What to know
This module introduces basic concepts relevant to the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants and the role of sequencing in their detection and definition.
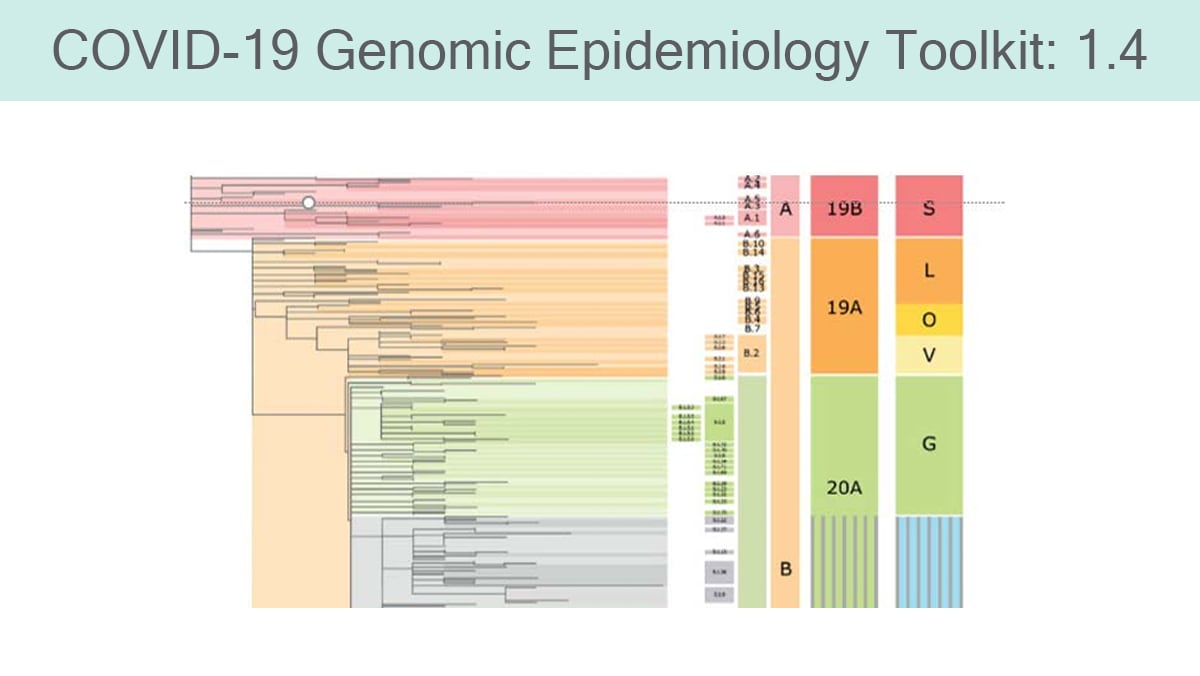
Module 1.4
Presenter: Michael Weigand, PhD | Bioinformatician, CDC
Download Presentation Slides [PDF – 16 slide]
Further Reading
- About variants of the virus that causes COVID-19. CDC.
- Genomic surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 variants. CDC.
- Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants (WHO).
- The coronavirus is evolving before our eyes. Hamblin. The Atlantic, 2021.
- Coronavirus variants and mutations. Corum and Zimmer. New York Times, 2021.
- Genetic Variants of SARS-CoV-2—What Do They Mean? Lauring and Hodcroft. JAMA, 2021.
Additional Resources
- CoVariants.org.
- SARS-CoV-2 mutation situation reports. Scripps Research.
- PANGO lineage global reports.
- Pangolin COVID-19 lineage assigner. COG-UK.
- Spread of a SARS-CoV-2 variant through Europe in the summer of 2020. Hodcroft, et al. Nature, 2020.
- Early introductions and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.1.7 in the United States. Alpert, et al. Cell, 2021.
- Linked Clusters of SARS-CoV-2 Variant B.1.351 — Maryland, January–February 2021.
- Emergence of a SARS-CoV-2 E484K variant of interest in Arizona. Skidmore, et al. medRxiv, 2021.
- Emergence of genomic diversity and recurrent mutations in SARS-CoV-2. van Dorp, et al. Infect Genet Evol, Sept 2020.
