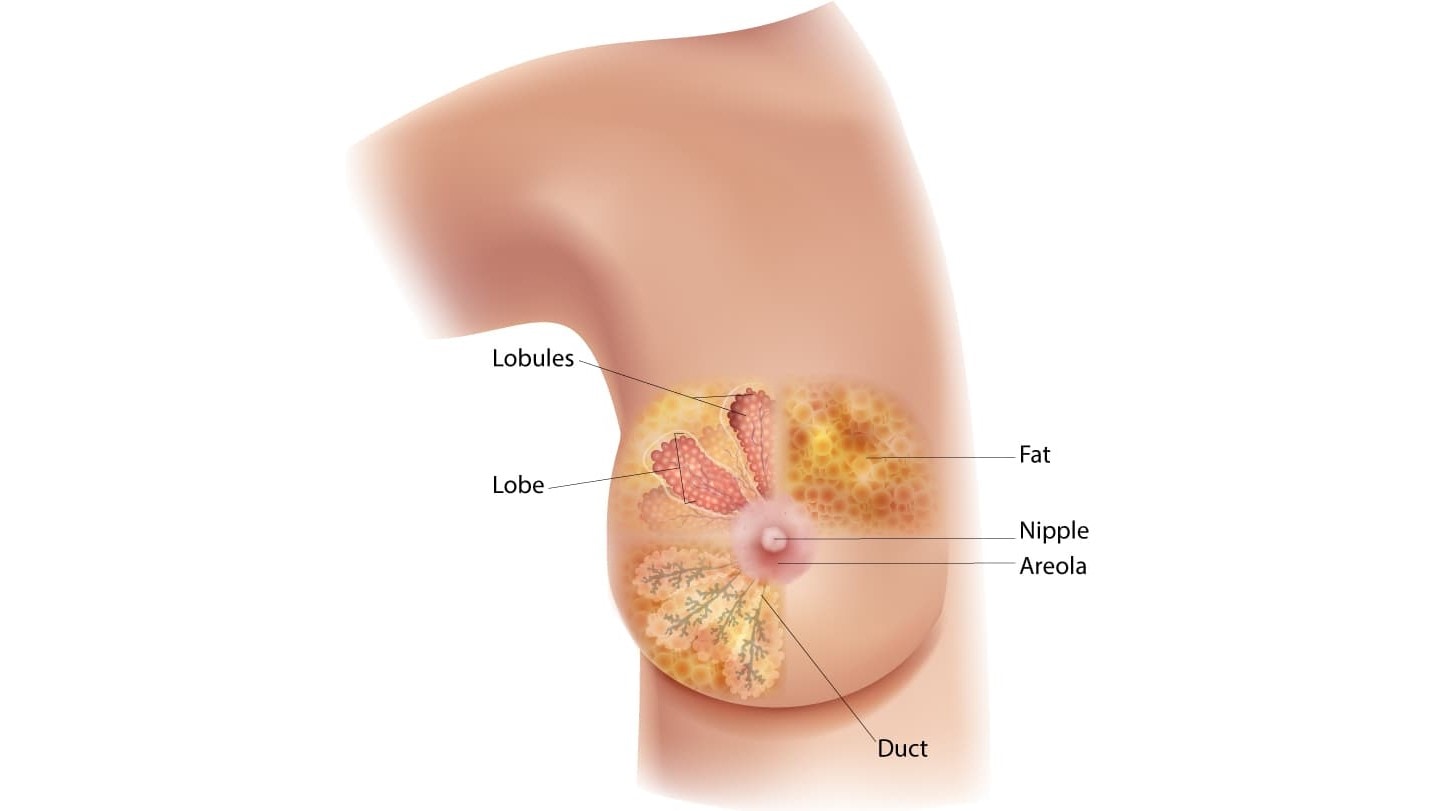
Parts of the breast
A breast is made up of three main parts: lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. The lobules are the glands that produce milk. The ducts are tubes that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which consists of fibrous and fatty tissue) surrounds and holds everything together.
Breast cancer is a disease in which cells in the breast grow out of control. There are different types of breast cancer. The type of breast cancer depends on which cells in the breast turn into cancer.
Most breast cancers begin in the ducts or lobules. Breast cancer can spread outside the breast through blood vessels and lymph vessels. When breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it is said to have metastasized.
Most common types
The most common types of breast cancer are invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma.
Invasive ductal carcinoma
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) is the most common type of breast cancer. About 70% to 80% of breast cancers are of this type. The cancer cells start in the tubes that carry milk to the nipple, called ducts, and spread to other parts of the breast. They may also spread through the lymph nodes or bloodstream to other parts of the body.
A person with IDC may feel a lump in the breast or underarm. Or the person may not have any symptoms, and a small lump may be seen on a mammogram. IDC can also cause symptoms other than a lump, such as breast pain, a change in the shape of the breast, or nipple discharge.
Invasive lobular carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) is the second most common type of breast cancer. About 10% to 15% of breast cancers are of this type. Cancer cells begin in the part of the breast that makes milk, called the lobules, and spread to nearby breast tissues. They can also spread to other parts of the body.
ILC does not typically make a lump. Instead, it appears as thickened connective tissue in the breast. So it is harder to see on a mammogram. A person with ILC may feel a hard or thickened area inside the breast or underarm, or other symptoms. ILC is more likely to form in both breasts than IDC.
Subtypes
Breast cancers are divided into subtypes based on the estrogen and progesterone hormone receptors they have and how much human epidermal growth factor (HER2) protein they make. The receptors let a breast cancer cell use these hormones in your body to grow. HER2 protein also helps breast cancers grow.
Breast cancers are checked to see if they have these receptors or protein. This lets your doctor understand your treatment options and the likelihood that the breast cancer will come back. Triple-negative breast cancer does not have receptors or make the HER2 protein. So doctors have fewer ways to treat this type of cancer.
Other types
There are several other less common types of breast cancer. Some examples are listed below.
Inflammatory breast cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer is a type of IDC that has spread to the breast skin. In inflammatory breast cancer, cancer cells block the lymph vessels in the skin of the breast. This makes the breast feel warm and look red and swollen. The breast may also look dimpled, like an orange, and the nipple may turn inward. Inflammatory breast cancer grows and spreads faster than other types of breast cancer.
For more information, please visit the National Cancer Institute.
Paget's disease of the breast
Paget's disease of the breast is a rare type of cancer that forms in the nipple and the skin around it, called the areola. It can cause flaky or scaly red skin that may tingle or itch. At first, doctors often confuse this cancer with eczema or other skin problems.
Most people with Paget's disease of the breast also have tumors in the same breast. These tumors are either ductal carcinoma in situ or invasive breast cancer. Ductal carcinoma in situ is a breast disease that may lead to invasive breast cancer. The cancer cells are only in the lining of the ducts and have not spread to other parts of the breast.
For more information, please visit the National Cancer Institute.
Do I need genetic counseling and testing?
If you have a strong family history of breast cancer, you may have changes in your genes that increase your risk of getting breast cancer and other cancers. If you have a higher risk of getting breast cancer, your doctor may talk about ways to manage your risk.
Your doctor may recommend that you see a genetic counselor. That's someone who talks to you about any history of cancer in your family to find out if you have a higher risk for getting breast cancer. The counselor may recommend that you get a genetic test.
