Cavities
Overview
- Cavities, also called tooth decay, are one of the greatest unmet health treatment needs.1
- Untreated cavities can cause pain and infections that may lead to problems with eating, speaking, playing, and learning.
- Untreated cavities can lead to abscess (a severe infection) under the gums which can spread to other parts of the body and have serious, and in rare cases fatal, results.
- Among children aged 6 to 8 years, over half (52%) have had a cavity in their primary (baby) teeth.1
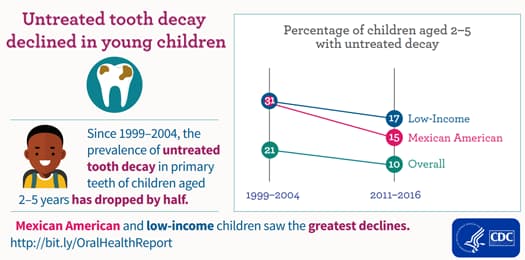
- Children from low-income families are twice as likely to have untreated cavities as higher-income children.1
- Among adolescents aged 12 to 19, more than half (57%) have had a cavity in their permanent teeth.1
- Among adults aged 20 and older, about 90% have had at least one cavity.2
- 1 in 4 adults aged 20 to 64 currently has at least one cavity.2
Featured Cavity Infographics
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vital signs: dental sealant use and untreated tooth decay among US school-aged children. MMWR. 2016;65(41):1141-1145.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Oral Health Surveillance Report: Trends in Dental Caries and Sealants, Tooth Retention, and Edentulism, United States, 1999–2004 to 2011–2016. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Dept of Health and Human Services; 2019. https://www.cdc.gov/oralhealth/publications/OHSR-2019-index.html