
Trichuriasis
[Trichuris trichiura]
Causal Agent
The nematode (roundworm) Trichuris trichiura, also called the human whipworm.
Life Cycle

The unembryonated eggs are passed with the stool  . In the soil, the eggs develop into a 2-cell stage
. In the soil, the eggs develop into a 2-cell stage  , an advanced cleavage stage
, an advanced cleavage stage  , and then they embryonate
, and then they embryonate  ; eggs become infective in 15 to 30 days. After ingestion (soil-contaminated hands or food), the eggs hatch in the small intestine, and release larvae
; eggs become infective in 15 to 30 days. After ingestion (soil-contaminated hands or food), the eggs hatch in the small intestine, and release larvae  that mature and establish themselves as adults in the colon
that mature and establish themselves as adults in the colon 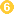 . The adult worms (approximately 4 cm in length) live in the cecum and ascending colon. The adult worms are fixed in that location, with the anterior portions threaded into the mucosa. The females begin to oviposit 60 to 70 days after infection. Female worms in the cecum shed between 3,000 and 20,000 eggs per day. The life span of the adults is about 1 year.
. The adult worms (approximately 4 cm in length) live in the cecum and ascending colon. The adult worms are fixed in that location, with the anterior portions threaded into the mucosa. The females begin to oviposit 60 to 70 days after infection. Female worms in the cecum shed between 3,000 and 20,000 eggs per day. The life span of the adults is about 1 year.
Geographic Distribution
The third most common round worm of humans. Worldwide, with infections more frequent in areas with tropical weather and poor sanitation practices, and among children. It is estimated that 800 million people are infected worldwide. Trichuriasis occurs in the southern United States.
Clinical Presentation
Most frequently asymptomatic. Heavy infections, especially in small children, can cause gastrointestinal problems (abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal prolapse) and possibly growth retardation.
T. trichiura eggs.









Cross-sections of T. trichiura stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E).






T. trichiura adults.




Laboratory Diagnosis
Microscopic identification of whipworm eggs in feces is evidence of infection. Because eggs may be difficult to find in light infections, a concentration procedure is recommended. Because the severity of symptoms depend on the worm burden, quantification of the latter (e.g. with the Kato-Katz technique) can prove useful.
Examination of the rectal mucosa by proctoscopy (or directly in case of prolapses) can occasionally demonstrate adult worms.
Treatment Information
Treatment information for trichuriasis can be found at:
DPDx is an educational resource designed for health professionals and laboratory scientists. For an overview including prevention, control, and treatment visit www.cdc.gov/parasites/.