Facts about Neural Tube Defects
Neural tube defects are severe birth defects of the brain and spine.
CDC urges all women of reproductive age to get 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid every day, in addition to consuming food with folate from a varied diet, to help prevent neural tube defects (NTDs).
NTDs occur when the neural tube does not close properly. The neural tube forms the early brain and spine. These types of birth defects develop very early during pregnancy, often before a woman knows she is pregnant.
The two most common NTDs are spina bifida (a spinal cord defect) and anencephaly (a brain defect).
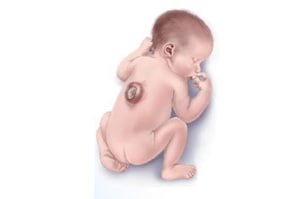
Open spina bifida

Anencephaly
Learn more about specific types of other birth defects >>
Women who have already had a pregnancy affected by a neural tube defect should consume 400 micrograms of folic acid every day.

If you have already had an NTD-affected pregnancy, CDC recommends consuming 400 mcg of folic acid each day, even if you are not planning to become pregnant. When planning to become pregnant, CDC recommends consuming 4,000 mcg of folic acid each day starting 1 month before becoming pregnant and during the first 3 months of pregnancy. This recommendation to take a higher dose of folic acid is based on data from the most rigorous type of scientific study involving women with a previous NTD-affected pregnancy. Dosages lower than 4,000 mcg of folic acid have not been studied in women who have had a previous NTD-affected pregnancy.
When planning to become pregnant, consult with your healthcare provider.
