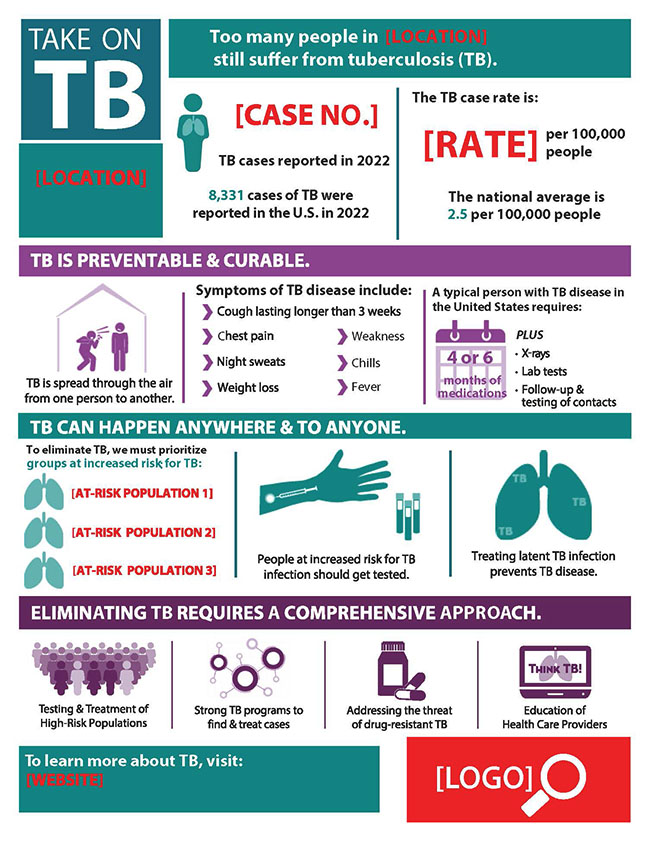
Customizable Take on TB Infographic with Instructions
Updated October 27, 2023
The customizable “Take on TB” infographic allows you to add state or local-level TB data in the template provided below. There is a detailed set of instructions to help customize this material.
Instructions:
- Chrome settings can interfere with this process. If you have issues, try downloading the PDF with Internet Explorer instead.
- Right-click this link [PDF – 1 MB] to download and save the PDF to your device.
- Open the PDF from your desktop, not your browser. Keep these instructions visible in another window if possible.
- Note that there are 9 editable areas: one image and eight text fields. They are not red like the image on this page.
- In the thumbnail graphic, editable text fields use red text to indicate the type of data to add in the field. Once you download the PDF, click on the placeholder text to edit. Data pertaining to your state can be found in Reported Tuberculosis in the United States, 2022.
- To replace the image labeled “Logo” click the magnifying glass. You will be prompted to browse for a file to replace “Logo” (.jpg, .png, and .gif will all work). Select an image to replace “Logo.” The image you select will be sized to fit the available space.
- Save your customized infographic with a new name.
- Print or share.
Take on TB
Too many people still suffer from tuberculosis (TB).
TB is preventable and curable.
- TB is spread through the air from one person to another.
- Symptoms of TB disease include:
- Cough lasting longer than 3 weeks
- Chest pain
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Weakness
- Chills
- Fever
- A typical person with TB disease in the United States requires 4 or 6 months of medication plus:
- X-rays
- Lab tests
- Follow-up and testing of contacts
TB can happen anywhere and to anyone.
- To eliminate TB, we must prioritize groups at increased risk for TB.
- People at increased risk for TB infection should get tested.
- Treating latent TB infection prevents TB disease.
Eliminating TB requires a comprehensive approach.
- Testing and treatment of populations at risk for TB
- Strong TB programs to find and treat cases
- Addressing the threat of drug-resistant TB
- Engaging affected communities and medical providers